Abstract
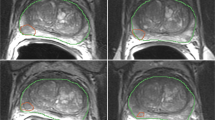
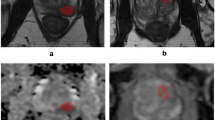
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the performance of radiomics analysis of MR images for the detection of prostate cancer. The radiomics analysis was conducted using axial T2-weighted images from 49 prostate cancers. The study employs a sophisticated hybrid descriptive-inferential method for the meticulous selection and reduction of features, followed by discriminant analysis to construct a robust predictive model. Among 71 radiomics features, original_glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis demonstrated exemplary performance in differentiating between the whole prostate gland and prostate cancer. It had an AUROC of 68.46 (95% CI 0.544 – 0.824; p = 0.022), sensitivity of 76.25%, specificity of 73.15%, and accuracy of 71.02%. Radiomic analysis of T2 weighted MR images was demonstrated to have clinical application in prostate cancer detection, paving the way for improved diagnostic procedures and tailor-made treatment plans for prostate cancer patients.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, L.M., Turkbey, B., Figg, W.D., Choyke, P.L.: Multiparametric MRI in prostate cancer management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 11, 346–353 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.69
Thompson, J., Lawrentschuk, N., Frydenberg, M., Thompson, L., Stricker, P.: The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer. BJU Int. 112, 6–20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12381
Cutaia, G., et al.: Radiomics and prostate MRI: current role and future applications. J. Imaging 7, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7020034
Stefano, A., et al.: Robustness of PET radiomics features: impact of co-registration with MRI. Appl. Sci. 11, 10170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110170
Aerts, H.J.W.L., et al.: Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 5, 4006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006
Cuocolo, R., et al.: Deep learning whole-gland and zonal prostate segmentation on a public MRI dataset. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 54, 452–459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27585
Gallotta, A., et al.: A novel algorithm for the prediction of prostate cancer in clinically suspected patients. Cancer Biomark. 13, 227–234 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-130357
Barone, S., et al.: Hybrid descriptive-inferential method for key feature selection in prostate cancer radiomics. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 37, 961–972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/asmb.2642
Kumar, V., et al.: Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 30, 1234–1248 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010
Alongi, P., et al.: Choline PET/CT features to predict survival outcome in high-risk prostate cancer restaging: a preliminary machine-learning radiomics study. Q. J. Nuclear Med. Molecular Imaging 66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.23736/S1824-4785.20.03227-6
Cairone, L., et al.: Robustness of radiomics features to varying segmentation algorithms in magnetic resonance images. Presented at the (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13321-3_41
Vernuccio, F., Cannella, R., Comelli, A., Salvaggio, G., Lagalla, R., Midiri, M.: [Radiomics and artificial intelligence: new frontiers in medicine.]. Recenti Prog Med. 111, 130–135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1701/3315.32853
Giambelluca, D., et al.: PI-RADS 3 lesions: role of prostate MRI texture analysis in the identification of prostate cancer. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 50, 175–185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpradiol.2019.10.009
Comelli, A., et al.: Deep learning-based methods for prostate segmentation in magnetic resonance imaging. Appl. Sci. 11, 782 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020782
Salvaggio, G., et al.: Deep learning network for segmentation of the prostate gland with median lobe enlargement in T2-weighted MR images: comparison with manual segmentation method. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 51, 328–333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpradiol.2021.06.006
Woźnicki, P., et al.: Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer characterization: combined use of radiomics model with PI-RADS and clinical parameters. Cancers (Basel). 12, 1767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071767
Bleker, J., Kwee, T.C., Dierckx, R.A.J.O., de Jong, I.J., Huisman, H., Yakar, D.: Multiparametric MRI and auto-fixed volume of interest-based radiomics signature for clinically significant peripheral zone prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 30, 1313–1324 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06488-y
Khalvati, F., Zhang, J., Chung, A.G., Shafiee, M.J., Wong, A., Haider, M.A.: MPCaD: a multi-scale radiomics-driven framework for automated prostate cancer localization and detection. BMC Med. Imaging 18, 16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-018-0258-4
Lee, H., Hwang, S. Il, Lee, H.J., Byun, S.-S., Lee, S.E., Hong, S.K.: Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted imaging for prostate cancer: Peripheral zone versus transition zone. PLoS One. 13, e0199636 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199636
Comelli, A., et al.: Tissue classification to support local active delineation of brain tumors. Presented (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39343-4_1
Agnello, L., Comelli, A., Ardizzone, E., Vitabile, S.: Unsupervised tissue classification of brain MR images for voxel-based morphometry analysis. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 26, 136–150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ali, M. et al. (2024). Prostate Cancer Detection: Performance of Radiomics Analysis in Multiparametric MRI. In: Foresti, G.L., Fusiello, A., Hancock, E. (eds) Image Analysis and Processing - ICIAP 2023 Workshops. ICIAP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14366. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51026-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51026-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-51025-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-51026-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)