Abstract
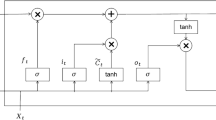
Solar flares release radioactive energy rapidly and have lethal effects on Space and Earth. Forecasting solar flares remains a challenging task as their occurrence is stochastic and multi-variable dependent. In this study, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) models, namely Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Units (GRU), and Simple Recurrent Neural Network (Simple RNN); and their Homogeneous and Heterogenous ensembles are compared for solar flare forecasting. This study adopts a dataset from the Space-weather Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) Active Region Patches, in correspondence with Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) X-ray flare data catalogs, which are made available by National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI). Solar flares emit X-rays when they occur. The focus of this study is on solar flares that are associated with an X-ray peak flux of at least \( 10^ {-6}\) Watts per square meter (\(W/m^{2}\)). The forecast period is 24 h prior to solar flare occurrence. Despite very comparable results from models, the Simple RNN surpassed the performance of other models. The LSTM model’s performance was most closely comparable to that of the Simple RNN. Comparison based on the True Skill Statistic (TSS), precision, and balanced accuracy (BACC), shows that this study produced better results than related studies that used LSTM models. This study improves the TSS by a margin of \(9\% \pm 0.009\) when compared to the benchmark study.
Supported by the University Of KwaZulu-Natal, National Research Foundation and Barclays Endowment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktukmak, M., et al.: Incorporating polar field data for improved solar flare prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.01730 (2022)
Bobra, M.G., et al.: Science platforms for heliophysics data analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.00878 (2023)
Bobra, M.G., Couvidat, S.: Solar flare prediction using SDO/HMI vector magnetic field data with a machine-learning algorithm. Astrophys. J. 798(2), 135 (2015)
Britz, D., Goldie, A., Luong, M.T., Le, Q.: Massive exploration of neural machine translation architectures. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.03906 (2017)
Campi, C., Benvenuto, F., Massone, A.M., Bloomfield, D.S., Georgoulis, M.K., Piana, M.: Feature ranking of active region source properties in solar flare forecasting and the uncompromised stochasticity of flare occurrence. Astrophys. J. 883(2), 150 (2019)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555 (2014)
Florios, K., et al.: Forecasting solar flares using magnetogram-based predictors and machine learning. Sol. Phys. 293(2), 28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1250-4
Gers, F.A., Schmidhuber, J., Cummins, F.: Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 12(10), 2451–2471 (2000)
Guo, C., Pleiss, G., Sun, Y., Weinberger, K.Q.: On calibration of modern neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1321–1330. PMLR (2017)
Haykin, S., Chen, Z., Becker, S.: Stochastic correlative learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 52(8), 2200–2209 (2004)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Kaneda, K., Wada, Y., Iida, T., Nishizuka, N., Kubo, Y., Sugiura, K.: Flare transformer: solar flare prediction using magnetograms and sunspot physical features. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1488–1503 (2022)
Kazachenko, M.D., Lynch, B.J., Savcheva, A., Sun, X., Welsch, B.T.: Toward improved understanding of magnetic fields participating in solar flares: statistical analysis of magnetic fields within flare ribbons. Astrophys. J. 926(1), 56 (2022)
Kuncheva, L.I., Whitaker, C.J.: Measures of diversity in classifier ensembles and their relationship with the ensemble accuracy. Mach. Learn. 51(2), 181 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022859003006
Lemen, J.R., et al.: The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Sol. Phys. 275, 17–40 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9776-8
Li, S., Li, W., Cook, C., Zhu, C., Gao, Y.: Independently recurrent neural network (IndRNN): building a longer and deeper RNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5457–5466 (2018)
Liu, H., Liu, C., Wang, J.T., Wang, H.: Predicting solar flares using a long short-term memory network. Astrophys. J. 877(2), 121 (2019)
Marzban, C.: The ROC curve and the area under it as performance measures. Weather Forecast. 19(6), 1106–1114 (2004)
Nishizuka, N., Sugiura, K., Kubo, Y., Den, M., Ishii, M.: Deep flare net (DeFN) model for solar flare prediction. Astrophys. J. 858(2), 113 (2018)
Niu, Z., Zhong, G., Yu, H.: A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 452, 48–62 (2021)
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.: The solar dynamics observatory (SDO). In: Chamberlin, P., Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B. (eds.) The Solar Dynamics Observatory, pp. 3–15. Springer, New York (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3673-7_2
Platts, J., Reale, M., Marsh, J., Urban, C.: Solar flare prediction with recurrent neural networks. J. Astronaut. Sci. 69(5), 1421–1440 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-022-00340-0
Qahwaji, R., Colak, T.: Automatic short-term solar flare prediction using machine learning and sunspot associations. Sol. Phys. 241, 195–211 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-006-0272-5
Raboonik, A., Safari, H., Alipour, N., Wheatland, M.S.: Prediction of solar flares using unique signatures of magnetic field images. Astrophys. J. 834(1), 11 (2016)
Ribeiro, F., Gradvohl, A.L.S.: Machine learning techniques applied to solar flares forecasting. Astron. Comput. 35, 100468 (2021)
Sagi, O., Rokach, L.: Ensemble learning: a survey. Wiley Interdisc. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 8(4), e1249 (2018)
Sun, Z., et al.: Predicting solar flares using CNN and LSTM on two solar cycles of active region data. Astrophys. J. 931(2), 163 (2022)
Wang, X., et al.: Predicting solar flares with machine learning: investigating solar cycle dependence. Astrophys. J. 895(1), 3 (2020)
Weiss, G., Goldberg, Y., Yahav, E.: On the practical computational power of finite precision RNNs for language recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.04908 (2018)
Yu, Y., Si, X., Hu, C., Zhang, J.: A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 31(7), 1235–1270 (2019)
Yuan, Y., Shih, F.Y., Jing, J., Wang, H.M.: Automated flare forecasting using a statistical learning technique. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 10(8), 785 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mngomezulu, M., Gwetu, M., Fonou-Dombeu, J.V. (2023). Solar Flare Forecasting Using Individual and Ensemble RNN Models. In: Bramer, M., Stahl, F. (eds) Artificial Intelligence XL. SGAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14381. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47994-6_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47994-6_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47993-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-47994-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)