Abstract
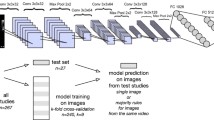
Echocardiography is a crucial and widely adopted imaging modality for diagnosing and monitoring cardiovascular diseases. Deep learning has been proven effective in analyzing medical images but is limited in echocardiograms due to the complexity of image acquisition and interpretation. One crucial initial step to address this is automatically identifying the correct echocardiogram video views. Several studies have used deep learning and traditional image-processing techniques for this task. The authors propose an ablation study on a multi-task learning scheme with a hierarchically structured model output that arranges views in a tree structure. The proposed model, named “Multi-task Residual Neural Network (MTRNN) with masked loss”, uses a conditional probabilistic training method and demonstrates superior performance for echocardiogram view classification. While the model has only been validated for the echocardiogram video classification task, it can be easily generalized to any medical image classification scenario with a hierarchical structure among the data labels.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaji, G., Subashini, T., Chidambaram, N.: Automatic classification of cardiac views in echocardiogram using histogram and statistical features. Procedia Comput. Sci. 46, 1569–1576 (2015)
Bannur, S., et al.: Hierarchical analysis of visual COVID-19 features from chest radiographs. ArXiv abs/2107.06618 (2021)
Charton, J., et al.: View classification of color doppler echocardiography via automatic alignment between doppler and b-mode imaging. In: Aylward, S., Noble, J.A., Hu, Y., Lee, S.L., Baum, Z., Min, Z. (eds.) ASMUS 2022. LNCS, pp. 64–71. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16902-1_7
Chen, H., Miao, S., Xu, D., Hager, G.D., Harrison, A.P.: Deep hiearchical multi-label classification applied to chest X-ray abnormality taxonomies. CoRR abs/2009.05609 (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.05609
Hsu, B.W.Y., Tseng, V.S.: Hierarchy-aware contrastive learning with late fusion for skin lesion classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 216, 106666 (2022)
Khaleel, M., Tavanapong, W., Wong, J., Oh, J., De Groen, P.: Hierarchical visual concept interpretation for medical image classification. In: 2021 IEEE 34th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), pp. 25–30. IEEE (2021)
Khaleel, M., Tavanapong, W., Wong, J., Oh, J., de Groen, P.: Hierarchical visual concept interpretation for medical image classification. In: 2021 IEEE 34th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), pp. 25–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMS52027.2021.00012
Kusunose, K.: Steps to use artificial intelligence in echocardiography. J. Echocardiogr. 19(1), 21–27 (2021)
Liao, Z., et al.: Echocardiography view classification using quality transfer star generative adversarial networks. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part II. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 687–695. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_76
Madani, A., Arnaout, R., Mofrad, M., Arnaout, R.: Fast and accurate view classification of echocardiograms using deep learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 1(1), 6 (2018)
Mitchell, C., et al.: Guidelines for performing a comprehensive transthoracic echocardiographic examination in adults: recommendations from the American society of echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 32(1), 1–64 (2019)
Østvik, A., Smistad, E., Aase, S.A., Haugen, B.O., Lovstakken, L.: Real-time standard view classification in transthoracic echocardiography using convolutional neural networks. Ultras. Med. Biol. 45(2), 374–384 (2019)
Otto, C.M.: Textbook of Clinical Echocardiography. Elsevier Health Sciences (2013)
Pham, H.H., Le, T.T., Tran, D.Q., Ngo, D.T., Nguyen, H.Q.: Interpreting chest X-rays via CNNs that exploit hierarchical disease dependencies and uncertainty labels. Neurocomputing 437, 186–194 (2021)
Sanh, V., Wolf, T., Ruder, S.: A hierarchical multi-task approach for learning embeddings from semantic tasks. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 6949–6956 (2019)
Seetharam, K., Raina, S., Sengupta, P.P.: The role of artificial intelligence in echocardiography. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 22, 1–8 (2020)
Shen, D., Wu, G., Suk, H.I.: Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 19, 221–248 (2017)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Vaseli, H., et al.: Designing lightweight deep learning models for echocardiography view classification. In: Medical Imaging 2019: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling, vol. 10951, pp. 93–99. SPIE (2019)
Wu, H., Bowers, D.M., Huynh, T.T., Souvenir, R.: Echocardiogram view classification using low-level features. In: 2013 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 752–755. IEEE (2013)
Zhang, Y., et al.: HKGB: an inclusive, extensible, intelligent, semi-auto-constructed knowledge graph framework for healthcare with clinicians’ expertise incorporated. Inf. Process. Manag. 57(6), 102324 (2020)
Zhao, J., Peng, Y., He, X.: Attribute hierarchy based multi-task learning for fine-grained image classification. Neurocomputing 395, 150–159 (2020)
Zhu, X., Bain, M.: B-CNN: branch convolutional neural network for hierarchical classification. ArXiv (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1709.09890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Charton, J. et al. (2023). Multi-task Learning for Hierarchically-Structured Images: Study on Echocardiogram View Classification. In: Kainz, B., Noble, A., Schnabel, J., Khanal, B., Müller, J.P., Day, T. (eds) Simplifying Medical Ultrasound. ASMUS 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14337. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44521-7_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44521-7_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44520-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44521-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)