Abstract
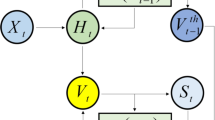
In recent years, spiking neural networks (SNNs) have gained significant attention due to bio-inspired working mechanism. The VGG-like and ResNet-like architectures are widely used for SNNs modeling. However, the spiking features of such architectures are generated by the layer-wise Integrate-and-Fire (IF) dynamics. The firing of deep neurons is independent of the neurons in the shallow layers. In this paper, we propose Multi-Compartment Spiking Neural Network (MC-SNN) that integrates the MPs of the shallow neurons to fire the deep neurons. Specifically, the MC-SNN is modeled by a Multi-Compartment Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (MC-LIF) neuron and an Adaptive Gating Unit (AGU). The MC-LIF neuron models the IF dynamics using the MPs from both deep and shallow layers, and the AGU adaptively scales the MPs of the MC-LIF neuron. These increase the information interaction between spiking neurons and improve the performance of SNNs. Besides, we design the Binarized Synaptic Encoder (BSE) to reduce the computation cost for the input of SNNs. Experimental results show that the MC-SNN performs well on the neuromorphic datasets, reaching 79.52% and 81.24% on CIFAR10-DVS and N-Caltech101, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, L., et al.: SimAM: a simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, pp. 11863–11874 (2021)
Chen, Z., Zhou, H., Lai, J., et al.: Contour-aware loss: boundary-aware learning for salient object segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 431–443 (2020)
Zhang, Q., et al.: Uncertainty modeling with second-order transformer for group re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 3318–3325 (2022)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., et al.: MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Maass, W.: Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 10(9), 1659–1671 (1997)
He, W., et al.: Comparing SNNs and RNNs on neuromorphic vision datasets: Similarities and differences. Neural Netw. 132, 108–120 (2020)
Gerstner, W., Kistler, W.M.: Spiking Neuron Models: Single Neurons, p. 2. Plasticity, Populations (2002)
Zenke, F., Vogels, T.P.: The remarkable robustness of surrogate gradient learning for instilling complex function in spiking neural networks. Neural Comput. 33(4), 899–925 (2021)
Rueckauer, B., Lungu, I.A., Hu, Y.H., et al.: Conversion of continuous-valued deep networks to efficient event-driven networks for image classification. Front. Neurosci. 11, 682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00682
Hu, Y., Tang, H., Pan, G.: Spiking deep residual networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (2021)
Yao, X., et al.: GLIF: a unified gated leaky integrate-and-fire neuron for spiking neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.13768 (2022)
Wu, Z., Zhang, H., Lin, Y., et al.: LIAF-Net: leaky integrate and analog fire network for lightweight and efficient spatiotemporal information processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(11), 6249–6262 (2021)
Fang, W., Yu, Z., Chen, Y., et al.: Incorporating learnable membrane time constant to enhance learning of spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2661–2671 (2021)
Han, B., Srinivasan, G., Roy, K.: RMP-SNN: residual membrane potential neuron for enabling deeper high-accuracy and low-latency spiking neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13558–13567 (2020)
Arriandiaga, A., Portillo, E., Espinosa-Ramos, J.I., et al.: Pulsewidth modulation-based algorithm for spike phase encoding and decoding of time-dependent analog data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(10), 3920–3931 (2019)
Garg, I., Chowdhury, S.S., Roy, K.: DCT-SNN: using DCT to distribute spatial information over time for low-latency spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4671–4680 (2021)
Rathi, N., Roy, K.: DIET-SNN: a low-latency spiking neural network with direct input encoding and leakage and threshold optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021)
Guerguiev, J., Lillicrap, T.P., Richards, B.A.: Towards deep learning with segregated dendrites eLife 6, e22901 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22901
Sun, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhao, F., et al.: Multi-compartment neuron and population encoding improved spiking neural network for deep distributional reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.07275 (2023)
Gao, T., Deng, B., Wang, J., et al.: Highly efficient neuromorphic learning system of spiking neural network with multi-compartment leaky integrate-and-fire neurons. Front. Neurosci. 16, 929644 (2022)
Li, H., et al.: CIFAR10-DVS: an event-stream dataset for object classification. Front. Neurosci. 11, 309–309 (2017)
Orchard, G., et al.: Converting static image datasets to spiking neuromorphic datasets using saccades. Front. Neurosci. 9, 437–437 (2015)
Wu, J., Chua, Y., Zhang, M., Li, G., Li, H., Tan, K.C.: A tandem learning rule for effective training and rapid inference of deep spiking neural networks. TNNLS (2021). 2, 3, 7
Meng, Q., Xiao, M., Yan, S., et al.: Training high-performance low-latency spiking neural networks by differentiation on spike representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12444–12453 (2022)
Zheng, H., Wu, Y., Deng, L., Hu, Y., Li, G.: Going deeper with directly-trained larger spiking neural networks. In: AAAI (2021). 1, 2, 4, 7
Deng, S., et al.: Temporal efficient training of spiking neural network via gradient re-weighting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.11946 (2022)
Zhou, Z., et al.: Spikformer: when Spiking Neural Network Meets Transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.15425 (2022)
Wang, S., Cheng, T.H., Lim, M.H.: LTMD: learning improvement of spiking neural networks with learnable thresholding neurons and moderate dropout. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 28350–28362 (2022)
Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., et al.: IM-Loss: information maximization loss for spiking neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 156–166 (2022)
Shymyrbay, A., Fouda, M.E., Eltawil, A.: Training-aware low precision quantization in spiking neural networks. In: 2022 56th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, pp. 1147–1151. IEEE (2022)
Zhu, R.J., Zhao, Q., Zhang, T., et al.: TCJA-SNN: temporal-channel joint attention for spiking neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.10177 (2022)
Wu, D., et al.: Optimising event-driven spiking neural network with regularisation and cutoff. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.09522 (2023)
Shen, G., Zhao, D., Zeng, Y.: EventMix: an efficient augmentation strategy for event-based data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12054 (2022)
Li, Y., et al. Neuromorphic data augmentation for training spiking neural networks. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part VII, pp. 631-649. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20071-7_37
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangzhou (202007030004); in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(62076258).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, X., Tang, J., Lai, J. (2023). Learning High-Performance Spiking Neural Networks with Multi-Compartment Spiking Neurons. In: Lu, H., et al. Image and Graphics. ICIG 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14356. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46308-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46308-2_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46307-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46308-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)