Abstract
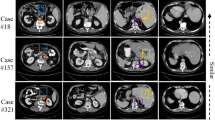
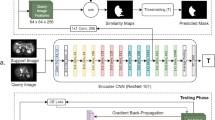
Few-shot segmentation (FSS) models have gained popularity in medical imaging analysis due to their ability to generalize well to unseen classes with only a small amount of annotated data. A key requirement for the success of FSS models is a diverse set of annotated classes as the base training tasks. This is a difficult condition to meet in the medical domain due to the lack of annotations, especially in volumetric images. To tackle this problem, self-supervised FSS methods for 3D images have been introduced. However, existing methods often ignore intra-volume information in 3D image segmentation, which can limit their performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel self-supervised volume-aware FSS framework for 3D medical images, termed VISA-FSS. In general, VISA-FSS aims to learn continuous shape changes that exist among consecutive slices within a volumetric image to improve the performance of 3D medical segmentation. To achieve this goal, we introduce a volume-aware task generation method that utilizes consecutive slices within a 3D image to construct more varied and realistic self-supervised FSS tasks during training. In addition, to provide pseudo-labels for consecutive slices, a novel strategy is proposed that propagates pseudo-labels of a slice to its adjacent slices using flow field vectors to preserve anatomical shape continuity. In the inference time, we then introduce a volumetric segmentation strategy to fully exploit the inter-slice information within volumetric images. Comprehensive experiments on two common medical benchmarks, including abdomen CT and MRI, demonstrate the effectiveness of our model over state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/sharif-ml-lab/visa-fss
M. Mozafari and A. Bitarafan—Equal Contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., Lucchi, A., Fua, P., Süsstrunk, S.: Slic superpixels. Tech. rep. (2010)
Balakrishnan, G., Zhao, A., Sabuncu, M.R., Guttag, J., Dalca, A.V.: An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9252–9260 (2018)
Bitarafan, A., Azampour, M.F., Bakhtari, K., Soleymani Baghshah, M., Keicher, M., Navab, N.: Vol2flow: segment 3d volumes using a sequence of registration flows. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Proceedings, Part IV, pp. 609–618. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16440-8_58
Bitarafan, A., Nikdan, M., Baghshah, M.S.: 3d image segmentation with sparse annotation by self-training and internal registration. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 25(7), 2665–2672 (2020)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
Chen, X., et al.: A deep learning-based auto-segmentation system for organs-at-risk on whole-body computed tomography images for radiation therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 160, 175–184 (2021)
Denner, S., et al.: Spatio-temporal learning from longitudinal data for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S. (eds.) BrainLes 2020. LNCS, vol. 12658, pp. 111–121. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_11
Ding, H., Sun, C., Tang, H., Cai, D., Yan, Y.: Few-shot medical image segmentation with cycle-resemblance attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 2488–2497 (2023)
Farshad, A., Makarevich, A., Belagiannis, V., Navab, N.: Metamedseg: volumetric meta-learning for few-shot organ segmentation. In: Domain Adaptation and Representation Transfer 2022, pp. 45–55. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16852-9_5
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Huttenlocher, D.P.: Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 59, 167–181 (2004)
Finn, C., Abbeel, P., Levine, S.: Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1126–1135. PMLR (2017)
Hesamian, M.H., Jia, W., He, X., Kennedy, P.: Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 32, 582–596 (2019)
Hospedales, T., Antoniou, A., Micaelli, P., Storkey, A.: Meta-learning in neural networks: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(9), 5149–5169 (2021)
Kavur, A.E., et al.: Chaos challenge-combined (ct-mr) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 69, 101950 (2021)
Landman, B., Xu, Z., Igelsias, J., Styner, M., Langerak, T., Klein, A.: Miccai multi-atlas labeling beyond the cranial vault-workshop and challenge. In: Proc. MICCAI Multi-Atlas Labeling Beyond Cranial Vault-Workshop Challenge. vol. 5, p. 12 (2015)
Li, X., Chen, H., Qi, X., Dou, Q., Fu, C.W., Heng, P.A.: H-denseunet: hybrid densely connected unet for liver and tumor segmentation from ct volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(12), 2663–2674 (2018)
Lutnick, B.: An integrated iterative annotation technique for easing neural network training in medical image analysis. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1(2), 112–119 (2019)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Ouyang, C., Biffi, C., Chen, C., Kart, T., Qiu, H., Rueckert, D.: Self-supervision with superpixels: training few-shot medical image segmentation without annotation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12374, pp. 762–780. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58526-6_45
Ouyang, C., Kamnitsas, K., Biffi, C., Duan, J., Rueckert, D.: Data efficient unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-modality image segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 669–677. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_74
Roy, A.G., Siddiqui, S., Pölsterl, S., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Squeeze & excite’guided few-shot segmentation of volumetric images. Med. Image Anal. 59, 101587 (2020)
Snell, J., Swersky, K., Zemel, R.: Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (2017)
Tang, H., Liu, X., Sun, S., Yan, X., Xie, X.: Recurrent mask refinement for few-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3918–3928 (2021)
Tsochatzidis, L., Koutla, P., Costaridou, L., Pratikakis, I.: Integrating segmentation information into CNN for breast cancer diagnosis of mammographic masses. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 200, 105913 (2021)
Wang, K., Liew, J.H., Zou, Y., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Panet: few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9197–9206 (2019)
Zhao, A., Balakrishnan, G., Durand, F., Guttag, J.V., Dalca, A.V.: Data augmentation using learned transformations for one-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8543–8553 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mozafari, M., Bitarafan, A., Azampour, M.F., Farshad, A., Soleymani Baghshah, M., Navab, N. (2023). VISA-FSS: A Volume-Informed Self Supervised Approach for Few-Shot 3D Segmentation. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14221. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43895-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43895-0_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43894-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43895-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)