Abstract
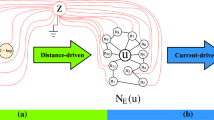
Unsupervised representation learning on bipartite graphs is of particular interest due to the lack of explicit labels and its application in a variety of domains. Several unsupervised representation learning methods make use of mutual information maximization between node-level and graph/sub-graph-level information. We argue that such methods are better suited to graph level tasks than node level tasks because local information in node representation is dominated by graph level information. Additionally, current approaches rely on building a global summary vector in which information diminishes as the graph scales. In this work, we concentrate on optimizing representations for node-level downstream tasks such as node classification/regression. The Bipartite Node Representation Learning (BipNRL) method, which aims to learn the node embeddings by maximizing MI between the node’s representation and self features without using summary vector is introduced. Furthermore, we propose the decoupled graph context loss on projected graphs to preserve the bipartite graph structure, enhancing representation for node-level tasks. Finally, we utilize attention-based neighborhood aggregation and modify the neighbourhood sampling algorithm to account for the high variance of node degree that is common in bipartite graphs. Extensive experiments show that BipNRL achieves cutting-edge results on multiple downstream tasks across diverse datasets.
Supported by organization Mastercard.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard, D.H.: Modular learning in neural networks. In AAAI, vol. 647 (1987)
Belghazi, M.I.: Mine: mutual information neural estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04062 (2018)
Cao, J., Lin, X., Guo, S., Liu, L., Liu, T., Wang, B.: Bipartite graph embedding via mutual information maximization. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 635–643 (2021)
Dong, W., Wu, J., Luo, Y., Ge, Z., Wang, P.: Node representation learning in graph via node-to-neighbourhood mutual information maximization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16620–16629 (2022)
Dong, Y., Chawla, N.V., Swami, A.: Metapath2vec: scalable representation learning for heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 135–144 (2017)
Frénay, B., Doquire, G., Verleysen, M.: Is mutual information adequate for feature selection in regression? Neural Netw. 48, 1–7 (2013)
Gao, M., Chen, L., He, X., Zhou, A.: Bine: bipartite network embedding. In: The 41st International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 715–724 (2018)
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: Node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 855–864 (2016)
Hamilton, W.L., Ying, R., Leskovec, J.: Inductive representation learning on large graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02216 (2017)
He, C.: Bipartite graph neural networks for efficient node representation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.11994 (2019)
Kingma, P., Welling, M., et al.: An introduction to variational autoencoders. Foundations Trends® Mach. Learn. 12(4), 307–392 (2019)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907 (2016)
Le, Q., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR (2014)
Park, C., Kim, D., Han, J., Hwanjo, Y.: Unsupervised attributed multiplex network embedding. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34,pp. 5371–5378 (2020)
Peng, Z.: Graph representation learning via graphical mutual information maximization. In: Proceedings of The Web Conference (2020)
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: Deepwalk: online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 701–710 (2014)
Sybrandt, J., Safro, I.: Fobe and hobe: first-and high-order bipartite embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.10953 (2019)
Tang, J., Qu, M., Wang, M., Zhang, M., Yan, J., Mei, Q.: Line: Large-scale information network embedding. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 1067–1077 (2015)
Vaswani, A.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (2017)
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10903 (2017)
Veličković, P., Fedus, W., Hamilton, W.L., Liò, P., Bengio, Y., Hjelm, R.D.: Deep graph infomax. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10341 (2018)
Velickovic, P., Fedus, W., Hamilton, W.L., Liò, P., Bengio, Y., Hjelm, R.D.: Deep graph infomax. ICLR (Poster) 2(3), 4 (2019)
Ying, R., He, R., Chen, K., Eksombatchai, P., Hamilton, W.L., Leskovec, J.: Graph convolutional neural networks for web-scale recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 974–983 (2018)
Zhang, D., Yin, J., Zhu, X., Zhang, C.: Attributed network embedding via subspace discovery. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 33(6), 1953–1980 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-019-00650-2
Zhang, Y., Xiong, Y., Kong, X., Zhu, Y.: Learning node embeddings in interaction graphs. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 397–406 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Poduval, P., Oberoi, G., Verma, S., Agarwal, A., Singh, K., Asthana, S. (2023). BipNRL: Mutual Information Maximization on Bipartite Graphs for Node Representation Learning. In: Koutra, D., Plant, C., Gomez Rodriguez, M., Baralis, E., Bonchi, F. (eds) Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: Research Track. ECML PKDD 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14172. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43421-1_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43421-1_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43420-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43421-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)