Abstract
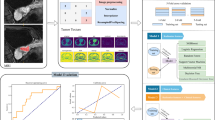
Purpose: To investigate the value of an stacking ensemble learning model based on conventional non-enhanced MRI sequences in the pathological grading of cervical cancer. Methods: We retrospectively included 98 patients with cervical cancer (54 well/moderately differentiated and 44 poorly differentiated). Radiomics features were extracted from T2WI Axi and T2WI Sag. Feature selection was performed by intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC), t-test, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). Logistic Regression (LR), Support Vector Machine (SVM), k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGB) were used as the first-layer base classifier, and LR as the second-layer meta-classifier in stacking ensemble learning model. The model performance was evaluated by the area under the curve (AUC) and accuracy. Results: In the basic classifiers, the XGB model showed the best performance, the average AUC was 0.74(0.69,0.76) and the accuracy was 0.73. It was followed by SVM, LR and KNN models, and the average AUC were 0.73(0.66,0.80), 0.71(0.62,0.78) and 0.66(0.61,0.72), respectively. The performance of stacking ensemble model showed effective improvement, with an average AUC of 0.77(0.67,0.84), and the accuracy was 0.83. Conclusions: The ensemble learning model based on conventional non-enhanced MRI sequences could identify poorly differentiated cervical cancer from well/moderately differentiated cervical cancer, and can provide more references for preoperative non-invasive assessment of cervical cancer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung, H., et al.: Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71(3), 209–249 (2021)
Xie, Y.L., et al.: The value of texture analysis based on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for differentiating cervical adenocarcinoma from squamous cell carcinoma and its prediction of stages. Radiol. Pract. 34(08), 835–840 (2019). (in Chinese)
Zhu, M., et al.: Pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratio predict clinical outcome and prognosis for cervical Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 483, 296–302 (2018)
Horn, L.C., et al.: Prognostic relevance of low-grade versus high-grade FIGO IB1 squamous cell uterine cervical carcinomas. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 145(2), 457–462 (2019)
Zhou, J., et al.: The prognostic value of histologic subtype in node-positive early-stage cervical cancer after hysterectomy and adjuvant radiotherapy. Int. J. Surg. 44, 1–6 (2017)
Vincens, E., et al.: Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in predicting residual disease in patients treated for stage IB2/II cervical carcinoma with chemoradiation therapy: correlation of radiologic findings with surgicopathologic results. Cancer 113(8), 2158–2165 (2008)
Zhang, Q., et al.: Whole-tumor texture model based on diffusion kurtosis imaging for assessing cervical cancer: a preliminary study. Eur. Radiol. 31(8), 5576–5585 (2021)
He, Z., et al.: The value of HPV genotypes combined with clinical indicators in the classification of cervical squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 22(1), 776 (2022)
Wang, C., et al.: Application of DCE-MRI combined with DWI in the evaluation of clinical staging of patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Pract. J. Cancer. 37(03), 492–494+500 (2022) (in Chinese)
Liu, J.R., et al.: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging to characterize pathological grading and stage of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Chin. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 12(12), 29–33 (2021). (in Chinese)
Rogosnitzky, M., Branch, S.: Gadolinium-based contrast agent toxicity: a review of known and proposed mechanisms. Biometals 29(3), 365–376 (2016)
Prince, M.R., et al.: Incidence of immediate gadolinium contrast media reactions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 196(2), W138–W143 (2011)
Lambin, P., et al.: Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 48(4), 441–446 (2012)
Gillies, R.J., Kinahan, P.E., Hricak, H.: Radiomics: images are more than pictures. Data. Radiol. 278(2), 563–577 (2016)
Lambin, P., et al.: Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14(12), 749–762 (2017)
Wang, W., et al.: Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics analysis: differentiation of subtypes of cervical cancer in the early stage. Acta Radiol. 63(6), 847–856 (2022)
Wang, T., et al.: Preoperative prediction of pelvic lymph nodes metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer using radiomics nomogram developed based on T2-weighted MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 114, 128–135 (2019)
Xiao, M., et al.: Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram for predicting lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 52(3), 885–896 (2020)
Xu, J.W., Yang, Y.: Ensemble learning methods: a research review. J. Yunnan Univ. 40(6), 1082–1092 (2018). (in Chinese)
Wolpert, D.H.: Stacked generalization. Neural Netw. 5(2), 241–259 (1992)
Koo, T.K., Li, M.Y.: A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 15(2), 155–163 (2016)
Matsuo, K., et al.: Association of tumor differentiation grade and survival of women with squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 29(6), e91 (2018)
Cui, Y.Q., et al.: Advances in radiomics of cervical cancer. Chin. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 11(06), 477–480 (2020). (in Chinese)
Ciolina, M., et al.: Texture analysis versus conventional MRI prognostic factors in predicting tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Radiol. Med. 124(10), 955–964 (2019)
Costantini, M., et al.: Diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer: relationship between apparent diffusion coefficient and tumour aggressiveness. Clin. Radiol. 65(12), 1005–1012 (2010)
Lin, Y., et al.: Correlation of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient with uterine cervical pathologic finding. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 204(5), 1125–1131 (2015)
Payne, G.S., et al.: Evaluation of magnetic resonance diffusion and spectroscopy measurements as predictive biomarkers in stage 1 cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 116(2), 246–252 (2010)
Kuang, F., et al.: The value of apparent diffusion coefficient in the assessment of cervical cancer. Eur. Radiol. 23(4), 1050–1058 (2013)
Zhou, G., Guo, F.L.: Research on ensemble learning. Comput. Technol. Autom. 37(04), 148–153 (2018). (in Chinese)
Liu, Y., Sun, J.F., Ding, S.: Diagnostic value of routine inflammatory markers combined with squamous cell carcinoma associated antigen and carbohydrate antigen 199 in cervical adenocarcinoma. Lab. Med. Clin. 18(07), 869–873 (2021). (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Z., Lv, F., Li, C., Liu, Y., Xiao, Z. (2023). The Value of Ensemble Learning Model Based on Conventional Non-Contrast MRI in the Pathological Grading of Cervical Cancer. In: Qin, W., Zaki, N., Zhang, F., Wu, J., Yang, F., Li, C. (eds) Computational Mathematics Modeling in Cancer Analysis. CMMCA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14243. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45087-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45087-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45086-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45087-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)