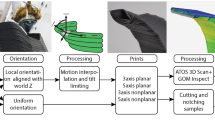
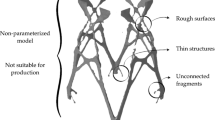
Abstract
In this study, we propose a novel approach to overcome the limitations of traditional 3D printing, including restricted degrees of freedom, the staircase effect, and the need for additional support for manufacturing overhanging features. Our method includes a curved layer slicing algorithm and a surface path planning algorithm. This work presents five key contributions: (1) it reduces most of the staircase effect commonly seen in 3D printing; (2) it eliminates most of the need for support structures typically required by traditional 3D printing; (3) its property of reducing most of the staircase effect and the need for support structures is applicable to complex topological shapes, including 1-loss models; (4) it achieves B-spline interpolation through Equidistant arc-length sampling, which is more efficient than Gauss-Legendre and other existing methods; and (5) it has a collision-free path planning strategy based on hierarchical priority to prevent collisions between the printing nozzle and the model being printed. Through rigorous simulation and comparison with other state-of-the-art algorithms, we have validated the feasibility and effectiveness of our approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aouaidjia, K., Sheng, B., Li, P., Kim, J., Feng, D.D.: Efficient body motion quantification and similarity evaluation using 3-D joints skeleton coordinates. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 51(5), 2774–2788 (2019)
Bhatt, P.M., Malhan, R.K., Shembekar, A.V., Yoon, Y.J., Gupta, S.K.: Expanding capabilities of additive manufacturing through use of robotics technologies: a survey. Addit. Manuf. 31, 100933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100933
Botsch, M., Kobbelt, L.: A remeshing approach to multiresolution modeling. In: Proceedings of the 2004 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Geometry Processing, pp. 185–192 (2004)
Chakraborty, D., Reddy, B.A., Choudhury, A.R.: Extruder path generation for curved layer fused deposition modeling. Comput. Aided Des. 40(2), 235–243 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2007.10.014
Crane, K., Weischedel, C., Wardetzky, M.: The heat method for distance computation. Commun. ACM 60(11), 90–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3131280
Dai, C.K., Lefebvre, S., Yu, K.M., Geraedts, J.M.P., Wang, C.C.L.: Planning jerk-optimized trajectory with discrete time constraints for redundant robots. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 17(4), 1711–1724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2020.2974771
Dai, C.K., Wang, C.C.L., Wu, C.M., Lefebvre, S., Fang, G.X., Liu, Y.J.: Support-free volume printing by multi-axis motion. ACM Trans. Graph. 37(4), 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3197517.3201342
Duran, C., Subbian, V., Giovanetti, M.T., Simkins, J.R., Beyette, F.R., Jr.: Experimental desktop 3D printing using dual extrusion and water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol. Rapid Prototyp. J. 21(5), 528–534 (2015)
Etienne, J., et al.: Curvislicer: slightly curved slicing for 3-axis printers. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 38(4), 1–11 (2019)
Fang, G., Zhang, T., Zhong, S., Chen, X., Zhong, Z., Wang, C.C.: Reinforced FDM: multi-axis filament alignment with controlled anisotropic strength. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 39(6), 1–15 (2020)
Li, Y., He, D., Wang, X., Tang, K.: Geodesic distance field-based curved layer volume decomposition for multi-axis support-free printing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.05938 (2020)
Liu, M., Yang, W.: Optimizing the design process of 3D printing services for personal customization. In: Marcus, A., Rosenzweig, E., Soares, M.M. (eds.) HCII 2023. LNCS, vol. 14031, pp. 497–513. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35696-4_36
Pandey, P.M., Reddy, N.V., Dhande, S.G.: Slicing procedures in layered manufacturing: a review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 9(5), 274–288 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1108/13552540310502185
Qian, J.L., Zhang, Y.T., Zhao, H.K.: Fast sweeping methods for eikonal equations on triangular meshes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(1), 83–107 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1137/050627083
Qin, Y., Chi, X., Sheng, B., Lau, R.W.: Guiderender: large-scale scene navigation based on multi-modal view frustum movement prediction. Vis. Comput. 1–11 (2023)
Shan, Y., Gan, D., Mao, H.: Curved layer slicing based on isothermal surface. Procedia Manufact. 53, 484–491 (2021)
Szydlo, T., Sendorek, J., Windak, M., Brzoza-Woch, R.: Dataset for anomalies detection in 3D printing. In: Paszynski, M., Kranzlmüller, D., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M.A. (eds.) ICCS 2021. LNCS, vol. 12745, pp. 647–653. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77970-2_50
Wang, M.Q., Zhang, H.G., Hu, Q.X., Liu, D., Herfried, L.: Research and implementation of a non-supporting 3D printing method based on 5-axis dynamic slice algorithm. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 57, 496–505 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2019.01.007
Xu, K., Li, Y.G., Chen, L.F., Tang, K.: Curved layer based process planning for multi-axis volume printing of freeform parts. Comput.-Aided Des. 114, 51–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2019.05.007
Zhang, T., et al.: S3-slicer: a general slicing framework for multi-axis 3D printing. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 41(6), 1–15 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zeng, Y., Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, J., Fan, S. (2024). A Novel Approach to Curved Layer Slicing and Path Planning for Multi-degree-of-Freedom 3D Printing. In: Sheng, B., Bi, L., Kim, J., Magnenat-Thalmann, N., Thalmann, D. (eds) Advances in Computer Graphics. CGI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14497. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50075-6_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50075-6_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50074-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50075-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)