Abstract
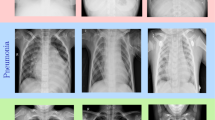
Covid-19 is a serious disease caused by the Sars-CoV-2 virus that has been first reported in China at late 2019 and has rapidly spread around the world. As the virus affects mostly the lungs, chest X-rays are one of the safest and most accessible ways of diagnosing the infection. In this paper, we propose the use of an approach for detecting Covid-19 in chest X-ray images through the extraction and classification of local and global percolation-based features. The method was applied in two datasets: one containing 2,002 segmented samples split into two classes (Covid-19 and Healthy); and another containing 1,125 non-segmented samples split into three classes (Covid-19, Healthy and Pneumonia). The 48 obtained percolation features were given as input to six different classifiers and then AUC and accuracy values were evaluated. We employed the 10-fold cross-validation method and evaluated the lesion sub-types with binary and multiclass classification using the Hermite Polynomial classifier, which had never been employed in this context. This classifier provided the best overall results when compared to other five machine learning algorithms. These results based in the association of percolation features and Hermite polynomial can contribute to the detection of the lesions by supporting specialists in clinical practices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandirali, M., et al.: Chest radiograph findings in asymptomatic and minimally symptomatic quarantined patients in codogno, italy during covid-19 pandemic. Radiology 295(3), E7–E7 (2020)
Căliman, A., Ivanovici, M.: Psoriasis image analysis using color lacunarity. In: 2012 13th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), pp. 1401–1406. IEEE (2012)
Chihara, T.S.: An introduction to orthogonal polynomials. Courier Corporation (2011)
Corman, V.M., et al.: Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-ncov) by real-time rt-pcr. Eurosurveillance 25(3), 2000045 (2020)
Cozzi, D., et al.: Chest x-ray in new coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) infection: findings and correlation with clinical outcome. Radiol. Med. (Torino) 125, 730–737 (2020)
Dong, E., Du, H., Gardner, L.: An interactive web-based dashboard to track covid-19 in real time. Lancet. Infect. Dis 20(5), 533–534 (2020)
Gomes, J.C., et al.: Ikonos: an intelligent tool to support diagnosis of covid-19 by texture analysis of x-ray images. Res. Biomed. Eng. 1–14 (2020)
Hassantabar, S., Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A.: Diagnosis and detection of infected tissue of covid-19 patients based on lung x-ray image using convolutional neural network approaches. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 140, 110170 (2020)
Hemdan, E.E.D., Shouman, M.A., Karar, M.E.: Covidx-net: a framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose covid-19 in x-ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.11055 (2020)
Hooshmand Moghaddam, V., Hamidzadeh, J.: New hermite orthogonal polynomial kernel and combined kernels in support vector machine classifier. Pattern Recogn. 60, 921–935 (2016)
Ismael, A.M., Şengür, A.: The investigation of multiresolution approaches for chest x-ray image based covid-19 detection. Health Inform. Sci. Syst. 8(1), 1–11 (2020)
Jain, R., Gupta, M., Taneja, S., Hemanth, D.J.: Deep learning based detection and analysis of covid-19 on chest x-ray images. Appl. Intell. 51(3), 1690–1700 (2021)
Kurmi, Y., Chaurasia, V., Ganesh, N.: Tumor malignancy detection using histopathology imaging. J. Med. Imaging Radiation Sci. 50(4), 514–528 (2019)
v7 Labs: Covid-19 x-ray dataset (2020). www.github.com/v7labs/covid-19-xray-dataset
Martins, A.S., et al.: A hermite polynomial algorithm for detection of lesions in lymphoma images. Pattern Anal. Appli. 1–13 (2020)
Mohammed, S., Alkinani, F., Hassan, Y.: Automatic computer aided diagnostic for covid-19 based on chest x-ray image and particle swarm intelligence. Inter. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 13(5), 63–73 (2020)
Nayak, S.R., Nayak, D.R., Sinha, U., Arora, V., Pachori, R.B.: Application of deep learning techniques for detection of covid-19 cases using chest x-ray images: a comprehensive study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 64, 102365 (2021)
Neves, L.A., et al.: Multi-scale lacunarity as an alternative to quantify and diagnose the behavior of prostate cancer. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(11), 5017–5029 (2014)
Öztürk, Ş, Özkaya, U., Barstuğan, M.: Classification of coronavirus (covid-19) from x-ray and ct images using shrunken features. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 31(1), 5–15 (2021)
Ozturk, T., Talo, M., Yildirim, E.A., Baloglu, U.B., Yildirim, O., Acharya, U.R.: Automated detection of covid-19 cases using deep neural networks with x-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103792 (2020)
Padierna, L.C., Carpio, M., Rojas-Domínguez, A., Puga, H., Fraire, H.: A novel formulation of orthogonal polynomial kernel functions for svm classifiers: the gegenbauer family. Pattern Recogn. 84, 211–225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.07.010, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320318302280
Redie, D.K., et al.: Diagnosis of covid-19 using chest x-ray images based on modified darkcovidnet model. Evolutionary Intell. 1–10 (2022)
Roberto, G.F., Nascimento, M.Z., Martins, A.S., Tosta, T.A., Faria, P.R., Neves, L.A.: Classification of breast and colorectal tumors based on percolation of color normalized images. Comput. Graph. 84, 134–143 (2019)
Shanableh, T., Assaleh, K.: Feature modeling using polynomial classifiers and stepwise regression. Neurocomputing 73(10–12), 1752–1759 (2010)
Sohrabi, C., et al.: World health organization declares global emergency: a review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (covid-19). Int. J. Surg. 76, 71–76 (2020)
Thangavelu, S.: Hermite and laguerre semigroups: some recent developments. In: Seminaires et Congres (to appear) (2006)
Toğaçar, M., Ergen, B., Cömert, Z.: Covid-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit social mimic optimization and structured chest x-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103805 (2020)
Tuncer, T., Dogan, S., Ozyurt, F.: An automated residual exemplar local binary pattern and iterative relieff based covid-19 detection method using chest x-ray image. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 203, 104054 (2020)
Velavan, T.P., Meyer, C.G.: The covid-19 epidemic. Tropical Med. Intern. Health 25(3), 278 (2020)
Zanaty, E., Afifi, A.: Generalized hermite kernel function for support vector machine classifications. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 42(8), 765–773 (2020)
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001, National Council for Scientific and Technological Development CNPq (Grants #132940/2019-1, #313643/2021-0 and #311404/2021-9), the State of Minas Gerais Research Foundation - FAPEMIG (Grants #APQ-00578-18 and #APQ-01129-21), the State of São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP (Grant #2022/03020-1). and the project NextGenAI - Center for Responsible AI (2022-C05i0102-02), supported by IAPMEI, and also by FCT plurianual funding for 2020-2023 of LIACC (UIDB/00027/2020 UIDP/00027/2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
F. Roberto, G. et al. (2024). Detection of Covid-19 in Chest X-Ray Images Using Percolation Features and Hermite Polynomial Classification. In: Vasconcelos, V., Domingues, I., Paredes, S. (eds) Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications. CIARP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14469. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49018-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49018-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49017-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49018-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)