Abstract
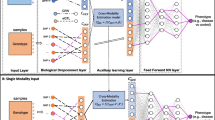
The modeling of the interaction between brain structure and function using deep learning techniques has yielded remarkable success in identifying potential biomarkers for different clinical phenotypes and brain diseases. However, most existing studies focus on one-way mapping, either projecting brain function to brain structure or inversely. This type of unidirectional mapping approach is limited by the fact that it treats the mapping as a one-way task and neglects the intrinsic unity between these two modalities. Moreover, when dealing with the same biological brain, mapping from structure to function and from function to structure yields dissimilar outcomes, highlighting the likelihood of bias in one-way mapping. To address this issue, we propose a novel bidirectional mapping model, named Bidirectional Mapping with Contrastive Learning (BMCL), to reduce the bias between these two unidirectional mappings via ROI-level contrastive learning. We evaluate our framework on clinical phenotype and neurodegenerative disease predictions using two publicly available datasets (HCP and OASIS). Our results demonstrate the superiority of BMCL compared to several state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T.M., McConaughy, S., Ivanova, M., Rescorla, L.: Manual for the ASEBA brief problem monitor (BPM), vol. 33. ASEBA, Burlington, VT (2011)
Airavaara, M., Pletnikova, O., Doyle, M.E., Zhang, Y.E., Troncoso, J.C., Liu, Q.R.: Identification of novel GDNF isoforms and cis-antisense GDNFOS gene and their regulation in human middle temporal gyrus of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 286(52), 45093–45102 (2011)
Bathelt, J., O’Reilly, H., Clayden, J.D., Cross, J.H., de Haan, M.: Functional brain network organisation of children between 2 and 5 years derived from reconstructed activity of cortical sources of high-density EEG recordings. Neuroimage 82, 595–604 (2013)
Calhoun, V.D., Sui, J.: Multimodal fusion of brain imaging data: a key to finding the missing link (s) in complex mental illness. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 1(3), 230–244 (2016)
Couppis, M.H., Kennedy, C.H.: The rewarding effect of aggression is reduced by nucleus accumbens dopamine receptor antagonism in mice. Psychopharmacology 197, 449–456 (2008)
Cui, H., et al.: BrainGB: a benchmark for brain network analysis with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2022)
Fischl, B.: Freesurfer. Neuroimage 62(2), 774–781 (2012)
Fornito, A., Zalesky, A., Bullmore, E.: Fundamentals of Brain Network Analysis. Academic Press, Cambridge (2016)
Freeman, D., Ha, D., Metz, L.: Learning to predict without looking ahead: world models without forward prediction. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C.F., Behrens, T.E., Woolrich, M.W., Smith, S.M.: FSL. Neuroimage 62(2), 782–790 (2012)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Variational graph auto-encoders. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.07308 (2016)
LaMontagne, P.J., et al.: Oasis-3: longitudinal neuroimaging, clinical, and cognitive dataset for normal aging and Alzheimer disease. MedRxiv pp. 2019–2012 (2019)
Lee, G., Nho, K., Kang, B., Sohn, K.A., Kim, D.: Predicting Alzheimer’s disease progression using multi-modal deep learning approach. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1952 (2019)
Lee, J., Lee, I., Kang, J.: Self-attention graph pooling. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3734–3743. PMLR (2019)
Li, X., et al.: BrainGNN: interpretable brain graph neural network for fMRI analysis. Med. Image Anal. 74, 102233 (2021)
Liu, Y., Ge, E., Qiang, N., Liu, T., Ge, B.: Spatial-temporal convolutional attention for mapping functional brain networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.02315 (2022)
Peterson, C.K., Shackman, A.J., Harmon-Jones, E.: The role of asymmetrical frontal cortical activity in aggression. Psychophysiology 45(1), 86–92 (2008)
Piras, I.S., et al.: Transcriptome changes in the Alzheimer’s disease middle temporal gyrus: importance of RNA metabolism and mitochondria-associated membrane genes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 70(3), 691–713 (2019)
Qi, S., Meesters, S., Nicolay, K., ter Haar Romeny, B.M., Ossenblok, P.: The influence of construction methodology on structural brain network measures: a review. J. Neurosci. Methods 253, 170–182 (2015)
Sundararajan, M., Taly, A., Yan, Q.: Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 3319–3328. PMLR (2017)
Tang, H., et al.: Hierarchical brain embedding using explainable graph learning. In: 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2022)
Tang, H., et al.: Signed graph representation learning for functional-to-structural brain network mapping. Med. Image Anal. 83, 102674 (2023)
Tang, H., Ma, G., Guo, L., Fu, X., Huang, H., Zhan, L.: Contrastive brain network learning via hierarchical signed graph pooling model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022)
Tewarie, P., et al.: Mapping functional brain networks from the structural connectome: relating the series expansion and eigenmode approaches. Neuroimage 216, 116805 (2020)
Van Essen, D.C., et al.: The Wu-Minn human connectome project: an overview. Neuroimage 80, 62–79 (2013)
Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., Nieto-Castanon, A.: Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2(3), 125–141 (2012)
Xu, K., et al.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2048–2057. PMLR (2015)
Yan, J., et al.: Modeling spatio-temporal patterns of holistic functional brain networks via multi-head guided attention graph neural networks (multi-head GaGNNs). Med. Image Anal. 80, 102518 (2022)
Yeh, C.H., Jones, D.K., Liang, X., Descoteaux, M., Connelly, A.: Mapping structural connectivity using diffusion MRI: challenges and opportunities. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 53(6), 1666–1682 (2021)
Ying, Z., You, J., Morris, C., Ren, X., Hamilton, W., Leskovec, J.: Hierarchical graph representation learning with differentiable pooling. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31 (2018)
Zhang, L., Wang, L., Zhu, D., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Predicting brain structural network using functional connectivity. Med. Image Anal. 79, 102463 (2022)
Zhang, W., Zhan, L., Thompson, P., Wang, Y.: Deep representation learning for multimodal brain networks. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12267, pp. 613–624. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59728-3_60
Zhen, L., Hu, P., Wang, X., Peng, D.: Deep supervised cross-modal retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10394–10403 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by NIH (R01AG071243, R01MH125928, R21AG065942, R01EY032125, and U01AG068057) and NSF (IIS 2045848 and IIS 1837956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ye, K. et al. (2023). Bidirectional Mapping with Contrastive Learning on Multimodal Neuroimaging Data. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14222. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43898-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43898-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43897-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43898-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)