Abstract
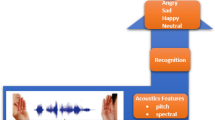
Emotional speech recognition is a challenging task for modern systems. The presence of emotions significantly changes the characteristics of speech. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for emotional speech recognition (EMO-AVSR). The proposed approach uses visual speech data to detect a person’s emotion first, followed by processing of speech by one of the pre-trained emotional audio-visual speech recognition models. We implement these models as a combination of spatio-temporal network for emotion recognition and a cross-modal attention fusion for automatic audio-visual speech recognition. We present experimental investigation that shows how different emotions (happy, anger, disgust, fear, sad, and neutral), valence (positive, neutral, and negative) and binary (emotional and neutral) affect automatic audio-visual speech recognition. The evaluation on CREMA-D data demonstrates up to 7.3% absolute accuracy improvement compared to the classical approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boháček, M., Hrúz, M.: Sign pose-based transformer for word-level sign language recognition. In: Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 182–191 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACVW54805.2022.00024
Cao, H., Cooper, D.G., Keutmann, M.K., Gur, R.C., Nenkova, A., Verma, R.: Crema-D: crowd-sourced emotional multimodal actors dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 5(4), 377–390 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2336244
Chen, C., Hu, Y., Zhang, Q., Zou, H., Zhu, B., Chng, E.S.: Leveraging modality-specific representations for audio-visual speech recognition via reinforcement learning. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 37, pp. 12607–12615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2212.05301
Chung, J.S., Zisserman, A.: Lip reading in the wild. In: Lai, S.-H., Lepetit, V., Nishino, K., Sato, Y. (eds.) ACCV 2016, Part II. LNCS, vol. 10112, pp. 87–103. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54184-6_6
Deng, D., Chen, Z., Zhou, Y., Shi, B.: Mimamo net: integrating micro-and macro-motion for video emotion recognition. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 2621–2628 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/AAAI.V34I03.5646
Dresvyanskiy, D., Ryumina, E., Kaya, H., Markitantov, M., Karpov, A., Minker, W.: End-to-end modeling and transfer learning for audiovisual emotion recognition in-the-wild. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 6(2), 11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/mti6020011
Du, Y., Crespo, R.G., Martínez, O.S.: Human emotion recognition for enhanced performance evaluation in E-learning. Progr. Artif. Intell. 12(2), 199–211 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-022-00278-2
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.V.: Nonverbal leakage and clues to deception. Psychiatry 32(1), 88–106 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1080/00332747.1969.11023575
Feng, D., Yang, S., Shan, S.: An efficient software for building lip reading models without pains. In: International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp. 1–2. IEEE (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMEW53276.2021.9456014
Feng, T., Hashemi, H., Annavaram, M., Narayanan, S.S.: Enhancing privacy through domain adaptive noise injection for speech emotion recognition. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7702–7706. IEEE (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/icassp43922.2022.9747265
Ghaleb, E., Popa, M., Asteriadis, S.: Multimodal and temporal perception of audio-visual cues for emotion recognition. In: International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), pp. 552–558. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACII.2019.8925444
Guo, L., Lu, Z., Yao, L.: Human-machine interaction sensing technology based on hand gesture recognition: a review. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 51(4), 300–309 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/THMS.2021.3086003
Haq, S., Jackson, P.J., Edge, J.: Audio-visual feature selection and reduction for emotion classification. In: Auditory-Visual Speech Processing (AVSP), Tangalooma, Australia (2008)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.90
Ivanko, D., et al.: MIDriveSafely: multimodal interaction for drive safely. In: International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI), pp. 733–735 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3536221.3557037
Ivanko, D., Ryumin, D., Axyonov, A., Kashevnik, A.: Speaker-dependent visual command recognition in vehicle cabin: methodology and evaluation. In: Karpov, A., Potapova, R. (eds.) SPECOM 2021. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 12997, pp. 291–302. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87802-3_27
Ivanko, D., Ryumin, D., Karpov, A.: A review of recent advances on deep learning methods for audio-visual speech recognition. Mathematics 11(12), 2665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122665
Ivanko, D., et al.: DAVIS: driver’s audio-visual speech recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 1141–1142 (2022)
Kashevnik, A., et al.: Multimodal corpus design for audio-visual speech recognition in vehicle cabin. IEEE Access 9, 34986–35003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3062752
Kim, B., Lee, J.: A deep-learning based model for emotional evaluation of video clips. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. Syst. 18(4), 245–253 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5391/IJFIS.2018.18.4.245
Koller, O., Ney, H., Bowden, R.: Deep learning of mouth shapes for sign language. In: International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp. 85–91 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2015.69
Livingstone, S.R., Russo, F.A.: The ryerson audio-visual database of emotional speech and song (RAVDESS): a dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in north American English. PLoS ONE 13(5), e0196391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196391
Lu, Y., Li, H.: Automatic lip-reading system based on deep convolutional neural network and attention-based long short-term memory. Appl. Sci. 9(8), 1599 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/APP9081599
