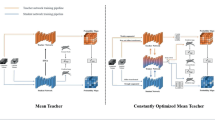
Abstract
Federated learning (FL) is an emerging technique for obtaining a global model while ensuring the data privacy of each client, which is particularly significant in protecting the patients’ privacy when conducting medical image analysis. However, previous FL methods for medical images typically assume a fully supervised setting where each client’s data is fully annotated, disregarding the fact that obtaining such extensive annotations may present significant obstacles due to the need for specialized expertise and the associated overhead costs. In this work, we focus on lesion segmentation for brain MRI images and propose a federated semi-supervised framework to address this problem. Formally, we introduce a Federated Co-Teachers algorithm (Fed-CoT) that extends the prevalent Mean Teacher algorithm into the federated learning framework, and demonstrate its effectiveness. Particularly, in Fed-CoT, two teacher models, namely sync-teacher and async-teacher, which capitalize on different weight updating schemes are leveraged to provide informative consistency regularization and to avoid overfitting to the noise of targets generated by a single teacher model. Our experimental results validate the merits of our proposed method and suggest that the federated learning model can benefit from extra data even without annotations. This approach relaxes the requirement for client participation in federated learning, making it easier to deploy in real applications.
G. Zhan and J. Deng—Contributed equally to this work.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, W., et al.: Semi-supervised learning for network-based cardiac MR image segmentation. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10434, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8_29
Bortsova, G., Dubost, F., Hogeweg, L., Katramados, I., de Bruijne, M.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via learning consistency under transformations. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11769, pp. 810–818. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_90
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Commowick, O., et al.: Objective evaluation of multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using a data management and processing infrastructure. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 13650 (2018)
Commowick, O., et al.: Multiple sclerosis lesions segmentation from multiple experts: the MICCAI 2016 challenge dataset. Neuroimage 244, 118589 (2021)
De Bruijne, M.: Machine learning approaches in medical image analysis: from detection to diagnosis (2016)
French, G., Laine, S., Aila, T., Mackiewicz, M., Finlayson, G.: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation needs strong, varied perturbations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.01916 (2019)
Hesamian, M.H., Jia, W., He, X., Kennedy, P.: Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 32, 582–596 (2019)
Lee, D.H., et al.: Pseudo-label: the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on Challenges in Representation Learning, ICML, vol. 3, p. 896 (2013)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated learning: challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 37(3), 50–60 (2020)
Li, W., et al.: Privacy-preserving federated brain tumour segmentation. In: Suk, H.-I., Liu, M., Yan, P., Lian, C. (eds.) MLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11861, pp. 133–141. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_16
Nie, D., Gao, Y., Wang, L., Shen, D.: ASDNet: attention based semi-supervised deep networks for medical image segmentation. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11073, pp. 370–378. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00937-3_43
Qi, X., Yang, G., He, Y., Liu, W., Islam, A., Li, S.: Contrastive re-localization and history distillation in federated CMR segmentation. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022, Proceedings, Part V, pp. 256–265. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_25
Rieke, N., et al.: The future of digital health with federated learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 3(1), 119 (2020)
Tajbakhsh, N., Jeyaseelan, L., Li, Q., Chiang, J.N., Wu, Z., Ding, X.: Embracing imperfect datasets: a review of deep learning solutions for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 63, 101693 (2020)
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Treadaway, K., et al.: Factors that influence adherence with disease-modifying therapy in MS. J. Neurol. 256, 568–576 (2009)
Wu, Y., He, K.: Group normalization. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11217, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_1
Yun, S., Han, D., Oh, S.J., Chun, S., Choe, J., Yoo, Y.: CutMix: regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6023–6032 (2019)
Zhang, H., Oguz, I.: Multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation - a survey of supervised CNN-based methods. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S. (eds.) BrainLes 2020. LNCS, vol. 12658, pp. 11–29. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhan, G., Deng, J., Cabezas, M., Ouyang, W., Barnett, M., Wang, C. (2023). Fed-CoT: Co-teachers for Federated Semi-supervised MS Lesion Segmentation. In: Celebi, M.E., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023 Workshops . MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14393. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47401-9_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47401-9_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47400-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-47401-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)