Abstract
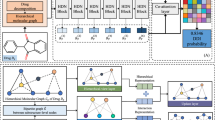
Adverse Drug-Drug Interactions(DDI) occur with drug combinations and mainly cause mortality and morbidity. The identification of potential DDI is essential for medical health. Most of the existing methods rely heavily on manually engineered domain knowledge, therefore, lack generalization and are inefficient. Drugs with similar molecular structures have similar chemical properties. The molecular structures of drugs can be obtained easily and the reactions between drugs are reactions between two molecular structures. In this paper, we proposed an artificially intelligent DDI prediction model, Molecular Structure-based Double-Central Drug-Drug Interaction prediction(MSDC-DDI). MSDC-DDI utilizes a double-central encoder and a cross-dependent schema to generate the representations of the drugs. MSDC-DDI made effective and accurate predictions, which achieved up to more than 99% in DDI prediction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia, J., Zhu, F., Ma, X., Cao, Z.W., Li, Y.X., Chen, Y.Z.: Mechanisms of drug combinations: interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8(2), 111–128 (2009)
Ryu, J.Y., Kim, H.U., Lee, S.Y.: Deep learning improves prediction of drug-drug and drug-food interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115(18), E4304–E4311 (2018)
Tatonetti, N.P., Ye, P.P., Daneshjou, R., Altman, R.B.: Data-driven prediction of drug effects and interactions. Sci. Transl. Med. 4(125), 125ra31–125ra31 (2012)
Whitebread, S., Hamon, J., Bojanic, D., Urban, L.: Keynote review: in vitro safety pharmacology profiling: an essential tool for successful drug development. Drug Discov. Today 10(21), 1421–1433 (2005)
Vilar, S., Harpaz, R., Uriarte, E., Santana, L., Rabadan, R., Friedman, C.: Drug-drug interaction through molecular structure similarity analysis. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 19(6), 1066–1074 (2012)
Vilar, S., et al.: Similarity-based modeling in large-scale prediction of drug-drug interactions. Nat. Protoc. 9(9), 2147–2163 (2014)
Gottlieb, A., Stein, G.Y., Oron, Y., Ruppin, E., Sharan, R.: INDI: a computational framework for inferring drug interactions and their associated recommendations. Mol. Syst. Biol. 8(1), 592 (2012)
Li, P., et al.: Large-scale exploration and analysis of drug combinations. Bioinformatics 31(12), 2007–2016 (2015)
Zhou, Y., Hou, Y., Shen, J., Huang, Y., Martin, W., Cheng, F.: Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 6(1), 1–18 (2020)
Deng, Y., Xu, X., Qiu, Y., Xia, J., Zhang, W., Liu, S.: A multimodal deep learning framework for predicting drug-drug interaction events. Bioinformatics 36(15), 4316–4322 (2020)
Zhang, C., Lu, Y., Zang, T.: CNN-DDI: a learning-based method for predicting drug-drug interactions using convolution neural networks. BMC Bioinform. 23(1), 1–12 (2022)
Lin, S., et al.: MDF-SA-DDI: predicting drug-drug interaction events based on multi-source drug fusion, multi-source feature fusion and transformer self-attention mechanism. Brief. Bioinform. 23(1), bbab421 (2022)
Wang, F., Lei, X., Liao, B., Wu, F.X.: Predicting drug-drug interactions by graph convolutional network with multi-kernel. Brief. Bioinform. 23(1), bbab511 (2022)
Celebi, R., Yasar, E., Uyar, H., Gumus, O., Dikenelli, O., Dumontier, M.: Evaluation of knowledge graph embedding approaches for drug-drug interaction prediction using linked open data (2018)
Karim, M.R., Cochez, M., Jares, J.B., Uddin, M., Beyan, O., Decker, S.: Drug-drug interaction prediction based on knowledge graph embeddings and convolutional-LSTM network. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics, pp. 113–123 (2019)
Chen, Y., Ma, T., Yang, X., Wang, J., Song, B., Zeng, X.: MUFFIN: multi-scale feature fusion for drug-drug interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 37(17), 2651–2658 (2021)
Yu, H., Dong, W., Shi, J.: RANEDDI: relation-aware network embedding for drug-drug interaction prediction. Inf. Sci. 582, 167–180 (2022)
Feng, Y.H., Zhang, S.W., Shi, J.Y.: DPDDI: a deep predictor for drug-drug interactions. BMC Bioinform. 21(1), 1–15 (2020)
Liu, Z., Wang, X.N., Yu, H., Shi, J.Y., Dong, W.M.: Predict multi-type drug-drug interactions in cold start scenario. BMC Bioinform. 23(1), 1–13 (2022)
Yu, Y., Huang, K., Zhang, C., Glass, L.M., Sun, J., Xiao, C.: SumGNN: multi-typed drug interaction prediction via efficient knowledge graph summarization. Bioinformatics 37(18), 2988–2995 (2021)
Lin, X., Quan, Z., Wang, Z.J., Ma, T., Zeng, X.: KGNN: knowledge graph neural network for drug-drug interaction prediction. In: IJCAI, vol. 380, pp. 2739–2745 (2020)
Hong, Y., Luo, P., Jin, S., Liu, X.: LaGAT: link-aware graph attention network for drug-drug interaction prediction. Bioinformatics (2022)
Scarselli, F., Gori, M., Tsoi, A.C., Hagenbuchner, M., Monfardini, G.: The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20(1), 61–80 (2008)
Nyamabo, A.K., Yu, H., Shi, J.Y.: SSI-DDI: substructure-substructure interactions for drug-drug interaction prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 22(6), bbab133 (2021)
Xu, N., Wang, P., Chen, L., Tao, J., Zhao, J.: MR-GNN: multi-resolution and dual graph neural network for predicting structured entity interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.09558 (2019)
Wang, H., Lian, D., Zhang, Y., Qin, L., Lin, X.: GoGNN: graph of graphs neural network for predicting structured entity interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.05537 (2020)
Nyamabo, A.K., Yu, H., Liu, Z., Shi, J.Y.: Drug-drug interaction prediction with learnable size-adaptive molecular substructures. Brief. Bioinform. 23(1), bbab441 (2022)
Zhu, X., Shen, Y., Lu, W.: Molecular substructure-aware network for drug-drug interaction prediction. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 4757–4761 (2022)
Gilmer, J., Schoenholz, S.S., Riley, P.F., Vinyals, O., Dahl, G.E.: Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1263–1272. PMLR (2017)
Ma, H., et al.: Cross-dependent graph neural networks for molecular property prediction. Bioinformatics 38(7), 2003–2009 (2022)
Weininger, D.: Smiles, a chemical language and information system. 1. introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 28(1), 31–36 (1988)
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.P.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: ICML (2011)
Wishart, D.S., et al.: DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(D1), D1074–D1082 (2018)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 28 (2014)
Wang, Y., Min, Y., Chen, X., Wu, J.: Multi-view graph contrastive representation learning for drug-drug interaction prediction. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 2921–2933 (2021)
Deac, A., Huang, Y.H., Veličković, P., Liò, P., Tang, J.: Drug-drug adverse effect prediction with graph co-attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00534 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baitai, C., Peng, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y. (2023). Molecular Structure-Based Double-Central Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction. In: Iliadis, L., Papaleonidas, A., Angelov, P., Jayne, C. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2023. ICANN 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14257. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44216-2_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44216-2_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44215-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44216-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)