Abstract
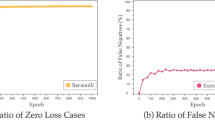
Knowledge graphs are large and useful sources widely used for natural question answering, Web search and data analytics. They describe facts about a certain domain of interest by representing them using entities interconnected via relations in the way of triples. However, due to the fact that they are created under the Open World Assumption, they are incomplete. Knowledge graph completion includes the triple classification task, for discerning correct from incorrect triples. In this regard, knowledge graph embedding models have been proposed for the knowledge graph completion tasks. However, knowledge graphs include only positive triples and training models with only positive triples over generalize, therefore, these models require negative examples. A random negative sampling generates low-quality negative triples which give rise to the zero loss problem during training. In this work, Good Negative Sampling, which is a negative sampling strategy that aims to improve the negative generation process by using background ontological knowledge is put forward. We prove our strategy on a state-of-the-art embedding model - KG-BERT for the triple classification task - on a benchmark dataset - FB13. As result, we demonstrate that the Good Negative Sampling strategy overcomes other state-of-the-art negative strategies, with significant differences.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M., et al.: PyKEEN 1.0: a python library for training and evaluating knowledge graph embeddings. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22(1), 3723–3728 (2021)
Artale, A., Calvanese, D., Kontchakov, R., Zakharyaschev, M.: The DL-Lite family and relations. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 36, 1–69 (2009)
Auer, S., Bizer, C., Kobilarov, G., Lehmann, J., Cyganiak, R., Ives, Z.: DBpedia: a nucleus for a web of open data. In: Aberer, K., et al. (eds.) ASWC/ISWC -2007. LNCS, vol. 4825, pp. 722–735. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76298-0_52
Bollacker, K., Evans, C., Paritosh, P., Sturge, T., Taylor, J.: Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 1247–1250 (2008)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26, 2013
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
d’Amato, C., Quatraro, N.F., Fanizzi, N.: Injecting background knowledge into embedding models for predictive tasks on knowledge graphs. In: Verborgh, R., et al. (eds.) ESWC 2021. LNCS, vol. 12731, pp. 441–457. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77385-4_26
Hogan, A., et al.: Knowledge graphs. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 54(4), 1–37 (2021)
Jain, N., Tran, T.-K., Gad-Elrab, M.H., Stepanova, D.: Improving knowledge graph embeddings with ontological reasoning. In: Hotho, A., et al. (eds.) ISWC 2021. LNCS, vol. 12922, pp. 410–426. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88361-4_24
Kamigaito, H., Hayashi, K.: Comprehensive analysis of negative sampling in knowledge graph representation learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10661–10675. PMLR (2022)
Kotnis, B., Nastase, V.: Analysis of the impact of negative sampling on link prediction in knowledge graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.06816 (2017)
Liu, H., Kairong, H., Wang, F.-L., Hao, T.: Aggregating neighborhood information for negative sampling for knowledge graph embedding. Neural Comput. Appl. 32, 17637–17653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04940-5
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26 (2013)
Nickel, M., Murphy, K., Tresp, V., Gabrilovich, E.: A review of relational machine learning for knowledge graphs. Proc. IEEE 104(1), 11–33 (2015)
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.-P., et al.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: ICML, vol. 11, pp. 3104482–3104584 (2011)
Peng, C., Xia, F., Naseriparsa, M., Osborne, F.: Knowledge graphs: opportunities and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 56, 13071–13102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10465-9
Socher, R., Chen, D., Manning, C.D., Ng, A.: Reasoning with neural tensor networks for knowledge base completion. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26 (2013)
Suchanek, F.M., Kasneci, G., Weikum, G.: Yago: a core of semantic knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 697–706 (2007)
Trouillon, T., Welbl, J., Riedel, S., Gaussier, É., Bouchard, G.: Complex embeddings for simple link prediction. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2071–2080. PMLR (2016)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Vrandečić, D., Krötzsch, M.: Wikidata: a free collaborative knowledgebase. Commun. ACM 57(10), 78–85 (2014)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 28 (2014)
Yang, B., Yih, W., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L.: Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6575 (2014)
Yao, L., Mao, C., Luo, Y.: KG-BERT: BERT for knowledge graph completion. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.03193 (2019)
Zhang, J., Chen, B., Zhang, L., Ke, X., Ding, H.: Neural, symbolic and neural-symbolic reasoning on knowledge graphs. AI Open 2, 14–35 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Yao, Q., Chen, L.: Simple and automated negative sampling for knowledge graph embedding. VLDB J. 30(2), 259–285 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-020-00640-7
Acknowledgments
This research has been partially sponsored by VLIR-UOS Network University Cooperation Programme-Cuba.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
López-Rodríguez, Y.A., Toledano-López, O.G., Hidalgo-Delgado, Y., González Diéz, H., Segundo-Guerrero, R. (2024). Good Negative Sampling for Triple Classification. In: Hernández Heredia, Y., Milián Núñez, V., Ruiz Shulcloper, J. (eds) Progress in Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition. IWAIPR 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14335. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49552-6_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49552-6_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49551-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49552-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)