Abstract
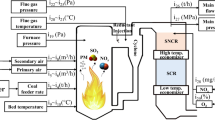
NOx is one of the main pollutants emitted by thermal power plants. Excessive NOx emissions not only cause many negative impacts on the environment but also cause great harm to human health. Power plant NOx prediction technology has drawn more and more attention from the industry. In this paper, a novel bidirectional long and short term memory network (Bi-LSTM) NOx soft-sensing model is proposed for the first time to dynamically predict NOx emissions from power plants in the form of time series. To get better prediction performance, a univariate model and a multivariate model are constructed for comparative study. Besides, Bi-LSTM and different algorithms are compared in the univariate model. In order to confirm the generalization ability of the model, two sets of NOx values of A and B emission outlets from different power plant historical data is used. The results show that the predictive power of univariate models is better than multivariate models. In univariate models, Bi-LSTM is better than other models. On the two sets of data with sampling intervals of 1 min and 2 min, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) could reach 2.105% and 4.45%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munawer, M.E.: Human health and environmental impacts of coal combustion and post-combustion wastes. J. Sustain. Min. 17, 87–96 (2018)
Zhang, K., Zhao, J., Zhu, Y.: MPC case study on a selective catalytic reduction in a power plant. J. Process. Control. 62, 1–10 (2018)
Nihalani, S.A., Mishra, Y., Juremalani, J.: Emission control technologies for thermal power plants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 330, 012122 (2018)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Nitrogen oxides (NOx), why and how they are controlled. EPA-456/F-99-006R. 48 (1999)
Xie, P., Gao, M., Zhang, H., Niu, Y., Wang, X.: Dynamic modeling for NOx emission sequence prediction of SCR system outlet based on sequence to sequence long short-term memory network. Energy 190, 116482 (2020)
Yang, G., Wang, Y., Li, X.: Prediction of the NOx emissions from thermal power plant using long-short term memory neural network. Energy 192, 116597 (2020)
Stamenković, L.J., Antanasijević, D.Z., Ristić, M., Perić-Grujić, A.A., Pocajt, V.V.: Prediction of nitrogen oxides emissions at the national level based on optimized artificial neural network model. Air Qual. Atmos. Heal. 10, 15–23 (2017)
Tuttle, J.F., Vesel, R., Alagarsamy, S., Blackburn, L.D., Powell, K.: Sustainable NOx emission reduction at a coal-fired power station through the use of online neural network modeling and particle swarm optimization. Control. Eng. Pract. 93, 104167 (2019)
Ilamathi, P., Selladurai, V., Balamurugan, K.: A novel approach for modelling of NOx emission reduction in a tangentially fired coal boiler. Int. J. Oil, Gas Coal Technol. 6, 449–461 (2013)
Ilamathi, P., Selladurai, V., Balamurugan, K., Sathyanathan, V.T.: ANN-GA approach for predictive modeling and optimization of NOx emission in a tangentially fired boiler. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 15, 125–131 (2013)
Wang, Y.L., et al.: Development of a NOx emission model with seven optimized input parameters for a coal-fired boiler. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 19, 315–328 (2018)
Li, Q., Yao, G.: Improved coal combustion optimization model based on load balance and coal qualities. Energy 132, 204–212 (2017)
Zhai, Y., Ding, X., Jin, X., Zhao, L.: Adaptive LSSVM based iterative prediction method for NOx concentration prediction in coal-fired power plant considering system delay. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 89, 106070 (2020)
Zhou, H., Zhao, J.P., Zheng, L.G., Wang, C.L., Cen, K.F.: Modeling NOx emissions from coal-fired utility boilers using support vector regression with ant colony optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 25, 147–158 (2012)
Safdarnejad, S.M., Tuttle, J.F., Powell, K.M.: Dynamic modeling and optimization of a coal-fired utility boiler to forecast and minimize NOx and CO emissions simultaneously. Comput. Chem. Eng. 124, 62–79 (2019)
Wang, C., Liu, Y., Zheng, S., Jiang, A.: Optimizing combustion of coal fired boilers for reducing NOx emission using Gaussian Process. Energy 153, 149–158 (2018)
Li, G.Q., Qi, X.-B., Chan, K.C.C., Chen, B.: Deep bidirectional learning machine for predicting NOx emissions and boiler efficiency from a coal-fired boiler. Energy Fuels 31, 11471–11480 (2017)
Tai, K.S., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Improved semantic representations from tree-structured long short-Term memory networks. In: ACL-IJCNLP 2015 - 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing, Proceedings of the Conference (2015)
Theis, L., Bethge, M.: Generative image modeling using spatial LSTMs. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2015)
Tan, P., et al.: Dynamic modeling of NOX emission in a 660 MW coal-fired boiler with long short-term memory. Energy 176, 429–436 (2019)
Govoni, N.A.: Generating sequences with RNN. Dict. Mark. Commun. 1–43 (2012)
Zhang, X., Kano, M., Matsuzaki, S.: A comparative study of deep and shallow predictive techniques for hot metal temperature prediction in blast furnace ironmaking. Comput. Chem. Eng. 130, 106575 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wen, X., Li, K. (2024). Predicting NOx Emission in Thermal Power Plants Based on Bidirectional Long and Short Term Memory Network. In: Wang, B., Hu, Z., Jiang, X., Zhang, YD. (eds) Multimedia Technology and Enhanced Learning. ICMTEL 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 535. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50580-5_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50580-5_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50579-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50580-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)