Abstract
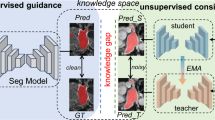
By fully utilizing unlabeled data, the semi-supervised learning (SSL) technique has recently produced promising results in the segmentation of medical images. Pseudo labeling and consistency regularization are two effective strategies for using unlabeled data. Yet, the traditional pseudo labeling method will filter out low-confidence pixels. The advantages of both high- and low-confidence data are not fully exploited by consistency regularization. Therefore, neither of these two methods can make full use of unlabeled data. We proposed a novel decoupled consistency semi-supervised medical image segmentation framework. First, the dynamic threshold is utilized to decouple the prediction data into consistent and inconsistent parts. For the consistent part, we use the method of cross pseudo supervision to optimize it. For the inconsistent part, we further decouple it into unreliable data that is likely to occur close to the decision boundary and guidance data that is more likely to emerge near the high-density area. Unreliable data will be optimized in the direction of guidance data. We refer to this action as directional consistency. Furthermore, in order to fully utilize the data, we incorporate feature maps into the training process and calculate the loss of feature consistency. A significant number of experiments have demonstrated the superiority of our proposed method. The code is available at https://github.com/wxfaaaaa/DCNet.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masood, S., Sharif, M., Masood, A., Yasmin, M., Raza, M.: A survey on medical image segmentation. Curr. Med. Imaging 11(1), 3–14 (2015)
Li, X., Yu, L., Chen, H., Fu, C.W., Xing, L., Heng, P.A.: Transformation-consistent self-ensembling model for semisupervised medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(2), 523–534 (2020)
Qiao, S., Shen, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, B., Yuille, A.: Deep co-training for semi-supervised image recognition. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 135–152 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Zhou, Y., et al.: Semi-supervised 3d abdominal multi-organ segmentation via deep multi-planar co-training. In: 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 121–140. IEEE (2019)
Xia, Y., et al.: 3D semi-supervised learning with uncertainty-aware multi-view co-training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 3646–3655 (2020)
Ouali, Y., Hudelot, C., Tami, M.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross-consistency training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12674–12684 (2020)
Ke, Z., Qiu, D., Li, K., Yan, Q., Lau, R.W.H.: Guided collaborative training for pixel-wise semi-supervised learning. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12358, pp. 429–445. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58601-0_26
Kim, J., Jang, J., Park, H.: Structured consistency loss for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04647 (2020)
French, G., Aila, T., Laine, S., Mackiewicz, M., Finlayson, G.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation needs strong, high-dimensional perturbations (2019)
Masood, S., et al.: Automatic choroid layer segmentation from optical coherence tomography images using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–18 (2019)
Wang, Y., et al.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation using unreliable pseudo-labels supplementary material (2022)
Bernard, O., et al.: Deep learning techniques for automatic MRI cardiac multi-structures segmentation and diagnosis: is the problem solved? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(11), 2514–2525 (2018)
Litjens, G., et al.: Evaluation of prostate segmentation algorithms for MRI: the promise12 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 18(2), 359–373 (2014)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on Challenges in Representation Learning, ICML, vol. 3, p. 896 (2013)
Arazo, E., Ortego, D., Albert, P., O’Connor, N.E., McGuinness, K.: Pseudo-labeling and confirmation bias in deep semi-supervised learning. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Rizve, M.N., Duarte, K., Rawat, Y.S., Shah, M.: In defense of pseudo-labeling: an uncertainty-aware pseudo-label selection framework for semi-supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.06329 (2021)
Chen, X., Yuan, Y., Zeng, G., Wang, J.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross pseudo supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2613–2622 (2021)
Bachman, P., Alsharif, O., Precup, D.: Learning with pseudo-ensembles. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (2014)
Sajjadi, M., Javanmardi, M., Tasdizen, T.: Regularization with stochastic transformations and perturbations for deep semi-supervised learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29 (2016)
Bortsova, G., Dubost, F., Hogeweg, L., Katramados, I., de Bruijne, M.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via learning consistency under transformations. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11769, pp. 810–818. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_90
Xu, Y., et al.: Dash: Semi-supervised learning with dynamic thresholding. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 11525–11536. PMLR (2021)
Zhang, B., et al.: FlexMatch: boosting semi-supervised learning with curriculum pseudo labeling. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 18408–18419 (2021)
Wang, Y., et al.: FreeMatch: self-adaptive thresholding for semi-supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.07246 (2022)
Luo, X., Chen, J., Song, T., Wang, G.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation through dual-task consistency. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 8801–8809 (2021)
Wu, Y., Xu, M., Ge, Z., Cai, J., Zhang, L.: Semi-supervised left atrium segmentation with mutual consistency training. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 297–306. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_28
Wu, Y., Wu, Z., Wu, Q., Ge, Z., Cai, J.: Exploring smoothness and class-separation for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.01324 (2022)
Luo, X., et al.: Efficient semi-supervised gross target volume of nasopharyngeal carcinoma segmentation via uncertainty rectified pyramid consistency. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 318–329. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_30
Laine, S., Aila, T.: Temporal ensembling for semi-supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.02242 (2016)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62002304), and also by Anhui Province KevLaboratory of Translational Cancer Research (KFKT 202308), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, F., Fei, J., Chen, Y., Huang, C. (2023). Decoupled Consistency for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14220. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43907-0_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43907-0_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43906-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43907-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)