Abstract
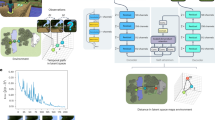
In recent years, the significance of artificial intelligence in comprehending the real-world has increased, by leveraging the inherent ability of humans to process intuitive physics on a computer. Prior investigations on real-world understanding have mainly relied on image inference to recognize the physical environment. In contrast, we propose an inference model that can predict the observed environment using both visual and physical features, emulating the predictive coding hypothesized to occur in the human brain, and detects change points in response to predictive events. Additionally, the model verifies the correctness of the timing of important physical events of objects, such as object collisions and disappearances. Furthermore, the results of the physical information prediction are also described as natural language sentences to confirm whether the model accurately recognizes the real-world and predicts the next behavior based on the physical information.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear, D.M., et al.: Physion: evaluating physical prediction from vision in humans and machines (2021)
Chang, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, S., Ma, S., Gao, W.: STIP: A SpatioTemporal Information-Preserving and Perception-Augmented model for High-Resolution video prediction (2022)
Chen, Z., et al.: ComPhy: compositional physical reasoning of objects and events from videos (2022)
Ding, M., Chen, Z., Du, T., Luo, P., Tenenbaum, J.B., Gan, C.: Dynamic visual reasoning by learning differentiable physics models from video and language (2021)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale (2020)
Duan, J., Dasgupta, A., Fischer, J., Tan, C.: A survey on machine learning approaches for modelling intuitive physics (2022)
Gao, Z., Tan, C., Wu, L., Li, S.Z.: SimVP: Simpler yet better video prediction (2022)
Ge, J., et al.: Learning the relation between similarity loss and clustering loss in Self-Supervised learning (2023)
Ha, D., Schmidhuber, J.: World models (2018)
Hafner, D., Lillicrap, T., Ba, J., Norouzi, M.: Dream to control: Learning behaviors by latent imagination (2019)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Johnson, J., Hariharan, B., van der Maaten, L., Fei-Fei, L., Zitnick, C.L., Girshick, R.B.: CLEVR: A diagnostic dataset for compositional language and elementary visual reasoning. CoRR abs/1612.06890 (2016), http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.06890
Kandukuri, R.K., Achterhold, J., Moeller, M., Stueckler, J.: Physical representation learning and parameter identification from video using differentiable physics. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 130(1), 3–16 (2022)
Kim, T., Ahn, S., Bengio, Y.: Variational temporal abstraction. CoRR abs/1910.00775 (2019), http://arxiv.org/abs/1910.00775
Kingma, Ba: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980 (2017)
LeCun, Y.: A path towards autonomous machine intelligence
Lee, S., Kim, H.G., Choi, D.H., Kim, H.I., Ro, Y.M.: Video prediction recalling long-term motion context via memory alignment learning (2021)
Li, Z., Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Zhang, Z.: Deconfounding physical dynamics with global causal relation and confounder transmission for counterfactual prediction. AAAI 36(2), 1536–1545 (2022)
Lin, Z., Li, M., Zheng, Z., Cheng, Y., Yuan, C.: Self-Attention ConvLSTM for spatiotemporal prediction. AAAI 34(07), 11531–11538 (2020)
Lotter, Kreiman, Cox: Deep predictive coding networks for video prediction and unsupervised learning. arXiv:1605.08104 (2017)
Lotter, W., Kreiman, G., Cox, D.: A neural network trained to predict future video frames mimics critical properties of biological neuronal responses and perception (2018)
Mao, J., Yang, X., Zhang, X., Goodman, N., Wu, J.: CLEVRER-Humans: Describing physical and causal events the human way (2022)
Pan, M., Zhu, X., Wang, Y., Yang, X.: Iso-Dream: Isolating and leveraging noncontrollable visual dynamics in world models (2022)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.J.: BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2002, pp. 311–318. Association for Computational Linguistics, USA (2002)
Piloto, L.S., Weinstein, A., Battaglia, P., Botvinick, M.: Intuitive physics learning in a deep-learning model inspired by developmental psychology. Nat. Hum. Behav. 6(9), 1257–1267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-022-01394-8
Tang, Q., Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Zhang, Z.: Intrinsic physical concepts discovery with Object-Centric predictive models (2023)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. CoRR abs/1706.03762 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
Wang, Y., Gao, Z., Long, M., Wang, J., Yu, P.S.: PredRNN++: Towards a resolution of the Deep-in-Time dilemma in spatiotemporal predictive learning (2018)
Wang, Y., et al.: PredRNN: a recurrent neural network for spatiotemporal predictive learning (2021)
Wu, B., Yu, S., Chen, Z., Tenenbaum, J.B., Gan, C.: STAR: a benchmark for situated reasoning in Real-World videos (2022)
Ye, T., Wang, X., Davidson, J., Gupta, A.: Interpretable intuitive physics model. In: Proceedings of (ECCV) European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 89–105 (2018)
Yi, K., et al.: CLEVRER: CoLlision events for video REpresentation and reasoning. arXiv:1910.01442 (2020)
Yi, K., et al.: Clevrer: collision events for video representation and reasoning. In: ICLR (2020)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP22J21786, JP22KJ1355, 23H03453 and JSPS Bilateral Program Number JPJSBP120213504.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kuroda, E., Kobayashi, I. (2023). Predictive Inference Model of the Physical Environment that Emulates Predictive Coding. In: Bifet, A., Lorena, A.C., Ribeiro, R.P., Gama, J., Abreu, P.H. (eds) Discovery Science. DS 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14276. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45275-8_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45275-8_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45274-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45275-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)