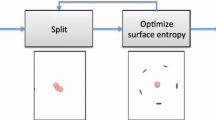
Abstract
Statistical Shape Modeling (SSM) is a quantitative method for analyzing morphological variations in anatomical structures. These analyses often necessitate building models on targeted anatomical regions of interest to focus on specific morphological features. We propose an extension to particle-based shape modeling (PSM), a widely used SSM framework, to allow shape modeling to arbitrary regions of interest. Existing methods to define regions of interest are computationally expensive and have topological limitations. To address these shortcomings, we use mesh fields to define free-form constraints, which allow for delimiting arbitrary regions of interest on shape surfaces. Furthermore, we add a quadratic penalty method to the model optimization to enable computationally efficient enforcement of any combination of cutting-plane and free-form constraints. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method on a challenging synthetic dataset and two medical datasets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins, P.R., et al.: Prediction of femoral head coverage from articulated statistical shape models of patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Orthop. Res. 40(9), 2113–2126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.25227
Atkins, P.R., et al.: Quantitative comparison of cortical bone thickness using correspondence-based shape modeling in patients with cam femoroacetabular impingement. J. Orthop. Res. 35(8), 1743–1753 (2017)
Atkins, P.R., et al.: Which two-dimensional radiographic measurements of cam femoroacetabular impingement best describe the three-dimensional shape of the proximal femur? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 477(1), 242 (2019)
Audenaert, E.A., Pattyn, C., Steenackers, G., De Roeck, J., Vandermeulen, D., Claes, P.: Statistical shape modeling of skeletal anatomy for sex discrimination: Their training size, sexual dimorphism, and asymmetry. Front. in Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7 (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00302,https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00302
Bhalodia, R., Dvoracek, L.A., Ayyash, A.M., Kavan, L., Whitaker, R., Goldstein, J.A.: Quantifying the severity of metopic craniosynostosis: a pilot study application of machine learning in craniofacial surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 31(3), 697–701 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006215
Bruse, J.L.: A statistical shape modelling framework to extract 3D shape biomarkers from medical imaging data: assessing arch morphology of repaired coarctation of the aorta. BMC Med. Imaging 16, 1–19 (2016)
Carriere, N., et al.: Apathy in Parkinson’s disease is associated with nucleus accumbens atrophy: a magnetic resonance imaging shape analysis. Mov. Disord. 29(7), 897–903 (2014)
Cates, J., et al.: Computational shape models characterize shape change of the left atrium in atrial fibrillation. Clin. Med. Insights: Cardiol. 8s1, CMC.S15710 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4137/CMC.S15710
Cates, J., Elhabian, S., Whitaker, R.: ShapeWorks. In: Statistical Shape and Deformation Analysis, pp. 257–298. Elsevier (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-810493-4.00012-2
Cates, J., Fletcher, P.T., Styner, M., Shenton, M., Whitaker, R.: Shape modeling and analysis with entropy-based particle systems. In: Karssemeijer, N., Lelieveldt, B. (eds.) Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 20th International Conference, IPMI 2007, Kerkrade, The Netherlands, July 2-6, 2007. Proceedings, pp. 333–345. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73273-0_28
Datar, M., Cates, J., Fletcher, P.T., Gouttard, S., Gerig, G., Whitaker, R.: Particle based shape regression of open surfaces with applications to developmental neuroimaging. In: Yang, G.-Z., Hawkes, D., Rueckert, D., Noble, A., Taylor, C. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2009, pp. 167–174. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04271-3_21
Davies, R.H., Twining, C.J., Cootes, T.F., Waterton, J.C., Taylor, C.J.: A minimum description length approach to statistical shape modeling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(5), 525–537 (2002)
Harris, M.D., Datar, M., Whitaker, R.T., Jurrus, E.R., Peters, C.L., Anderson, A.E.: Statistical shape modeling of cam femoroacetabular impingement. J. Orthop. Res. 31(10), 1620–1626 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22389
Jacxsens, M., et al.: Thinking outside the glenohumeral box: Hierarchical shape variation of the periarticular anatomy of the scapula using statistical shape modeling. J. Orthop. Res. 38(10), 2272–2279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24589
Jacxsens, M., Elhabian, S.Y., Brady, S.E., Chalmers, P.N., Tashjian, R.Z., Henninger, H.B.: Coracoacromial morphology: a contributor to recurrent traumatic anterior glenohumeral instability? J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 28(7), 1316–1325 (2019)
Lenz, A.L.: Statistical shape modeling of the talocrural joint using a hybrid multi-articulation joint approach. Sci. Rep. 11(1),(2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86567-7
Merle, C., et al.: How many different types of femora are there in primary hip osteoarthritis? an active shape modeling study. J. Orthop. Res. 32(3), 413–422 (2014)
Merle, C., et al.: High variability of acetabular offset in primary hip osteoarthritis influences acetabular reaming-a computed tomography-based anatomic study. J. Arthroplasty 34(8), 1808–1814 (2019)
Sarkalkan, N., Weinans, H., Zadpoor, A.A.: Statistical shape and appearance models of bones. Bone 60, 129–140 (2014)
Thompson, D.W., et al.: On growth and form. On growth and form. (1942)
van Buuren, M., et al.: Statistical shape modeling of the hip and the association with hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 29(5), 607–618 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2020.12.003,https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S106345842031219X
Zachow, S.: Computational planning in facial surgery. Facial Plast. Surg. 31(05), 446–462 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, H., Morris, A., Elhabian, S.Y. (2023). Particle-Based Shape Modeling for Arbitrary Regions-of-Interest. In: Wachinger, C., Paniagua, B., Elhabian, S., Li, J., Egger, J. (eds) Shape in Medical Imaging. ShapeMI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14350. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46914-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46914-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46913-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46914-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)