Abstract
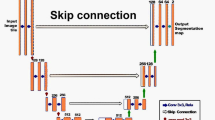
Deep neural networks have been widely applied in dichotomous medical image segmentation (DMIS) of many anatomical structures in several modalities, achieving promising performance. However, existing networks tend to struggle with task-specific, heavy and complex designs to improve accuracy. They made little instructions to which feature channels would be more beneficial for segmentation, and that may be why the performance and universality of these segmentation models are hindered. In this study, we propose an instructive feature enhancement approach, namely IFE, to adaptively select feature channels with rich texture cues and strong discriminability to enhance raw features based on local curvature or global information entropy criteria. Being plug-and-play and applicable for diverse DMIS tasks, IFE encourages the model to focus on texture-rich features which are especially important for the ambiguous and challenging boundary identification, simultaneously achieving simplicity, universality, and certain interpretability. To evaluate the proposed IFE, we constructed the first large-scale DMIS dataset Cosmos55k, which contains 55,023 images from 7 modalities and 26 anatomical structures. Extensive experiments show that IFE can improve the performance of classic segmentation networks across different anatomies and modalities with only slight modifications. Code is available at https://github.com/yezi-66/IFE.
L. Liu and H. Zhou—Contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Khalek, S., Ishak, A.B., Omer, O.A., Obada, A.S.: A two-dimensional image segmentation method based on genetic algorithm and entropy. Optik 131, 414–422 (2017)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: IEEE CVPR (2009)
Bakas, S., et al.: Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the brats challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.02629 (2018)
Bernard, O., et al.: Deep learning techniques for automatic MRI cardiac multi-structures segmentation and diagnosis: is the problem solved? IEEE TMI 37(11), 2514–2525 (2018)
Bilic, P., et al.: The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (LiTS). MIA 84, 102680 (2023)
Cao, G., Xie, X., Yang, W., Liao, Q., Shi, G., Wu, J.: Feature-fused SSD: fast detection for small objects. In: SPIE ICGIP, vol. 10615 (2018)
Chang, H.H., Zhuang, A.H., Valentino, D.J., Chu, W.C.: Performance measure characterization for evaluating neuroimage segmentation algorithms. Neuroimage 47(1), 122–135 (2009)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE TPAMI 40(4), 834–848 (2017)
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: IEEE CVPR (2017)
Codella, N.C., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). In: ISBI (2018)
Crum, W.R., Camara, O., Hill, D.L.: Generalized overlap measures for evaluation and validation in medical image analysis. IEEE TMI 25(11), 1451–1461 (2006)
Dubuisson, M.P., Jain, A.K.: A modified Hausdorff distance for object matching. In: IEEE ICPR (1994)
Fan, D.P., Ji, G.P., Cheng, M.M., Shao, L.: Concealed object detection. IEEE TPAMI 44(10), 6024–6042 (2021)
Gong, Y., Sbalzarini, I.F.: Curvature filters efficiently reduce certain variational energies. IEEE TIP 26(4), 1786–1798 (2017)
Hou, Q., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: IEEE CVPR (2021)
Howard, A., et al.: Searching for MobileNetV3. In: IEEE ICCV (2019)
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A., Petersen, J., Maier-Hein, K.H.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Meth. 18(2), 203–211 (2021)
Jha, D., et al.: Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset. In: Ro, Y.M., et al. (eds.) MMM 2020. LNCS, vol. 11962, pp. 451–462. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37734-2_37
Ji, W., et al.: Learning calibrated medical image segmentation via multi-rater agreement modeling. In: IEEE CVPR (2021)
Ji, Y., et al.: AMOS: a large-scale abdominal multi-organ benchmark for versatile medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08023 (2022)
Kavur, A.E., et al.: Chaos challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. MIA 69, 101950 (2021)
Litjens, G., et al.: Evaluation of prostate segmentation algorithms for MRI: the PROMISE12 challenge. MIA 18(2), 359–373 (2014)
Luo, X., et al.: WORD: a large scale dataset, benchmark and clinical applicable study for abdominal organ segmentation from CT image. MIA 82, 102642 (2022)
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., Pritch, Y., Hornung, A.: Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: IEEE CVPR (2012)
Qin, X., Dai, H., Hu, X., Fan, D.P., Shao, L., Van Gool, L.: Highly accurate dichotomous image segmentation. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) Computer Vision, ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13678, pp. 38–56. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19797-0_3
Raghu, M., Unterthiner, T., Kornblith, S., Zhang, C., Dosovitskiy, A.: Do vision transformers see like convolutional neural networks? Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 12116–12128 (2021)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Sekuboyina, A., et al.: Verse: a vertebrae labelling and segmentation benchmark for multi-detector CT images. MIA 73, 102166 (2021)
Simpson, A.L., et al.: A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09063 (2019)
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., Alemi, A.: Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: AAAI (2017)
Zhao, Z., Chen, H., Wang, L.: A coarse-to-fine framework for the 2021 kidney and kidney tumor segmentation challenge. In: Heller, N., Isensee, F., Trofimova, D., Tejpaul, R., Papanikolopoulos, N., Weight, C. (eds.) KiTS 2021. LNCS, vol. 13168, pp. 53–58. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98385-7_8
Zhong, Z., et al.: Squeeze-and-attention networks for semantic segmentation. In: IEEE CVPR (2020)
Zhou, D., et al.: Iou loss for 2D/3D object detection. In: IEEE 3DV (2019)
Zhou, Y., et al.: Prior-aware neural network for partially-supervised multi-organ segmentation. In: IEEE ICCV (2019)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M.M.R., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE TMI 39(6), 1856–1867 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors of this paper sincerely appreciate all the challenge organizers and owners for providing the public MIS datasets including AbdomenCT-1K, ACDC, AMOS 2022, BraTS20, CHAOS, CRAG, crossMoDA, EndoTect 2020, ETIS-Larib Polyp DB, iChallenge-AMD, iChallenge-PALM, IDRiD 2018, ISIC 2018, I2CVB, KiPA22, KiTS19& KiTS21, Kvasir-SEG, LUNA16, Multi-Atlas Labeling Beyond the Cranial Vault (Abdomen), Montgomery County CXR Set, M&Ms, MSD, NCI-ISBI 2013, PROMISE12, QUBIQ 2021, SIIM-ACR, SLIVER07, VerSe19 & VerSe20, Warwick-QU, and WORD.
This work was supported by the grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62171290, 62101343), Shenzhen-Hong Kong Joint Research Program (No. SGDX20201103095613036), and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovations Committee (No. 20200812143441001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, L. et al. (2023). Instructive Feature Enhancement for Dichotomous Medical Image Segmentation. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14223. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43901-8_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43901-8_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43900-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43901-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)