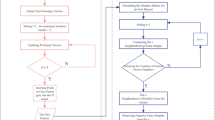
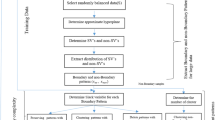
Abstract
Data irregularities, such as small disjuncts, class skew and imbalance, and outliers significantly affect the performance of classifiers. In this paper, we focus on identifying small disjuncts, which hitherto, has been addressed mainly by rule-based or inductive algorithms. Small disjuncts have been identified as distribution-based irregularities which provide significant learning, although they cover a subset of examples in the training set, which may be considered as being rare. Such samples are more error-prone than large disjuncts. Eliminating small disjuncts by removal or pruning is seen to affect the learning of the classifier adversely. Widely used non-rule-based learning algorithms like SVM, kNN, Logistic Regression, and Neural networks perform poorly in the presence of small disjuncts in the dataset. In this paper, a novel Sequential Ellipsoidal Partitioning method is proposed to identify small disjuncts in the dataset. This method is a supervised classifier that iteratively partitions the dataset into Minimum Volume Ellipsoids that contain points of the same label; this is performed based on the idea of Reduced Convex Hulls. By allowing an ellipsoid that contains points of one label to contain a few points of the other, such small disjuncts may be identified. As we discuss, the proposed technique is agnostic of underlying data distributions and is applicable as a supervised classifier when the datasets are highly skewed and imbalanced even. We demonstrate the performance of the approach using a few publicly available datasets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, K.P., Bredensteiner, E.J.: Duality and geometry in SVM classifiers. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 57–64. ICML 2000, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA (2000)
Bland, R.G., Goldfarb, D., Todd, M.J.: The ellipsoid method: a survey. Oper. Res. 29(6), 1039–1091 (1981). http://www.jstor.org/stable/170362
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Introduction to Applied Linear Algebra: Vectors, Matrices, and Least Squares. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2018)
Das, S., Datta, S., Chaudhuri, B.B.: Handling data irregularities in classification: foundations, trends, and future challenges. Pattern Recogn. 81, 674–693 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.03.008
Dua, D., Graff, C.: UCI machine learning repository (2017). http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Holte, R.C., Acker, L.E., Porter, B.W.: Concept learning and the problem of small disjuncts. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 1, pp. 813–818. IJCAI 1989, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA (1989)
Jo, T., Japkowicz, N.: Class imbalances versus small disjuncts. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsletter 6(1), 40–49 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1007730.1007737
Kong, Q., Zhu, Q.: Incremental procedures for partitioning highly intermixed multi-class datasets into hyper-spherical and hyper-ellipsoidal clusters. Data Knowl. Eng. 63(2), 457–477 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2007.03.006
Niranjan, R., Rao, S.: Classification with trust: a supervised approach based on sequential ellipsoidal partitioning (2023). http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.10487
Prati, R.C., Batista, G.E.A.P.A., Monard, M.C.: Learning with class skews and small disjuncts. In: Bazzan, A.L.C., Labidi, S. (eds.) SBIA 2004. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3171, pp. 296–306. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28645-5_30
Sun, P., Freund, R.M.: Computation of minimum-volume covering ellipsoids. Oper. Res. 52(5), 690–706 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.1040.0115
Tukey, J.W.: Exploratory Data Analysis. Addison-Wesley, Boston (1977)
Weiss, G.M.: Learning with rare cases and small disjuncts. In: Prieditis, A., Russell, S. (eds.) Machine Learning Proceedings 1995, pp. 558–565. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (CA) (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-55860-377-6.50075-X
Weiss, G.M.: The impact of small disjuncts on classifier learning. In: Stahlbock, R., Crone, S., Lessmann, S. (eds.) Data Mining. Annals of Information Systems, vol. 8, pp. 193–226. Springer, Boston (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1280-0_9
Weiss, G.M., Hirsh, H.: A quantitative study of small disjuncts. AAAI/IAAI 2000(665–670), 15 (2000)
Acknowledgements
Ranjani Niranjan would like to thank Prateeksha Foundation for providing financial support for her doctoral program at IIIT-Bangalore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Niranjan, R., Rao, S. (2023). Handling Small Disjuncts and Class Skew Using Sequential Ellipsoidal Partitioning. In: Maji, P., Huang, T., Pal, N.R., Chaudhury, S., De, R.K. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence. PReMI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14301. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45170-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45170-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45169-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45170-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)