Abstract
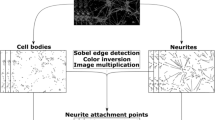
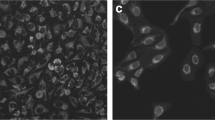
This work presents a novel approach for the automated characterization of neurons in primary culture from phase-contrast images. Direct characterization of neurons from these images is very challenging due to the complexity of the images. Over time in culture neurons change shape and size, and extend neuronal connections (i.e., neurites) between them. Also, cultured neurons are accompanied by other cell types, mainly glial cells, which may be difficult to distinguish from neurons. In this study we have applied U-Net segmentation to isolate and extract individual neurons, while also addressing the challenges posed by the presence of other cell types and structures in the culture. We then used YOLO object detection to classify and localize neurons accurately. Combining these two models, we have been able to successfully characterize neurons within these complex cultures. Our findings demonstrate the potential of this approach for a more comprehensive analysis of neurons in challenging environments. The present work is part of a larger study aimed to fully analyze neuronal behaviour throughout development.
This research has been funded by the Instituto Universitario de Tecnología Industrial de Asturias (IUTA), grant SV-22-GIJÓN-1- 22, Agencia Estatal de Investigación, grant MCI-21-PID2020-119087RB-I00, and GRUPIN SV-PA-21-AYUD/2021/52132.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbelle, A., Raviv, T.R.: Microscopy cell segmentation via adversarial neural networks
Arbelle, A., Raviv, T.R.: Microscopy cell segmentation via convolutional LSTM networks
Bamford, P., Lovell, B.C.: Unsupervised cell nucleus segmentation with active contours. Signal Process. 71, 203–213
Beucher, S.: Use of watersheds in contour detection
Cabrera-Garcia, D., Warm, D., de la Fuente, P., Fernández-Sánchez, M.T., Novelli, A., Villanueva-Balsera, J.M.: Early prediction of developing spontaneous activity in cultured neuronal networks. Scient. Reports 11(1) (2021)
Cetin, S., Knez, D., Gobec, S., Kos, J., Pišlar, A.: Cell models for Alzheimer’s and parkinson’s disease: at the interface of biology and drug discovery. Biomed. Pharmacotherapy 149, 112–924 (2022)
Eglen, R., Gilchrist, A., Reisine, T.: An overview of drug screening using primary and embryonic stem cells. Combinatorial Chem. High Throughput Screen. 11(7), 566–572 (2008)
Fang, Y., Guo, X., Chen, K., Zhou, Z., Ye, Q.: Accurate and automated detection of surface knots on sawn timbers using yolo-v5 model. BioResources 16(3), 5390–5406 (2021)
Fernández, M.T., Zitko, V., Gascón, S., Novelli, A.: The marine toxin okadaic acid is a potent neurotoxin for cultured cerebellar neurons. Life Sci. 49(19), PL157–PL162 (1991)
Gupta, A., et al.: Deep learning in image cytometry: A review. Cytometry A 95, 366–380 (2019)
He, F., Huang, X., Wang, X., Qiu, S., Jiang, F., Ling, S.H.: A neuron image segmentation method based deep boltzmann machine and cv model. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 89, 101–871 (2021)
Ho, S.Y., Chao, C.Y., Huang, H.L., Chiu, T.W., Charoenkwan, P., Hwang, E.: NeurphologyJ: an automatic neuronal morphology quantification method and its application in pharmacological discovery. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1) (2011)
Hung, J., et al.: Applying faster R-CNN for object detection on malaria images. arXiv:1804.09548 (2018)
Işin, A., Direkoǧlu, C., Şah, M.: Review of MRI-based brain tumor image segmentation using deep learning methods, pp. 317–324. Elsevier B.V. (2016)
Jiang, J., Kao, P.Y., Belteton, S.A., Szymanski, D.B., Manjunath, B.S.: Accurate 3d cell segmentation using deep feature and CRF refinement (2019)
Karri, M., Annavarapu, C.S.R., Mallik, S., Zhao, Z., Acharya, U.R.: Multi-class nucleus detection and classification using deep convolutional neural network with enhanced high dimensional dissimilarity translation model on cervical cells. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 42, 797–814 (2022)
Kasper-Eulaers, M., Hahn, N., Berger, S., Sebulonsen, T., Myrland, O., Kummervold, P.E.: Short communication: detecting heavy goods vehicles in rest areas in winter conditions using yolov5. Algorithms 14(4) (2021)
Lee, S.Y., et al.: Image analysis using machine learning for automated detection of hemoglobin h inclusions in blood smears: A method for morphologic detection of rare cells. J. Pathol. Inform. 12(1), 18 (2021)
Litjens, G., et al.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Liu, R., Dai, W., Wu, T., Wang, M., Wan, S., Liu, J.: Aimic: deep learning for microscopic image classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 226, 107–162 (2022)
Lou, X., Schiegg, M., Hamprecht, F.A.: Active structured learning for cell tracking: algorithm, framework, and usability. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33, 849–860 (2014)
Meijering, E.: Cell segmentation: 50 years down the road [life sciences]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 29, 140–145 (2012)
Pérez-Gómez, A., Novelli, A., Fernández-Sánchez, M.T.: Na\(<\)sup\(>+<\)/sup\(>\)/k\(<\)sup\(>+<\)/sup\(>\)-ATPase inhibitor palytoxin enhances vulnerability of cultured cerebellar neurons to domoic acid via sodium-dependent mechanisms. J. Neurochem. (2010)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation
Rosca, A., et al.: Impact of environmental neurotoxic: current methods and usefulness of human stem cells. Heliyon 6(12), e05,773 (2020)
Schmidt, U., Weigert, M., Broaddus, C., Myers, G.: Cell detection with star-convex polygons (2018)
Wang, Z., Jin, L., Wang, S., Xu, H.: Apple stem/calyx real-time recognition using yolo-v5 algorithm for fruit automatic loading system. Postharvest Biology and Technology 185 (2022)
Wood, L.B., et al.: Identification of neurotoxic cytokines by profiling Alzheimer’s disease tissues and neuron culture viability screening. Sci. Reports 5(1) (2015)
Wu, H., Souedet, N., Jan, C., Clouchoux, C., Delzescaux, T.: A general deep learning framework for neuron instance segmentation based on efficient unet and morphological post-processing. Comput. Biol. Med. 150, 106–180 (2022)
Wu, Q., Merchant, F.A., Castleman, K.R.: Microscope image processing, 1st edn. Elsevier/Academic Press
Yi, J., et al.: Multi-scale cell instance segmentation with keypoint graph based bounding boxes
Yin, C., et al.: Network science characteristics of brain-derived neuronal cultures deciphered from quantitative phase imaging data. Sci. Reports 10(1), 15,078
Zhang, L., Lu, L., Nogues, I., Summers, R.M., Liu, S., Yao, J.: Deeppap: deep convolutional networks for cervical cell classification (2018)
Zhu, N., Liu, C., Singer, Z.S., Danino, T., Laine, A.F., Guo, J.: Segmentation with residual attention u-net and an edge-enhancement approach preserves cell shape features
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Puerta, P. et al. (2023). Neuron Characterization in Complex Cultures Using a Combined YOLO and U-Net Segmentation Approach. In: García Bringas, P., et al. 18th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2023). SOCO 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 749. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42529-5_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42529-5_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-42528-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-42529-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)