Luna-Jiménez, C., Kleinlein, R., Griol, D., Callejas, Z., Montero, J.M., Fernández-Martínez, F.: A proposal for multimodal emotion recognition using aural transformers and action units on RAVDESS dataset. Appl. Sci. 12(1), 327 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010327
Ma, P., Haliassos, A., Fernandez-Lopez, A., Chen, H., Petridis, S., Pantic, M.: Auto-AVSR: audio-visual speech recognition with automatic labels. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10096889
Ma, P., Wang, Y., Petridis, S., Shen, J., Pantic, M.: Training strategies for improved lip-reading. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 8472–8476. IEEE (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746706
Mahbub, U., Ahad, M.A.R.: Advances in human action, activity and gesture recognition. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 155, 186–190 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.11.003
Makino, T., et al.: Recurrent neural network transducer for audio-visual speech recognition. In: Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), pp. 905–912. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ASRU46091.2019.9004036
Martin, O., Kotsia, I., Macq, B., Pitas, I.: The eNTERFACE’05 audio-visual emotion database. In: International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW), pp. 8–8. IEEE (2006)
McFee, B., et al.: Librosa: audio and music signal analysis in python. In: Python in Science Conference, vol. 8, pp. 18–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.25080/MAJORA-7B98E3ED-003
Milošević, M., Glavitsch, U.: Combining Gaussian mixture models and segmental feature models for speaker recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 2042–2043 (2017)
Milošević, M., Glavitsch, U.: Robust self-supervised audio-visual speech recognition. In: Interspeech, pp. 2118–2122 (2022). https://doi.org/10.21437/interspeech.2022-99
Muppidi, A., Radfar, M.: Speech emotion recognition using quaternion convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6309–6313. IEEE (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414248
Pan, X., Ying, G., Chen, G., Li, H., Li, W.: A deep spatial and temporal aggregation framework for video-based facial expression recognition. IEEE Access 7, 48807–48815 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907271
Ryumin, D., Ivanko, D., Axyonov, A.: Cross-language transfer learning using visual information for automatic sign gesture recognition. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 48, 209–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-xlviii-2-w3-2023-209-2023
Ryumin, D., Ivanko, D., Ryumina, E.: Audio-visual speech and gesture recognition by sensors of mobile devices. Sensors 23(4), 2284 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042284
Ryumin, D., Karpov, A.A.: Towards automatic recognition of sign language gestures using kinect 2.0. In: Antona, M., Stephanidis, C. (eds.) UAHCI 2017, Part II. LNCS, vol. 10278, pp. 89–101. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58703-5_7
Ryumina, E., Dresvyanskiy, D., Karpov, A.: In search of a robust facial expressions recognition model: a large-scale visual cross-corpus study. Neurocomputing 514, 435–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.10.013
Ryumina, E., Ivanko, D.: Emotional speech recognition based on lip-reading. In: Prasanna, S.R.M., Karpov, A., Samudravijaya, K., Agrawal, S.S. (eds.) SPECOM 2022. LNCS, vol. 13721, pp. 616–625. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20980-2_52
Ryumina, E., Karpov, A.: Comparative analysis of methods for imbalance elimination of emotion classes in video data of facial expressions. J. Tech. Inf. Technol. Mech. Opt. 129(5), 683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.17586/2226-1494-2020-20-5-683-691
Schoneveld, L., Othmani, A., Abdelkawy, H.: Leveraging recent advances in deep learning for audio-visual emotion recognition. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 146, 1–7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.03.007
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Son Chung, J., Senior, A., Vinyals, O., Zisserman, A.: Lip reading sentences in the wild. In: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6447–6456 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.367
Takashima, Y., et al.: Audio-visual speech recognition using bimodal-trained bottleneck features for a person with severe hearing loss. In: Interspeech, pp. 277–281 (2016). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2016-721
Tamura, S., et al.: Audio-visual speech recognition using deep bottleneck features and high-performance lipreading. In: Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), pp. 575–582. IEEE (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/APSIPA.2015.7415335
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4489–4497 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.510
Valstar, M., et al.: AVEC 2016: depression, mood, and emotion recognition workshop and challenge. In: International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, pp. 3–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2988257.2988258
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), vol. 30 (2017)
Xu, X., Wang, Y., Jia, J., Chen, B., Li, D.: Improving visual speech enhancement network by learning audio-visual affinity with multi-head attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14964 (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2206.14964
Yang, J., Wang, K., Peng, X., Qiao, Y.: Deep recurrent multi-instance learning with spatio-temporal features for engagement intensity prediction. In: International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI), pp. 594–598 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3242969.3264981
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project No. 22-11-00321).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ivanko, D., Ryumina, E., Ryumin, D., Axyonov, A., Kashevnik, A., Karpov, A. (2023). EMO-AVSR: Two-Level Approach for Audio-Visual Emotional Speech Recognition. In: Karpov, A., Samudravijaya, K., Deepak, K.T., Hegde, R.M., Agrawal, S.S., Prasanna, S.R.M. (eds) Speech and Computer. SPECOM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14338. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48309-7_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48309-7_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-48308-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-48309-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)