Abstract
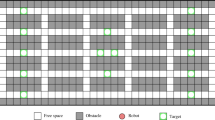
Multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) is a problem of coordinating the movements of multiple agents operating a shared environment that has numerous industrial and research applications. In many practical cases the agents (robots) have limited visibility of the environment and must rely on local observations to make decisions. This scenario, known as partially observable MAPF (PO-MAPF), can be solved through decentralized approaches. In recent years, several learnable algorithms have been proposed for solving PO-MAPF. However, their performance is oftentimes not validated out-of-distribution (OOD), and the code is often not properly open-sourced. In this study, we conduct a comprehensive empirical evaluation of one of the state-of-the-art decentralized PO-MAPF algorithms, Distributed Heuristic Communication (DHC), Ma, Z., Luo, Y., Ma, H.: Distributed heuristic multi-agent path finding with communication. In: 2021 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 8699–8705. IEEE, Xi’an, China (2021), which incorporates communication between agents. Our experiments reveal that the performance of DHC deteriorates when agents encounter complete packet loss during communication. To address this issue, we propose a novel algorithm called DHC-R that employs a similar architecture to the original DHC but introduces randomness into the graph neural network-based communication block, preventing the passage of some data packets during training. Empirical evaluation confirms that DHC-R outperforms DHC in scenarios with packet loss. Open-sourced model weights and the codebase are provided: https://github.com/acforvs/dhc-robust-mapf.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Partially-Observable Grid Environment for Multiple Agents: https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/pogema. Last accessed 11 May 2023
Ma, Z., Luo, Y., Ma, H.: Distributed heuristic multi-agent path finding with communication. In: 2021 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 8699–8705. IEEE, Xi’an, China (2021)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (1998)
Zelinsky, A.: A mobile robot exploration algorithm. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8(6), 707–717 (1992)
Hart, P.E., Nilsson, N.J., Raphael, B.: A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 4(2), 100–107 (1968)
Wagner, G., Choset, H.: M*: A complete multirobot path planning algorithm with performance bounds. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 3260–3267. IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA (2011)
Ferner, C., Wagner, G., Choset, H.: ODrM* optimal multirobot path planning in low dimensional search spaces. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3854–3859. IEEE, Karlsruhe, Germany (2013)
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A., Sturtevant, N.R.: Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding. Artif. Intell. 219, 40–66 (2015)
Boyarski. E.: Iterative-deepening conflict-based search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-20), pp. 4084–4090. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, Yokohama (2020)
Barer, M., Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A.: Suboptimal variants of the conflict-based search algorithm for the multi-agent pathfinding problem. Front. Artif. Intell. Appl. 263, 961–962 (2014)
Andreychuk, A., Yakovlev, K., Surynek, P., Atzmon, D., Stern, R.: Multi-agent pathfinding with continuous time. Artif. Intell. 305, 103 (2022)
Surynek, P., Felner, A., Stern, R., Boyarski, E.: Efficient SAT approach to multi-agent path finding under the sum of costs objective. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Second European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 810–818. IOS Press, The Hague, The Netherlands (2016)
Lam, E., Le Bodic, P., Harabor, D.D., Stuckey, P.J.: Branch-and-cut-and-price for multi-agent pathfinding. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-19), pp. 1289–1296. International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization, Macao, China (2019)
Yakovlev, K.S., Andreychuk, A.A., Skrynnik, A.A., Panov, A.I.: Planning and learning in multi-agent path finding. Dokl. Math. 106(1), 79–84 (2022)
Sunehag, P.: Value-decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 2085–2087. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden (2018)
Sartoretti, G.: PRIMAL: pathfinding via reinforcement and imitation multi-agent learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 4(3), 2378–2385 (2019)
Li, W., Chen, H., Jin, B., Tan, W., Zha, H., Wang, X.: Multi-Agent Path Finding with Prioritized Communication Learning. In: 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 10695–10701. Philadelphia, PA, USA (2022)
Li, Q., Gama, F., Ribeiro, A., Prorok, A.: Graph Neural Networks for Decentralized Path Planning. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 1901–1903. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Auckland, New Zealand (2020)
Ma, Z., Luo, Y., Pan, J.: Learning selective communication for multi-agent path finding. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7(2), 1455–1462 (2022)
Learnable Decentralized MAPF using reinforcement learning with local communication. https://github.com/acforvs/dhc-robust-mapf. Last accessed 11 May 2023
Stern, R., et al., Multi-agent pathfinding: definitions, variants, and benchmarks. In: Symposium on Combinatorial Search (SoCS), pp. 151–158 (2019)
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Mathematics and Computer Science Department of St. Petersburg State University, with special thanks to Aleksandr Avdiushenko for providing access to computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Savinov, V., Yakovlev, K. (2023). DHC-R: Evaluating “Distributed Heuristic Communication” and Improving Robustness for Learnable Decentralized PO-MAPF. In: Ronzhin, A., Sadigov, A., Meshcheryakov, R. (eds) Interactive Collaborative Robotics. ICR 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14214. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43111-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43111-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43110-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43111-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)