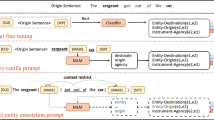
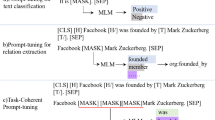
Abstract
Compared to traditional supervised learning methods, utilizing prompt tuning for relation extraction tasks is a challenging endeavor in the real world. By inserting a template segment into the input, prompt tuning has proven effective for certain classification tasks. However, applying prompt tuning to relation extraction tasks, which involve mapping multiple words to a single label, poses challenges due to difficulties in precisely defining a template and mapping labels to the appropriate words. Prior approaches do not take full advantage of entities and have also overlooked the semantic connections between words in relation label. To address these limitations, we propose a semantic enhancement with prompt (SE-Prompt) which integrates entity and relation knowledge by incorporating two main contributions: semantic enhancement and subject-object relation refinement. These methods empower our model to effectively leverage relation labels and tap into the knowledge contained in pre-trained models. Our experiments on three datasets, under both fully supervised and low-resource settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for relation extraction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt, C., Gabryszak, A., Hennig, L.: TACRED revisited: a thorough evaluation of the TACRED relation extraction task. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.14855 (2020)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901 (2020)
Chen, X., et al.: KnowPrompt: knowledge-aware prompt-tuning with synergistic optimization for relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, pp. 2778–2788 (2022)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Gao, T., Fisch, A., Chen, D.: Making pre-trained language models better few-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15723 (2020)
Guo, Z., Zhang, Y., Lu, W.: Attention guided graph convolutional networks for relation extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.07510 (2019)
Han, X., Zhao, W., Ding, N., Liu, Z., Sun, M.: PTR: prompt tuning with rules for text classification. AI Open 3, 182–192 (2022)
Harting, T., Mesbah, S., Lofi, C.: LOREM: language-consistent open relation extraction from unstructured text. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020, pp. 1830–1838 (2020)
Joshi, M., Chen, D., Liu, Y., Weld, D.S., Zettlemoyer, L., Levy, O.: SpanBERT: improving pre-training by representing and predicting spans. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 8, 64–77 (2020)
Kambhatla, N.: Combining lexical, syntactic, and semantic features with maximum entropy models for information extraction. In: Proceedings of the ACL Interactive Poster and Demonstration Sessions, pp. 178–181 (2004)
Le, Q., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1188–1196. PMLR (2014)
Li, X.L., Liang, P.: Prefix-tuning: optimizing continuous prompts for generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.00190 (2021)
Liu, P., Yuan, W., Fu, J., Jiang, Z., Hayashi, H., Neubig, G.: Pre-train, prompt, and predict: a systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 55(9), 1–35 (2023)
Liu, X., et al.: GPT understands, too. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.10385 (2021)
Liu, Y., et al.: RoBERTa: a robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 (2019)
Peters, M.E., et al.: Knowledge enhanced contextual word representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.04164 (2019)
Qian, L., Zhou, G., Kong, F., Zhu, Q., Qian, P.: Exploiting constituent dependencies for tree kernel-based semantic relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (Coling 2008), pp. 697–704 (2008)
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
Raffel, C., et al.: Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 21(1), 5485–5551 (2020)
Schick, T., Schütze, H.: Exploiting cloze questions for few shot text classification and natural language inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.07676 (2020)
Shen, Y., Ma, X., Tang, Y., Lu, W.: A trigger-sense memory flow framework for joint entity and relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 1704–1715 (2021)
Shin, T., Razeghi, Y., Logan IV, R.L., Wallace, E., Singh, S.: AutoPrompt: eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.15980 (2020)
Soares, L.B., FitzGerald, N., Ling, J., Kwiatkowski, T.: Matching the blanks: distributional similarity for relation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.03158 (2019)
Stoica, G., Platanios, E.A., Póczos, B.: Re-TACRED: addressing shortcomings of the TACRED dataset. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 13843–13850 (2021)
Wu, T., et al.: Curriculum-meta learning for order-robust continual relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 10363–10369 (2021)
Xue, F., Sun, A., Zhang, H., Chng, E.S.: GDPNet: refining latent multi-view graph for relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 14194–14202 (2021)
Yamada, I., Asai, A., Shindo, H., Takeda, H., Matsumoto, Y.: LUKE: deep contextualized entity representations with entity-aware self-attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.01057 (2020)
Zeng, D., Liu, K., Chen, Y., Zhao, J.: Distant supervision for relation extraction via piecewise convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1753–1762 (2015)
Zeng, D., Liu, K., Lai, S., Zhou, G., Zhao, J.: Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network. In: Proceedings of COLING 2014, the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 2335–2344 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Zhong, V., Chen, D., Angeli, G., Manning, C.D.: Position-aware attention and supervised data improve slot filling. In: Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2017)
Zhou, P., et al.: Attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (volume 2: Short papers), pp. 207–212 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, C., Li, D., He, X. (2023). SE-Prompt: Exploring Semantic Enhancement with Prompt Tuning for Relation Extraction. In: Yang, X., et al. Advanced Data Mining and Applications. ADMA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14179. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46674-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46674-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46673-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46674-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)