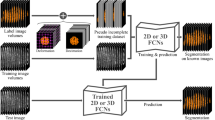
Abstract
Supervised deep learning methods offer the potential for automating lesion segmentation in routine clinical brain imaging, but performance is dependent on label quality. In practice, obtaining high-quality labels from experienced annotators for large-scale datasets is not always feasible, while noisy labels from less experienced annotators are often available. Prior studies focus on either label refinement methods or on learning to segment with noisy labels, but there has been little work on integrating these approaches within a unified framework. To address this gap, we propose a novel multitask framework for end-to-end noisy-label refinement and lesion segmentation. Our approach minimizes the discrepancy between the refined label and the predicted segmentation mask, and is highly customizable for scenarios with multiple sets of noisy labels, incomplete ground truth coverage and/or 2D/3D scans. In extensive experiments on both proprietary and public clinical brain imaging datasets, we demonstrate that our end-to-end framework offers strong performance improvements over prevailing baselines on both label refinement and lesion segmentation. Our proposed framework maintains performance gains over baselines even when ground truth labels are available for only 25–50% of the dataset. Our approach has implications for effective medical image segmentation in settings that are replete with noisy labels but sparse on ground truth annotation.
Y. Yu and J. Wang—Contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkus, Z., Galimzianova, A., Hoogi, A., Rubin, D.L., Erickson, B.J.: Deep learning for brain MRI segmentation: state of the art and future directions. J. Digital Imaging 30, 449–459 (2017)
Bertels, J., et al.: Optimizing the dice score and jaccard index for medical image segmentation: theory and practice. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 92–100. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_11
Cai, Z., Xin, J., Shi, P., Zhou, S., Wu, J., Zheng, N.: Meta pixel loss correction for medical image segmentation with noisy labels. In: Medical Image Learning with Limited and Noisy Data: First International Workshop, MILLanD 2022, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2022, Singapore, September 22, 2022, Proceedings. pp. 32–41. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16760-7_4
Cheng, G., Ji, H., Tian, Y.: Walking on two legs: learning image segmentation with noisy labels. In: Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 330–339. PMLR (2020)
Guo, R., Pagnucco, M., Song, Y.: Learning with noise: mask-guided attention model for weakly supervised nuclei segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12902, pp. 461–470. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87196-3_43
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9908, pp. 630–645. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_38
Huttenlocher, D.P., Klanderman, G.A., Rucklidge, W.J.: Comparing images using the hausdorff distance. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 15(9), 850–863 (1993)
Karimi, D., Dou, H., Warfield, S.K., Gholipour, A.: Deep learning with noisy labels: exploring techniques and remedies in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 65, 101759 (2020)
Kim, J., Kim, M., Kang, H., Lee, K.: U-gat-it: Unsupervised generative attentional networks with adaptive layer-instance normalization for image-to-image translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.10830 (2019)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on challenges in representation learning, ICML. p. 896 (2013)
Lee, J., et al.: A pixel-level coarse-to-fine image segmentation labelling algorithm. Sci. Reports 12(1), 8672 (2022)
Li, S., Gao, Z., He, X.: Superpixel-Guided Iterative Learning from Noisy Labels for Medical Image Segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12901, pp. 525–535. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_50
Menze, B.H., et al.: The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (brats). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(10), 1993–2024 (2014)
Myronenko, A.: 3D MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Autoencoder Regularization. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S., Kuijf, H., Keyvan, F., Reyes, M., van Walsum, T. (eds.) BrainLes 2018. LNCS, vol. 11384, pp. 311–320. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11726-9_28
Obuchowicz, R., Oszust, M., Piorkowski, A.: Interobserver variability in quality assessment of magnetic resonance images. BMC Med. Imaging 20, 1–10 (2020)
Rajpurkar, P., et al.: Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: a retrospective comparison of the chexnext algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 15(11), e1002686 (2018)
Ranjbarzadeh, R., Bagherian Kasgari, A., Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S., Anari, S., Naseri, M., Bendechache, M.: Brain tumor segmentation based on deep learning and an attention mechanism using MRI multi-modalities brain images. Sci. Reports 11(1), 1–17 (2021)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Warfield, S.K., Zou, K.H., Wells, W.M.: Simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (staple): an algorithm for the validation of image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 23(7), 903–921 (2004)
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., Tu, Z., He, K.: Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1492–1500 (2017)
Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, J., Cheng, K.T., Yang, X.: Label refinement with an iterative generative adversarial network for boosting retinal vessel segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.02589 (2019)
Zhang, L., et al.: Learning to Segment When Experts Disagree. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12261, pp. 179–190. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_18
Zhang, L., et al.: Disentangling human error from the ground truth in segmentation of medical images. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 15750–15762. ACL (2020)
Zhang, M., et al.: Characterizing label errors: confident learning for noisy-labeled image segmentation. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12261, pp. 721–730. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_70
Zhen, L., Hu, P., Wang, X., Peng, D.: Deep supervised cross-modal retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10394–10403 (2019)
Zheng, G., Awadallah, A.H., Dumais, S.: Meta label correction for noisy label learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 11053–11061 (2021)
Acknowledgements
Research efforts were supported by funding and infrastructure for deep learning and medical imaging research from the Institute for Infocomm Research, Science and Engineering Research Council, A*STAR, Singapore and the National Neuroscience Institute, Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yu, Y. et al. (2023). A Multitask Framework for Label Refinement and Lesion Segmentation in Clinical Brain Imaging. In: Xue, Z., et al. Medical Image Learning with Limited and Noisy Data. MILLanD 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14307. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44917-8_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44917-8_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47196-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44917-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)