Abstract
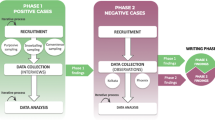
Teams have become building blocks of organizations, leading to an exponential increase in team studies, including team effectiveness studies in Scrum software development. However, research on measuring Scrum team effectiveness based on objective measures, contrary to self-reporting with Likert scales, is absent. Through a design science research methodology with literature review, focus groups, interviews, and an expert panel, 29 objective measures were identified contributing to seven team effectiveness concepts. All measures can be quantified or directly derived from work management systems, such as Jira or Azure DevOps. Examples include the number of solved retrospective items after a new sprint, contributing to the team effectiveness concept ‘Continuous Improvement’, and the number of times a sprint goal has been achieved, contributing to both ‘Team Morale’ and ‘Stakeholder Satisfaction’. In this way, the study offers proof of the benefits of agile, especially Scrum, software development through effective teams as well as providing practitioners a first insight in benchmarking their Scrum team effectiveness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
WMS
- 2.
TE
- 3.
CE
- 4.
SC
- 5.
R
- 6.
TA
- 7.
MS
- 8.
TM
- 9.
SS
References
Benders, J., Van Hootegem, G.: Teams and their context: moving the team discussion beyond existing dichotomies. J. Manage. Stud. 36(5), 609–628 (1999)
Buljac-Samardzic, M., Doekhie, K.D., van Wijngaarden, J.D.: Interventions to improve team effectiveness within health care: a systematic review of the past decade. Hum. Resour. Health 18(1), 1–42 (2020)
Delgado Pinã, M.I., María Romero Martínez, A., Gómez Martínez, L.: Teams in organizations: a review on team effectiveness. Team Perform. Manage. Int. J. 14(1/2), 7–21 (2008)
Doolen, T.L., Hacker, M.E., Van Aken, E.: Managing organizational context for engineering team effectiveness. Team Perform. Manage. Int. J. 12(5/6), 138–154 (2006)
Fransen, J., Kirschner, P.A., Erkens, G.: Mediating team effectiveness in the context of collaborative learning: the importance of team and task awareness. Comput. Hum. Behav. 27(3), 1103–1113 (2011)
Hackman, J.R., Morris, C.G.: Group tasks, group interaction process, and group performance effectiveness: a review and proposed integration. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 8, 45–99 (1975)
Imbrie, P., Maller, S., Immekus, J.: Assessing team effectiveness. In: 2005 Annual Conference, pp. 10–229 (2005)
Jahedi, S., Méndez, F.: On the advantages and disadvantages of subjective measures. J. Econ. Behav. Org. 98, 97–114 (2014)
Joshi, A., Kale, S., Chandel, S., Pal, D.K.: Likert scale: explored and explained. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 7(4), 396 (2015)
Kitchenham, B.: Procedures for performing systematic reviews 33, 1–26 (2004)
Lemieux-Charles, L., McGuire, W.L.: What do we know about health care team effectiveness? A review of the literature. Med. Care Res. Rev. 63(3), 263–300 (2006)
Mathieu, J.E., Gallagher, P.T., Domingo, M.A., Klock, E.A.: Embracing complexity: reviewing the past decade of team effectiveness research. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psych. Organ. Behav. 6, 17–46 (2019)
Moe, N.B., Dingsøyr, T.: Scrum and team effectiveness: theory and practice. In: Abrahamsson, P., Baskerville, R., Conboy, K., Fitzgerald, B., Morgan, L., Wang, X. (eds.) XP 2008. LNBIP, vol. 9, pp. 11–20. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68255-4_2
One, V.: 14th annual state of agile development survey. Version One, INC. (2020). https://stateofagile.com/#ufh-c-7027494-state-of-agile
Peffers, K., Tuunanen, T., Rothenberger, M.A., Chatterjee, S.: A design science research methodology for information systems research. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 24(3), 45–77 (2007)
Purwanto, A.: Benefit of benchmarking methods in several industries: a systematic literature review. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 11(8), 508–518 (2020)
Rashidi, M.N., Begum, R.A., Mokhtar, M., Pereira, J.: The conduct of structured interviews as research implementation method. J. Adv. Res. Des. 1(1), 28–34 (2014)
Raymond, J.: Benchmarking in public procurement. Benchmarking Int. J. 15(6), 782–793 (2008)
Salas, E., Sims, D.E., Burke, C.S.: Is there a “big five” in teamwork? Small Group Res. 36(5), 555–599 (2005)
Schwaber, K., Sutherland, J.: The Scrum Guide, vol. 21, p. 1 (2011)
Scissons, E.H.: All numbers are not created equal: measurement issues in assessing board governance. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2(2), 20–26 (2002)
Verwijs, C., Russo, D.: A theory of scrum team effectiveness. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 32, 1–51 (2023)
Wohlin, C., Runeson, P., Höst, M., Ohlsson, M., Regnell, B., Wesslén, A.: Experimentation in Software Engineering-An Introduction. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Doedrecht (2000)
Wright, D.B., Gaskell, G.D., O’Muircheartaigh, C.A.: How much is ‘quite a bit’? Mapping between numerical values and vague quantifiers. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 8(5), 479–496 (1994)
Yang, M.C., Jin, Y.: An examination of team effectiveness in distributed and colocated engineering teams. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 24(2), 400 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Beek, K., Wagenaar, G., Kester, L., Overbeek, S., de Rooij, E. (2023). Measuring Team Effectiveness in Scrum. In: Fernandes, J.M., Travassos, G.H., Lenarduzzi, V., Li, X. (eds) Quality of Information and Communications Technology. QUATIC 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1871. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43703-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43703-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43702-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43703-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)