Abstract
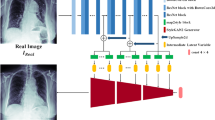
A powerful mechanism for detecting anomalies in a self-supervised manner was demonstrated by model training on normal data, which can then be used as a baseline for scoring anomalies. Recent studies on diffusion models (DMs) have shown superiority over generative adversarial networks (GANs) and have achieved better-quality sampling over variational autoencoders (VAEs). Owing to the inherent complexity of the systems being modeled and the increased sampling times in the long sequence, DMs do not scale well to high-resolution imagery or a large amount of training data. Furthermore, in anomaly detection, DMs based on the Gaussian process do not control the target anomaly size and fail to repair the anomaly image, which led us to the development of a simplex diffusion and selective denoising \( ((SD)^2) \) model. \( (SD)^2 \) does not require a full sequence of Markov chains in image reconstruction for anomaly detection, which reduces the time complexity, samples from the simplex noise diffusion process that have control over the anomaly size and are trained to reconstruct the selective features that help to repair the anomaly. \( (SD)^2 \) significantly outperformed the publicly available Brats2021 and Phenomena detection from X-ray image datasets compared to the self-supervised model. The source code is made publicly available at https://github.com/MAXNORM8650/SDSquare.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy, S., Bhattacharyya, D., Bandyopadhyay, S.K., Kim, T.H.: Heterogeneity of human brain tumor with lesion identification, localization, and analysis from MRI. Inform. Med. Unlocked 13, 139–150 (2018)
Roy, S., Shoghi, K.I.: Computer-aided tumor segmentation from T2-weighted MR images of patient-derived tumor xenografts. In: Karray, F., Campilho, A., Yu, A. (eds.) ICIAR 2019. LNCS, vol. 11663, pp. 159–171. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27272-2_14
Kabiraj, A., Meena, T., Reddy, P.B., Roy, S.: Detection and classification of lung disease using deep learning architecture from x-ray images. In: Bebis, G., et al. (eds.) ISVC 2022. LNCS, vol. 13598, pp. 444–455. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20713-6_34
Kumar, K., Kumar, H., Wadhwa, P.: Encoder-decoder (LSTM-LSTM) network-based prediction model for trend forecasting in currency market. In: Thakur, M., Agnihotri, S., Rajpurohit, B.S., Pant, M., Deep, K., Nagar, A.K. (eds.) Soft Computing for Problem Solving. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 547, pp. 211–223. Springer, Singapore (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6525-8_17
Kingma, D.P., Welling, M.: An introduction to variational autoencoders. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 12(4), 307 (2019)
Baumgartner, C.F., Koch, L.M., Tezcan, K.C., Ang, J.X., Konukoglu, E.: Visual feature attribution using Wasserstein GANs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8309–8319 (2018)
Goodfellow, I.J., et al.: Generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.2661 (2014)
Pirnay, J., Chai, K.: Inpainting transformer for anomaly detection. In: Sclaroff, S., Distante, C., Leo, M., Farinella, G.M., Tombari, F. (eds.) ICIAP 2022. LNCS, vol. 13232, pp. 394–406. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06430-2_33
Pinaya, W.H.L., et al.: Unsupervised brain anomaly detection and segmentation with transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.11650(2021)
Meissen, F., Kaissis, G., Rueckert, D.: Challenging current semi-supervised anomaly segmentation methods for brain MRI. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S. (eds.) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, BrainLes 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 12962, pp. 63–74. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08999-2_5
Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 6840–6851 (2020)
Song, J., Meng, C., Ermon, S.: Denoising diffusion implicit models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.02502 (2020)
Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A.: Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 8780–8794 (2021)
Wolleb, J., Bieder, F., Sandkühler, R., Cattin, P.C.: Diffusion models for medical anomaly detection. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 13438, pp. 35–45. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16452-1_4
Wyatt, J., Leach, A., Schmon, S.M., Willcocks, C. G.: AnoDDPM: anomaly detection with denoising diffusion probabilistic models using simplex noise. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 650–656 (2022)
Perlin, K.: Association for computing machinery. In: SIGGRAPH (vol. 2, p. 681) (2002)
Ristea, N.C., et al.: Self-supervised predictive convolutional attentive block for anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13576–13586 (2022)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Baid, U., et al.: The RSNA-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS 2021 benchmark on brain tumor segmentation and radiogenomic classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.02314 (2021)
Kermany, D., Zhang, K., Goldbaum, M.: Labeled optical coherence tomography (OCT) and chest X-ray images for classification. Mendeley Data 2(2), 651 (2018)
Pathak, D., Krahenbuhl, P., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Efros, A.A.: Context encoders: feature learning by inpainting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2536–2544 (2016)
Schlegl, T., Seeböck, P., Waldstein, S.M., Schmidt-Erfurth, U., Langs, G.: Unsupervised anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks to guide marker discovery. In: Niethammer, M., et al. (eds.) IPMI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10265, pp. 146–157. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, K., Chakraborty, S., Roy, S. (2023). Self-supervised Diffusion Model for Anomaly Segmentation in Medical Imaging. In: Maji, P., Huang, T., Pal, N.R., Chaudhury, S., De, R.K. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence. PReMI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14301. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45170-6_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45170-6_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45169-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45170-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)