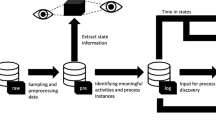
Abstract
Cyber-physical systems embedded in various areas connected to the internet generate unprecedented volumes of data. Humans frequently interact with these systems, thus allowing companies to analyze the data and gain valuable insights into user-product interactions. To analyze the underlying behavior recorded in data, process-mining techniques can be used. However, to apply process mining, the low-level measurements have to be transformed into an event log. In this work, we analyze enriched and transformed connected-vehicle data dealing with an assistance system using process-mining techniques. We analyze the time spent in states of the system, compare behavior between different models using Kruskal-Wallis’ and Dunn’s test, and discover reasons for state switching. We demonstrate how companies can apply process mining on data collected by internet-of-things devices to understand the usage, ratify system requirements, and develop their products.
This research is supported by Ford-RWTH Aachen University Alliance program. We thank the Alexander von Humboldt (AvH) Stiftung for supporting our research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Process Mining - Data Science in Action, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49851-4
Adriansyah, A.: Aligning observed and modeled behavior. Ph.D. thesis, Mathematics and Computer Science (2014). https://doi.org/10.6100/IR770080
Adriansyah, A., van Dongen, B.F., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Conformance checking using cost-based fitness analysis. In: EDOC, pp. 55–64. IEEE Computer Society (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/EDOC.2011.12
Astromskis, S., Janes, A., Mairegger, M.: A process mining approach to measure how users interact with software: an industrial case study. In: ICSSP, pp. 137–141. ACM (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2785592.2785612
Beyel, H.H., Makke, O., Yuan, F., Gusikhin, O., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Analyzing cyber-physical systems in cars: a case study. In: DATA, pp. 195–204. SCITEPRESS (2023). https://doi.org/10.5220/0012136000003541
Bolt, A., de Leoni, M., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: A visual approach to spot statistically-significant differences in event logs based on process metrics. In: Nurcan, S., Soffer, P., Bajec, M., Eder, J. (eds.) CAiSE 2016. LNCS, vol. 9694, pp. 151–166. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39696-5_10
Cameranesi, M., Diamantini, C., Potena, D.: Discovering process models of activities of daily living from sensors. In: Teniente, E., Weidlich, M. (eds.) BPM 2017. LNBIP, vol. 308, pp. 285–297. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74030-0_21
van Dongen, B.F., de Medeiros, A.K.A., Verbeek, H.M.W., Weijters, A.J.M.M., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: The ProM framework: a new era in process mining tool support. In: Ciardo, G., Darondeau, P. (eds.) ICATPN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3536, pp. 444–454. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11494744_25
Dunn, O.J.: Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6(3), 241–252 (1964). https://doi.org/10.2307/1266041
van Eck, M.L., Sidorova, N., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Enabling process mining on sensor data from smart products. In: RCIS, pp. 1–12. IEEE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/RCIS.2016.7549355
Fisher, R.A.: Statistical methods for research workers. In: Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L. (eds.) Breakthroughs in Statistics, pp. 66–70. Springer, New York (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4380-9_6
Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., Palaniswami, M.: Internet of things (IoT): a vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 29(7), 1645–1660 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2013.01.010
Janiesch, C., et al.: The internet of things meets business process management: a manifesto. IEEE Syst. Man Cybern. Mag. 6(4), 34–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSMC.2020.3003135
Keates, O.: Integrating IoT with BPM to provide value to cattle farmers in Australia. In: Di Francescomarino, C., Dijkman, R., Zdun, U. (eds.) BPM 2019. LNBIP, vol. 362, pp. 119–129. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37453-2_11
Koschmider, A., Janssen, D., Mannhardt, F.: Framework for process discovery from sensor data. In: EMISA, pp. 32–38. CEUR-WS.org (2020)
Kruskal, W.H., Wallis, W.A.: Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 47(260), 583–621 (1952). https://doi.org/10.2307/2280779
Lee, E.A.: Cyber physical systems: Design challenges. In: IEEE (ISORC), pp. 363–369. IEEE Computer Society (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISORC.2008.25
de Leoni, M., van der Aalst, W.M.P., Dees, M.: A general process mining framework for correlating, predicting and clustering dynamic behavior based on event logs. Inf. Syst. 56, 235–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2015.07.003
Leotta, F., Marrella, A., Mecella, M.: IoT for BPMers. Challenges, case studies and successful applications. In: Hildebrandt, T., van Dongen, B.F., Röglinger, M., Mendling, J. (eds.) BPM 2019. LNCS, vol. 11675, pp. 16–22. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26619-6_3
Reisig, W.: Petri Nets: An Introduction. EATCS Monographs on Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 4. Springer, Heidelberg (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69968-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Beyel, H.H., Makke, O., Gusikhin, O., van der Aalst, W.M.P. (2024). Analyzing Behavior in Cyber-Physical Systems in Connected Vehicles: A Case Study. In: De Weerdt, J., Pufahl, L. (eds) Business Process Management Workshops. BPM 2023. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 492. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50974-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50974-2_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50973-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50974-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)