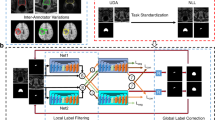
Abstract
It has recently been shown that deep learning models for anatomical segmentation in medical images can exhibit biases against certain sub-populations defined in terms of protected attributes like sex or ethnicity. In this context, auditing fairness of deep segmentation models becomes crucial. However, such audit process generally requires access to ground-truth segmentation masks for the target population, which may not always be available, especially when going from development to deployment. Here we propose a new method to anticipate model biases in biomedical image segmentation in the absence of ground-truth annotations. Our unsupervised bias discovery method leverages the reverse classification accuracy framework to estimate segmentation quality. Through numerical experiments in synthetic and realistic scenarios we show how our method is able to successfully anticipate fairness issues in the absence of ground-truth labels, constituting a novel and valuable tool in this field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Code for the full RCA pipeline based on deep registration networks is publicly available at https://github.com/ngaggion/UBD_SourceCode.
- 2.
For JSRT, Montgomery and Shenzhen we used the original annotations. For PadChest, we used the annotations released in the Chest X-ray Landmark Database [7] publicly available at https://github.com/ngaggion/Chest-xray-landmark-dataset.
References
Bustos, A., Pertusa, A., Salinas, J.M., de la Iglesia-Vayá, M.: PadChest: a large chest x-ray image dataset with multi-label annotated reports. Med. Image Anal. 66, 101797 (2020)
Candemir, S., et al.: Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(2), 577–590 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2290491
Cubero, L., Serrano, J., Castelli, J., De Crevoisier, R., Acosta, O., Pascau, J.: Exploring uncertainty for clinical acceptability in head and neck deep learning-based oar segmentation. In: IEEE ISBI 2023. IEEE (2023)
Czolbe, S., Arnavaz, K., Krause, O., Feragen, A.: Is segmentation uncertainty useful? In: Feragen, A., Sommer, S., Schnabel, J., Nielsen, M. (eds.) IPMI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12729, pp. 715–726. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78191-0_55
Fournel, J., et al.: Medical image segmentation automatic quality control: a multi-dimensional approach. Med. Image Anal. 74, 102213 (2021)
Fu, Y., Lei, Y., Wang, T., Curran, W.J., Liu, T., Yang, X.: A review of deep learning based methods for medical image multi-organ segmentation. Physica Med. 85, 107–122 (2021)
Gaggion, N., Mansilla, L., Mosquera, C., Milone, D.H., Ferrante, E.: Improving anatomical plausibility in medical image segmentation via hybrid graph neural networks: applications to chest x-ray analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2022.3224660. https://doi.org/10.1109
Gaggion, N., Vakalopoulou, M., Milone, D.H., Ferrante, E.: Multi-center anatomical segmentation with heterogeneous labels via landmark-based models. In: 20th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE (2023)
Jaeger, S., et al.: Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(2), 233–245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2284099
Krishnakumar, A., Prabhu, V., Sudhakar, S., Hoffman, J.: UDIS: unsupervised discovery of bias in deep visual recognition models. In: British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), vol. 1, p. 3 (2021)
Lahoti, P., et al.: Fairness without demographics through adversarially reweighted learning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 728–740 (2020)
Larrazabal, A.J., Nieto, N., Peterson, V., Milone, D.H., Ferrante, E.: Gender imbalance in medical imaging datasets produces biased classifiers for computer-aided diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 117(23), 12592–12594 (2020)
Liu, X., Glocker, B., McCradden, M.M., Ghassemi, M., Denniston, A.K., Oakden-Rayner, L.: The medical algorithmic audit. Lancet Digit. Health 4(5), e384–e397 (2022)
Mansilla, L., Ferrante, E.: Segmentación multi-atlas de imágenes médicas con selección de atlas inteligente y control de calidad automático. In: XXIV Congreso Argentino de Ciencias de la Computación (La Plata, 2018) (2018)
Mansilla, L., Milone, D.H., Ferrante, E.: Learning deformable registration of medical images with anatomical constraints. Neural Netw. 124, 269–279 (2020)
Puyol-Antón, E., et al.: Fairness in cardiac MR image analysis: an investigation of bias due to data imbalance in deep learning based segmentation. In: de Bruijne, M., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2021, Part III. LNCS, vol. 12903, pp. 413–423. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_39
Ricci Lara, M.A., Echeveste, R., Ferrante, E.: Addressing fairness in artificial intelligence for medical imaging. Nat. Commun. 13(1), 1–6 (2022)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015, Part III. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Schrouff, J., Chen, C., et al.: Diagnosing failures of fairness transfer across distribution shift in real-world medical settings. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 19304–19318 (2022)
Shiraishi, J., et al.: Development of a digital image database for chest radiographs with and without a lung nodule: receiver operating characteristic analysis of radiologists’ detection of pulmonary nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 174(1), 71–74 (2000)
Valindria, V.V., et al.: Reverse classification accuracy: predicting segmentation performance in the absence of ground truth. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(8), 1597–1606 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Argentina’s National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), which covered the salaries of E.F., R.E. and D.M., and the fellowships of N.G. and L.M. The authors gratefully acknowledge NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of the GPUs used for this research, and the support of Universidad Nacional del Litoral (Grants CAID-PIC-50220140100084LI, 50620190100145LI), ANPCyT (PICT-PRH-2019-00009) and the Google Award for Inclusion Research (AIR) Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gaggion, N., Echeveste, R., Mansilla, L., Milone, D.H., Ferrante, E. (2023). Unsupervised Bias Discovery in Medical Image Segmentation. In: Wesarg, S., et al. Clinical Image-Based Procedures, Fairness of AI in Medical Imaging, and Ethical and Philosophical Issues in Medical Imaging. CLIP EPIMI FAIMI 2023 2023 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14242. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45249-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45249-9_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45248-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45249-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)