Abstract
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a widely used analytical technique for identifying the molecular structure of complex organic compounds. However, NMR data interpretation can be complex and challenging to decipher. This paper presents a practical approach utilising a generic constraint satisfaction (CS) to interpret NMR spectra and determine molecular structures. It is based on the translation of NMR signals into the sets of constraints on molecular structure. When solved by a constraint solver, these constraints generate a set of all possible molecular structures consistent with the observed NMR spectra data. Based on our previous work accompanied by a prototype implementation, we report here further developments and improvements. These include more precise modelling of NMR constraints and new implementation using the constraint modelling language MiniZinc. We enhance the user experience by adding more functionalities to the system and providing a graphical user interface. Spectroscopists can select from a list of complementary constraints obtained/known outside the scope of NMR. We integrate the PubChem database to find matches for molecular structures. In addition, we use the Cheminfo website’s prediction services to provide users with convenient and on-demand access to NMR predictions. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we conducted extensive experiments on diverse NMR spectra from a range of 20 problems. By applying all the constraints, we were found to provide accurate and efficient solutions in all cases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
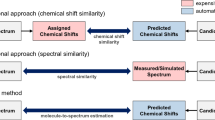
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Detailed introduction to all relevant chemical concepts is out of the scope of this paper. An interested reader with a Computer Science background may find an appropriate introduction in [6].
References
Alharbi, H.A., Barsukov, I., Grosman, R., Lisitsa, A.: Molecular fragments from incomplete, real-life NMR data: framework for spectra analysis with constraint solvers. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Volume 3: ICAART, pp. 834–841. INSTICC, SciTePress (2022). https://doi.org/10.5220/0010915800003116
Burns, D.C., Mazzola, E.P., Reynolds, W.F.: The role of computer-assisted structure elucidation (case) programs in the structure elucidation of complex natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 36(6), 919–933 (2019)
Carissan, Y., Hagebaum-Reignier, D., Prcovic, N., Terrioux, C., Varet, A.: Using constraint programming to generate benzenoid structures in theoretical chemistry. In: Simonis, H. (ed.) CP 2020. LNCS, vol. 12333, pp. 690–706. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58475-7_40
Cheminfo website. http://www.cheminfo.org/. Accessed 22 Jan 2023
Elyashberg, M., Williams, A.: ACD/structure elucidator: 20 years in the history of development. Molecules 26(21), 6623 (2021)
Elyashberg, M.E., Williams, A.J.: Computer-Based Structure Elucidation from Spectral Data. LNC, vol. 89. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46402-1
Elyashberg, M.E., Blinov, K.A., Williams, A.J., Martirosian, E.R., Molodtsov, S.G.: Application of a new expert system for the structure elucidation of natural products from their 1D and 2D NMR data. J. Nat. Prod. 65(5), 693–703 (2002)
Gugisch, R., et al.: MOLGEN 5.0, a molecular structure generator. In: Advances in Mathematical Chemistry and Applications, pp. 113–138. Elsevier (2015)
Kessler, P., Godejohann, M.: Identification of tentative marker in Corvina and Primitivo wines with CMC-se. Magn. Reson. Chem. 56(6), 480–492 (2018)
Kim, S., et al.: PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1), D1202–D1213 (2016)
Kind, T., Fiehn, O.: Metabolomic database annotations via query of elemental compositions: mass accuracy is insufficient even at less than 1 ppm. BMC Bioinf. 7(1), 1–10 (2006)
Koichi, S., et al.: Chemical structure elucidation from 13C NMR chemical shifts: Efficient data processing using bipartite matching and maximal clique algorithms. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 54(4), 1027–1035 (2014)
Landrum, G.: RDKit: open-source cheminformatics software. GitHub SourceForge 10, 3592822 (2016)
McKay, B.D., Piperno, A.: Practical graph isomorphism, II. J. Symb. Comput. 60, 94–112 (2014)
Mnova structure elucidation. http://mestrelab.com/software/mnova/. Accessed 21 Feb 2023
Nethercote, N., Stuckey, P.J., Becket, R., Brand, S., Duck, G.J., Tack, G.: MiniZinc: towards a standard CP modelling language. In: Bessière, C. (ed.) CP 2007. LNCS, vol. 4741, pp. 529–543. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74970-7_38
Omrani, M.A., Naanaa, W.: A constrained molecular graph generation with imposed and forbidden fragments. In: Proceedings of the 9th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1–5 (2016)
Omrani, M.A., Naanaa, W.: Constraints for generating graphs with imposed and forbidden patterns: an application to molecular graphs. Constraints 25, 1–22 (2019)
Patiny, L., Bolaños, A., Castillo, A.M., Bernal, A., Wist, J.: Teaching NMR spectra analysis with NMR. cheminfo.org. Magn. Reson. Chem. 56(6), 529–534 (2018)
Schulte, C., Tack, G., Lagerkvist, M.Z.: Modeling and programming with GECODE. In: Schulte, Christian and Tack, Guido and Lagerkvist, Mikael, vol. 1 (2010)
Smith, D.H., Gray, N.A., Nourse, J.G., Crandell, C.W.: The DENDRAL project: recent advances in computer-assisted structure elucidation. Anal. Chim. Acta 133(4), 471–497 (1981)
Ulrich, E.L., et al.: BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(suppl_1), D402–D408 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alharbi, H.A., Barsukov, I., Grosman, R., Lisitsa, A. (2023). Interpreting NMR Spectra by Constraint Solving. In: Bramer, M., Stahl, F. (eds) Artificial Intelligence XL. SGAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14381. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47994-6_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47994-6_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47993-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-47994-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)