Abstract
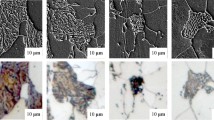
The purpose of this study is to create a computerized system that can automatically evaluate microstructure images of steel materials, specifically focusing on ferrite, using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model. Steel materials play a crucial role in our everyday lives, and their mechanical properties and reliability are determined by their microstructure, which is influenced by heat treatment and processing. It is essential to ensure the quality of steel, as problems can arise if the microstructure and mechanical properties are not adequately assessed before shipping. To accomplish this, the study involved preparing four different steel specimens with varying material properties and heating conditions, which were then photographed using a digital camera. The proposed CNN model was tested and validated to accurately classify the ferrite substances, and it was found that even a simple CNN structure could achieve high accuracy in image classification. The implementation of this system will alleviate the burden of human visual inspection. The paper provides detailed information on the preparation of the steel specimens, the method used to capture the images, the structure of the proposed CNN model, the experimental conditions, the validation methods employed, and the results obtained.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Todai, M., et al.: Effect of building direction on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy additively manufactured by electron beam melting. Addit. Manuf. 13, 61–70 (2017)
Nagase, T., Hori, T., Todai, M., Sun, S.-H., Nakano, T.: Additive manufacturing of dense components in beta-titanium alloys with crystallographic texture from a mixture of pure metallic element powders. Mater. Des. 173, 107771 (2019)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86, 2278–2324 (1998)
Yanase, Y., Miyauchi, H., Matsumoto, H., Yokota, K.: Densification behavior and microstructures of the Al-10%Si-0.35% Mg alloy fabricated by selective laser melting: from experimental observation to machine learning. J. Japan Inst. Metals 84(12), 365–373 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2320/jinstmet.J2020021
Saka, T.: Crystal classification of aluminum alloy using deep learning. J. Japan Instit. Metals Mater. 84(8), 276–283 (2020)
Hatakeyama-Sato, K.: Machine learning for material science. Brain Neural Networks 28(1), 20–27 (2021)
Bartomiej, M., Grzegorz, K., Jan, K., Ulrich, P.: Autonomous interpretation of microstructure of steel and special alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 949, 24–31 (2019)
Ioffe S., Szegedy C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: International Conference Machine Learning (2015). https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167. Accessed on 14 Dec 2022
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 1929–1958 (2014)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814. Haifa, Israel (2010)
Priddy, K.L., Keller, P.E.: Dealing with Limited Amounts of Data. In Artificial Neural Networks—An Introduction, Chapter 11, pp. 101–105. SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA, USA (2005)
Shorten, C., Khoshgoftaar, T.M.: A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 6, 60 (2019)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323, 533–536 (1986)
Bishop, C.M.: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kato, S., Oshita, A., Kubo, T., Todai, M. (2024). Classification of Steel Microstructure Image Using CNN. In: Barolli, L. (eds) Advances on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing . 3PGCIC 2023. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 189. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46970-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46970-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46969-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46970-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)