Abstract
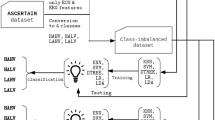
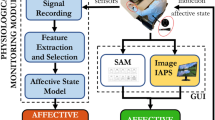
This paper presents two feature extraction methods for training different classification models for the detection of pleasure and displeasure defined by high and low valence levels using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). The study involved fifty-four volunteers who were presented with emotion-inducing image blocks while their prefrontal cortex brain activity was recorded by an fNIRS device. Results from the participants’ responses to a questionnaire showed no significant differences in valence-related scores. The study used statistical and ROCKET methods to extract features and trained six models to discriminate high and low valence. The results showed that ROCKET features performed best with kNN, MLP and SVM classifiers. The research highlighted the potential of different feature extraction methods to improve the accuracy of biosignal analysis from fNIRS devices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, N.S.: An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 46(3), 175–185 (1992)
Chen, T., Guestrin, C.: XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 785–794. ACM (2016)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Dempster, A., Petitjean, F., Webb, G.I.: Rocket: exceptionally fast and accurate time series classification using random convolutional kernels. arXiv:1910.13051 (2019)
Ekman, P.: Universal and cultural differences in facial expression of emotions, pp. 207–283. University of Nebraska Press (1972)
Fishburn, F.A., Ludlum, R.S., Vaidya, C.J., Medvedev, A.V.: Temporal derivative distribution repair (TDDR): a motion correction method for fNIRS. Neuroimage 184, 171–179 (2019)
García-Pérez, E., Sánchez-Reolid, D., Sánchez-Reolid, R., Fernández-Caballero, A., Latorre, J.M., Borja, A.L.: Electroencephalographic signal processing from brain-computer-interface following image-based emotion induction. In: Julián, V., Carneiro, J., Alonso, R.S., Chamoso, P., Novais, P. (eds.) ISAmI 2022. LNCS, pp. 239–248. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22356-3_23
Ho, T.K.: Random decision forests. In: 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 278–282. IEEE (1995)
Lang, P.J., Bradley, M.M., Cuthbert, B.N.: International affective picture system (IAPS): affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. Technical report. A-8, University of Florida (2008)
Lang, P.J.: Behavioral Treatment and Bio-behavioral Assessment: Computer Applications. Ablex Publishing (1980)
Martínez-Rodrigo, A., García-Martínez, B., Alcaraz, R., González, P., Fernández-Caballero, A.: Multiscale entropy analysis for recognition of visually elicited negative stress from EEG recordings. Int. J. Neural Syst. 29(2), 1850038 (2019)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Peirce, J., et al.: PsychoPy2: experiments in behavior made easy. Behav. Res. Methods 51(1), 195–203 (2019)
Pollonini, L., Olds, C., Abaya, L., Bortfeld, H., Beauchamp, M.S., Oghalai, J.S.: Phoebe: a method for real time mapping of optodes-scalp coupling in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 7(12), 5104–5119 (2016)
Rish, I.: An empirical study of the Naive Bayes classifier. In: IJCAI 2001 Workshop on Empirical Methods in Artificial Intelligence, vol. 3, pp. 41–46 (2001)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088), 533–536 (1986)
Russell, J.: A circumplex model of affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 39(6), 1161–1178 (1980)
Sánchez-Reolid, R., et al.: Emotion classification from EEG with a low-cost BCI versus a high-end equipment. Int. J. Neural Syst. 32(10), 2250041 (2022)
Sánchez-Reolid, R., López de la Rosa, F., Sánchez-Reolid, D., López, M.T., Fernández-Caballero, A.: Machine learning techniques for arousal classification from electrodermal activity: a systematic review. Sensors 22(22) (2022)
Acknowledgements
Grants PID2020-115220RB-C21 and EQC2019-006063-P funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 and by “ERDF A way to make Europe”. Grant 2022-GRIN-34436 funded by Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha and by “ERDF A way of making Europe”. Grant PTA2019-016876-I funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 and by “ESF Investing in your future”. This research was also supported by CIBERSAM, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sánchez-Reolid, D., Sánchez-Reolid, R., Fernández-Caballero, A., Borja, A.L. (2023). Pleasure and Displeasure Identification from fNIRS Signals. In: Novais, P., et al. Ambient Intelligence – Software and Applications – 14th International Symposium on Ambient Intelligence. ISAmI 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 770. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43461-7_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43461-7_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43460-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43461-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)