Abstract
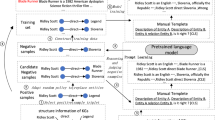
At present, knowledge graph completion (KGC) is mainly divided into structure-based methods and language-based methods, which characterize the structural information and semantic information of knowledge graphs, respectively. Though existing works have developed methods to integrate both information, we argue their end-to-end training manner suffers discrepancy, compatibility, resources redundancy issues. Therefore, we propose a novel two-stage training paradigm for tackling KGC task, i.e. information adaptation and refinement (KGCIAR). Specifically, KGCIAR has two stages, 1) adaptation and 2) refinement. In the adaptation stage, we fine-tune the PLM with the input of descriptive information and supervised by the KG structural information. In the second refinement stage, we freeze the adapted PLM model and infer the description embeddings of entities and relations. Then, those embeddings are leveraged as the entity/relation initial embeddings. Finally, we train a lightweight KGC model. Moreover, we devise two novel objectives for knowledge adaptation, which are self-supervised adaptation and structure-aware contrastive adaptation. Furthermore, we systematically compare the performance of different lightweight KGC models for information refinement. The experiments on KGC task and various variants analyses demonstrate that KGCIAR is effective in harnessing both structure and language information in KG.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Alammary, A.S.: Bert models for arabic text classification: a systematic review. Appl. Sci. 12(11), 5720 (2022)
Alayrac, J.B., et al.: Flamingo: a visual language model for few-shot learning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 23716–23736 (2022)
Amit, S.: Introducing the knowledge graph. America: Official Blog of Google (2012)
Amit, S.: Introducing the knowledge graph: Things, not strings. Official Blog (of Google) (2012)
Bollacker, K., Evans, C., Paritosh, P., Sturge, T., Taylor, J.: Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 1247–1250 (2008)
Bommasani, R., et al.: On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258 (2021)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26 (2013)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901 (2020)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
Chen, Z., Wang, Y., Zhao, B., Cheng, J., Zhao, X., Duan, Z.: Knowledge graph completion: a review. IEEE Access 8, 192435–192456 (2020)
Daza, D., Cochez, M., Groth, P.: Inductive entity representations from text via link prediction. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 798–808 (2021)
Dettmers, T., Minervini, P., Stenetorp, P., Riedel, S.: Convolutional 2d knowledge graph embeddings. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Gao, T., Yao, X., Chen, D.: Simcse: simple contrastive learning of sentence embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.08821 (2021)
Hogan, A., et al.: Knowledge graphs. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 54(4), 1–37 (2021)
Huang, X., Zhang, J., Li, D., Li, P.: Knowledge graph embedding based question answering. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 105–113 (2019)
Ji, G., He, S., Xu, L., Liu, K., Zhao, J.: Knowledge graph embedding via dynamic mapping matrix. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (volume 1: Long papers), pp. 687–696 (2015)
Ji, S., Pan, S., Cambria, E., Marttinen, P., Philip, S.Y.: A survey on knowledge graphs: representation, acquisition, and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(2), 494–514 (2021)
Jing, L., Vincent, P., LeCun, Y., Tian, Y.: Understanding dimensional collapse in contrastive self-supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.09348 (2021)
Lin, Y., Han, X., Xie, R., Liu, Z., Sun, M.: Knowledge representation learning: a quantitative review. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.10901 (2018)
Lin, Y., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 29 (2015)
Liu, Yet al.: Roberta: a robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 (2019)
Nguyen, D.Q., Nguyen, T.D., Nguyen, D.Q., Phung, D.: A novel embedding model for knowledge base completion based on convolutional neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.02121 (2017)
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.P., et al.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: ICML, vol. 11, pp. 3104482–3104584 (2011)
Raffel, C., et al.: Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 21(1), 5485–5551 (2020)
Ramesh, A., et al.: Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8821–8831. PMLR (2021)
Reimers, N., Gurevych, I.: Sentence-bert: sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.10084 (2019)
Sowa, J.F.: Semantic networks. Encyclopedia Artifi. Intell. 2, 1493–1511 (1992)
Sun, Z., Deng, Z.H., Nie, J.Y., Tang, J.: Rotate: knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.10197 (2019)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (2017)
Vrandečić, D., Krötzsch, M.: Wikidata: a free collaborative knowledgebase. Commun. ACM 57(10), 78–85 (2014)
Wang, B., Shen, T., Long, G., Zhou, T., Wang, Y., Chang, Y.: Structure-augmented text representation learning for efficient knowledge graph completion. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 1737–1748 (2021)
Wang, L., Zhao, W., Wei, Z., Liu, J.: Simkgc: simple contrastive knowledge graph completion with pre-trained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.02167 (2022)
Wang, Q., Mao, Z., Wang, B., Guo, L.: Knowledge graph embedding: a survey of approaches and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(12), 2724–2743 (2017)
Wang, S., et al.: Metakrec: collaborative meta-knowledge enhanced recommender system. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 665–674. IEEE (2022)
Wang, T., Isola, P.: Understanding contrastive representation learning through alignment and uniformity on the hypersphere. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 9929–9939. PMLR (2020)
Wang, X., et al.: Kepler: a unified model for knowledge embedding and pre-trained language representation. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Ling. 9, 176–194 (2021)
Wang, Y., Liu, Z., Fan, Z., Sun, L., Yu, P.S.: Dskreg: differentiable sampling on knowledge graph for recommendation with relational gnn. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 3513–3517 (2021)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 28 (2014)
Wang, Z., Ng, P., Ma, X., Nallapati, R., Xiang, B.: Multi-passage bert: a globally normalized bert model for open-domain question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08167 (2019)
Xie, R., Liu, Z., Jia, J., Luan, H., Sun, M.: Representation learning of knowledge graphs with entity descriptions. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 30 (2016)
Yang, B., Yih, W.t., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L.: Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6575 (2014)
Yang, Y., et al.: Improving multilingual sentence embedding using bi-directional dual encoder with additive margin softmax. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.08564 (2019)
Yao, L., Mao, C., Luo, Y.: Kg-bert: bert for knowledge graph completion. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.03193 (2019)
Yuan, L., et al.: Florence: A new foundation model for computer vision. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.11432 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Yao, Q., Kwok, J.T.: Bilinear scoring function search for knowledge graph learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, Y., Shang, B., Wang, C., Zhao, Y. (2023). Knowledge Graph Completion with Information Adaptation and Refinement. In: Yang, X., et al. Advanced Data Mining and Applications. ADMA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14177. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46664-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46664-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46663-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46664-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)