Abstract
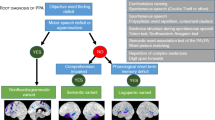
Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA) is a syndrome causing progressive deterioration of language and speech due to brain degeneration. Three variants exist: non-fluent variant (nfvPPA), semantic variant(svPPA) and logopenic variant (lvPPA). While fMRI is the most accepted diagnostic tool (and neurological exploration), it is expensive and takes even months to deliver results. Cheaper and faster tools are needed for earlier diagnosis and treatment initiation. Some studies have attempted automatic diagnosis using acoustic and linguistic features with ML and DL techniques. However, none have included Latin language patients or analyzed the effect of cognitive tests. This work proposes a methodology based on three main steps: i) a new assessment tool (PPATool) combining ACE-III and MLSE with three language tasks: verbal fluency, repetition and naming, and ii) an IDA process to obtain an ML model trained with our own two-class (PPA/Healthy) dataset, and iii) ranking the relevance of tasks in PPATool from models performance. The results obtained after deploying the IDA process on the dataset obtained from an early-stage clinical trial, show that the verbal fluency data outperforms the rest of the tasks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyanov, B., Hadjitodorov, S.: Acoustic analysis of pathological voices: a voice analysis system for the screening and laryngeal diseases. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Maga. 16(4), 74–82 (1997)
de la Cal, E., Gallucci, A., Villar, J.R., Yoshida, K., Koeppen, M.: Simple meta-optimization of the feature MFCC for public emotional datasets classification. In: Sanjurjo González, H., Pastor López, I., García Bringas, P., Quintián, H., Corchado, E. (eds.) HAIS 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12886, pp. 659–670. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86271-8_55
de la Cal, E., Gallucci, A., Villar, J.R., Yoshida, K., Koeppen, M.: A first prototype of an emotional smart speaker, pp. 304–313 (2022)
Cho, S., Nevler, N., Shellikeri, S., Ash, S., Liberman, M.: Automatic classification of primary progressive aphasia patients using lexical and acoustic features. In: Proceedings of Language Resources and Evaluation Conference 2020 workshop on Resources and Processing of Linguistic, Para-linguistic and Extra-linguistic Data from People with Various Forms of Cognitive/Psychiatric/Developmental Impairments, June, pp. 60–65 (2020)
Fan, W., Xu, X., Xing, X., Chen, W., Huang, D.: LSSED: a large-scale dataset and benchmark for speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - Proceedings, June 2021, pp. 641–645 (2021)
Fraser, K.C., et al.: Automated classification of primary progressive aphasia subtypes from narrative speech transcripts. Cortex 55(1), 43–60 (2014)
Gorno-Tempini, M.L., et al.: Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 76(11), 1006–1014 (2011)
Hoffman, P., Sajjadi, S.A., Patterson, K., Nestor, P.J.: Data-driven classification of patients with primary progressive aphasia. Brain Lang. 174(July), 86–93 (2017)
Matias-Guiu, J.A., et al.: Spanish version of the mini-linguistic state examination for the diagnosis of primary progressive aphasia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 83(2), 771–778 (2021)
Orozco-Arroyave, J.R., Arias-Londoño, J.D., Vargas-Bonilla, J.F., González-Rátiva, M.C., Nöth, E.: New Spanish speech corpus database for the analysis of people suffering from Parkinson’s disease. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, LREC 2014, December 2014, pp. 342–347 (2014)
Patel, N., et al.: A ‘Mini Linguistic State Examination’ to classify primary progressive aphasia (2022)
Ranjan Sahoo, T., Patra, S.: Silence removal and endpoint detection of speech signal for text independent speaker identification. Image Graph. Signal Process. 6, 27–35 (2014)
Riello, M., et al.: Neural correlates of letter and semantic fluency in primary progressive aphasia. Brain Sci. 12(1), 1 (2021)
Rofes, A., De Aguiar, V., Ficek, B., Wendt, H., Webster, K., Tsapkini, K.: The role of word properties in performance on fluency tasks in people with primary progressive aphasia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 68(4), 1521–1534 (2019)
Themistocleous, C., Webster, K., Afthinos, A., Tsapkini, K.: Part of speech production in patients with primary progressive aphasia: an analysis based on natural language processing. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 30(1s), 466–480 (2021)
Acknowledgement
The research has been funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economics and Industry, grant PID2020-112726RB-I00, by the Spanish Research Agency (AEI, Spain) under grant agreement RED2018-102312-T (IA-Biomed), and by the Ministry of Science and Innovation under CERVERA Excellence Network project CER-20211003 (IBERUS) and Missions Science and Innovation project MIG-20211008 (INMERBOT). Also, by Principado de Asturias, grant SV-PA-21-AYUD/2021/50994. By European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (project DIH4CPS) under Grant Agreement no 872548. And by CDTI (Centro para el Desarrollo Tecnológico Industrial) under projects CER-20211003 and CER-20211022 and by ICE (Junta de Castilla y León) under project CCTT3/20/BU/0002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
J. Valdés Cuervo, A., Herrera, E., A. de la Cal, E. (2023). A Preliminary Study of MLSE/ACE-III Stages for Primary Progressive Aphasia Automatic Identification Using Speech Features. In: García Bringas, P., et al. 18th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO 2023). SOCO 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 750. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42536-3_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42536-3_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-42535-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-42536-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)