Abstract
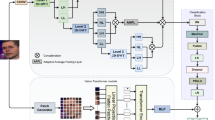
Face manipulation technologies pose a great threat to the current digital media. Although previous methods have achieved excellent detection performance, they tend to focus on specific artifacts and lead to overfitting. Erasing-based augmentations can alleviate this issue, but they still suffer from high randomness and fixed shapes. Therefore, we propose a novel face masking method named Landmarks Based Erasing (LBE), which exploits the geometric information of the face and forgery attention map to perform erasure, thereby forcing the network to mine discriminative features from other face regions. Furthermore, Wavelet Packet with Attention (WPA) mechanism module is designed to extract multi-level frequency features, providing a complementary perspective to LBE module. Finally, we employ a score fusion strategy to fuse two types of complementary feature information for forgery detection. Extensive experiments on three large public datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art detection performance and exhibits good generalization ability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deepfakes (2018). www.github.com/deepfakes/faceswap
FaceSwap (2018). www.github.com/MarekKowalski/FaceSwap/
FaceApp (2019). www.faceapp.com/app
Afchar, D., Nozick, V., Yamagishi, J., Echizen, I.: MesoNet: a compact facial video forgery detection network. In: 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS) (2018)
Cao, Y., Xu, J., Lin, S., Wei, F., Hu, H.: GCNet: non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2019)
Chen, Z., Yang, H.: Manipulated face detector: joint spatial and frequency domain attention network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.029581(2), 4 (2020)
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
Dai, Y., Fei, J., Wang, H., Xia, Z.: Attentional local contrastive learning for face forgery detection. In: Pimenidis, E., Angelov, P., Jayne, C., Papaleonidas, A., Aydin, M. (eds.) ICANN 2022, Part I. LNCS, vol. 13529, pp. 709–721. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15919-0_59
Dang, H., Liu, F., Stehouwer, J., Liu, X., Jain, A.: On the detection of digital face manipulation (2019)
Das, S., Seferbekov, S., Datta, A., Islam, M., Amin, M., et al.: Towards solving the deepfake problem: an analysis on improving deepfake detection using dynamic face augmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3776–3785 (2021)
Frank, J., Eisenhofer, T., Schnherr, L., Fischer, A., Kolossa, D., Holz, T.: Leveraging frequency analysis for deep fake image recognition (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 (2017)
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aila, T.: A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4401–4410 (2019)
King, D.E.: Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1755–1758 (2009)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Li, L., Bao, J., Yang, H., Chen, D., Wen, F.: FaceShifter: towards high fidelity and occlusion aware face swapping. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.13457 (2019)
Li, L., et al.: Face X-ray for more general face forgery detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5001–5010 (2020)
Li, Y., Yang, X., Sun, P., Qi, H., Lyu, S.: Celeb-DF: a large-scale challenging dataset for deepfake forensics. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020)
Qian, Y., Yin, G., Sheng, L., Chen, Z., Shao, J.: Thinking in frequency: face forgery detection by mining frequency-aware clues. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12357, pp. 86–103. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_6
Rssler, A., Cozzolino, D., Verdoliva, L., Riess, C., Thies, J., Niener, M.: FaceForensics++: learning to detect manipulated facial images (2019)
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 618–626 (2017)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Tan, M., Le, Q.: EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6105–6114. PMLR (2019)
Wang, C., Deng, W.: Representative forgery mining for fake face detection (2021)
Wolter, M., Blanke, F., Heese, R., Garcke, J.: Wavelet-packets for deepfake image analysis and detection. Mach. Learn. 111, 1–33 (2022)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 13001–13008 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62001493), the Hunan Provincial Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project (QL20220009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cao, J., Deng, J., Yin, X., Zhang, Z., Chen, H. (2023). Semantic and Frequency Representation Mining for Face Manipulation Detection. In: Iliadis, L., Papaleonidas, A., Angelov, P., Jayne, C. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2023. ICANN 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14256. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44213-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44213-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44212-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44213-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)