Abstract
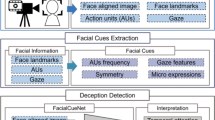
As the development of deep learning (DL) techniques has progressed, the creation of convincing synthetic media, known as deepfakes, has become increasingly easy, raising significant concern about the use of these videos to spread false information and potentially manipulate public opinion. In recent years, deep neural networks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), have been used for deepfake detection systems, exploiting the inconsistencies and the artifacts introduced by generation algorithms. Taking into account the main limitation of fake videos to realistically reproduce the natural human emotion patterns, in this paper, we present FEAD-D, a publicly available tool for deepfake detection performing facial expression analysis. Our system exploits data from the DeepFake Detection Challenge (DFDC) and consists of a model based on bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) capable of detecting a fake video in about two minutes with an overall accuracy of 84.29% on the test set (i.e. comparable with the current state-of-the-art, while consisting of fewer parameters), showing that emotional analysis can be used as a robust and reliable method for deepfake detection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
The code is available here: https://github.com/priamus-lab/FEAD-D_Facial-Expression-Analysis-in-Deepfake-Detection.
- 4.
- 5.
The code is available here: https://github.com/priamus-lab/FEAD-D_Facial-Expression-Analysis-in-Deepfake-Detection.
References
Selim seferbekov: Winner of deepfake detection challenge. https://github.com/selimsef/dfdc_deepfake_challenge
Agarwal, S., Hu, L., Ng, E., Darrell, T., Li, H., Rohrbach, A.: Watch those words: Video falsification detection using word-conditioned facial motion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 4710–4719 (2023)
Almars, A.M.: Deepfakes detection techniques using deep learning: a survey. J. Comput. Commun. 9(5), 20–35 (2021)
Bonettini, N., Cannas, E.D., Mandelli, S., Bondi, L., Bestagini, P., Tubaro, S.: Video face manipulation detection through ensemble of CNNs. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (icpr), pp. 5012–5019. IEEE (2021)
Dolhansky, B.: Joanna Bitton. The deepfake detection challenge dataset, B.P.J.L.R.H.M.W.C.C.F. (2020)
Coccomini, D.A., Messina, N., Gennaro, C., Falchi, F.: Combining efficientnet and vision transformers for video deepfake detection. In: Image Analysis and Processing-ICIAP 2022: 21st International Conference, Lecce, Italy, May 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part III. pp. 219–229. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06433-3_19
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR, 2009, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Dumitru, Ian Goodfellow, W.C.Y.B.: Challenges in representation learning: Facial expression recognition challenge (2013)
Hosler, B., et al.: Do deepfakes feel emotions? a semantic approach to detecting deepfakes via emotional inconsistencies. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, pp. 1013–1022 (June 2021)
Kaur, S., Kumar, P., Kumaraguru, P.: Deepfakes: temporal sequential analysis to detect face-swapped video clips using convolutional long short-term memory. J. Electron. Imaging 29(3), 033013 (2020)
López-Gil, J.M., Gil, R., García, R., et al.: Do deepfakes adequately display emotions? a study on deepfake facial emotion expression. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022 (2022)
Maras, M.H., Alexandrou, A.: Determining authenticity of video evidence in the age of artificial intelligence and in the wake of deepfake videos. Int. J. Evidence Proof 23(3), 255–262 (2019)
Mittal, T., Bhattacharya, U., Chandra, R., Bera, A., Manocha, D.: Emotions don’t lie: An audio-visual deepfake detection method using affective cues. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 2823–2832 (2020)
Nirkin, Y., Wolf, L., Keller, Y., Hassner, T.: Deepfake detection based on discrepancies between faces and their context. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(10), 6111–6121 (2021)
Prashnani, E., Goebel, M., Manjunath, B.: Generalizable deepfake detection with phase-based motion analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.09363 (2022)
Rana, M.S., Nobi, M.N., Murali, B., Sung, A.H.: Deepfake detection: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access (2022)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Westerlund, M.: The emergence of deepfake technology: a review. Technol. Innov. Manage. Rev. 9(11) (2019)
Wodajo, D., Atnafu, S.: Deepfake video detection using convolutional vision transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.11126 (2021)
Yadav, G., Maheshwari, S., Agarwal, A.: Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization based enhancement for real time video system. In: 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), pp. 2392–2397 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2014.6968381
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the CINECA award under the ISCRA initiatives, for the availability of high-performance computing resources and support within the projects IsC80_FEAD-D and IsC93_FEAD-DII. We also acknowledge the NVIDIA AI Technology Center, EMEA, for its support and access to computing resources. This work has been supported by BullyBuster - PRIN 2017 Project, funded by MIUR (CUP: E24I19000590001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gravina, M., Galli, A., De Micco, G., Marrone, S., Fiameni, G., Sansone, C. (2023). FEAD-D: Facial Expression Analysis in Deepfake Detection. In: Foresti, G.L., Fusiello, A., Hancock, E. (eds) Image Analysis and Processing – ICIAP 2023. ICIAP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14234. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43153-1_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43153-1_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43152-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43153-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)