Abstract
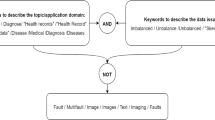
We showcase and demonstrate IDPP, a Pyrus-based tool that offers a collection of pipelines for the analysis of imbalanced datasets. Like Pyrus, IDPP is a web-based, low-code/no-code graphical modelling environment for ML and data analytics applications. On a case study from the medical domain, we solve the challenge of re-using AI/ML models that do not address data with imbalanced class by implementing ML algorithms in Python that do the re-balancing. We then use these algorithms and the original ML models in the IDPP pipelines. With IDPP, our low-code development approach to balance datasets for AI/ML applications can be used by non-coders. It simplifies the data-preprocessing stage of any AI/ML project pipeline, which can potentially improve the performance of the models. The tool demo will showcase the low-code implementation and no-code reuse and repurposing of AI-based systems through end-to end Pyrus pipelines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
All code, information on datasets used and the results are published on GitHub at: https://github.com/singhad/class_imbalance_pyrus.
- 4.
- 5.
References
Al-Areqi, S., Lamprecht, A.-L., Margaria, T.: Constraints-driven automatic geospatial service composition: workflows for the analysis of sea-level rise impacts. In: Gervasi, O., et al. (eds.) ICCSA 2016. LNCS, vol. 9788, pp. 134–150. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42111-7_12
Devarriya, D., Gulati, C., Mansharamani, V., Sakalle, A., Bhardwaj, A.: Unbalanced breast cancer data classification using novel fitness functions in genetic programming. Expert Syst. Appl. 140, 112866 (2020), https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417419305767
Kuo, N., Finfer, S., Jorm, L., Barbieri, S.: Synthetic acute hypotension and sepsis datasets based on mimic-iii and published as part of the health gym project, https://physionet.org/content/synthetic-mimic-iii-health-gym/1.0.0/
Lamprecht, A.-L., Margaria, T., Steffen, B.: Seven variations of an alignment workflow - an illustration of agile process design and management in Bio-jETI. In: Măndoiu, I., Sunderraman, R., Zelikovsky, A. (eds.) ISBRA 2008. LNCS, vol. 4983, pp. 445–456. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79450-9_42
Lamprecht, A.L., Margaria, T., Steffen, B., Sczyrba, A., Hartmeier, S., Giegerich, R.: Genefisher-p: variations of genefisher as processes in Bio-jETI. BMC Bioinformatics 9(4), 1–15 (2008)
Lemaître, G., Nogueira, F., Aridas, C.K.: Imbalanced-learn: a python toolbox to tackle the curse of imbalanced datasets in machine learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18(17), 1–5 (2017), http://jmlr.org/papers/v18/16-365.html
Liu, T., Fan, W., Wu, C.: Data for: A hybrid machine learning approach to cerebral stroke prediction based on imbalanced medical-datasets 1 (2019), https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/x8ygrw87jw/1
Margaria, T.: From Computational Thinking to Constructive Design with Simple Models. In: Margaria, T., Steffen, B. (eds.) ISoLA 2018. LNCS, vol. 11244, pp. 261–278. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03418-4_16
Margaria, T., Schieweck, A.: The Digital Thread in Industry 4.0. In: Ahrendt, W., Tapia Tarifa, S.L. (eds.) IFM 2019. LNCS, vol. 11918, pp. 3–24. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34968-4_1
Margaria, T., Steffen, B.: Business process modeling in the jABC: the one-thing approach. In: Handbook of research on business process modeling, pp. 1–26. IGI Global (2009)
Margaria, T., Steffen, B.: Continuous model-driven engineering. Computer 42(10), 106–109 (2009)
Minguett Pirela, O.M.: Evaluation of machine learning classification techniques for handling class imbalance in medical datasets. M.Sc. in Artificial Intelligence, University of Limerick (2022)
Naujokat, S., Lybecait, M., Kopetzki, D., Steffen, B.: Cinco: a simplicity-driven approach to full generation of domain-specific graphical modeling tools. Int. J. Softw. Tools Technol. Transfer 20, 327–354 (2018)
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, E.A.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Xie, Z.: Building risk prediction models for type 2 diabetes using machine learning techniques. Prev. Chronic Dis. 16, e130 (2019)
Xu, Z., Shen, D., Nie, T., Kou, Y.: A hybrid sampling algorithm combining m-smote and ENN based on random forest for medical imbalanced data. J. Biomed. Inf. 107, 103465 (2020)
Zweihoff, P., Steffen, B.: Pyrus: an online modeling environment for no-code data-analytics service composition. In: Margaria, T., Steffen, B. (eds.) ISoLA 2021. LNCS, vol. 13036, pp. 18–40. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89159-6_2
Acknowledgments
This research was partially funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) under Grant Number 18/CRT/6223 - SFI Centre of Research Training in AI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Singh, A., Minguett, O. (2024). IDPP: Imbalanced Datasets Pipelines in Pyrus. In: Kofroň, J., Margaria, T., Seceleanu, C. (eds) Engineering of Computer-Based Systems. ECBS 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14390. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49252-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49252-5_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49251-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49252-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)