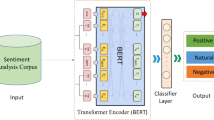
Abstract
In this paper, we present an enhanced BERT methodology for sentiment classification of a Tunisian corpus. We introduce a Tunisian optimized BERT model, named TunRoBERTa, which surpasses the performance of Multilingual-BERT, CNN, CNN combined with LSTM, and RoBERTa. Additionally, we incorporate TunRoBERTa as an embedding technique with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). The experimental results demonstrate that the combination of TunRoBERTa and CNN yields the highest performance compared to the previous models. Our findings outperform Multilingual-BERT, CNN, and CNN combined with LSTM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
References
Ameur, H., Jamoussi, S., Ben Hamadou, A.: Exploiting emoticons to generate emotional dictionaries from Facebook pages. In: Czarnowski, I., Caballero, A.M., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds.) Intelligent Decision Technologies 2016. SIST, vol. 57, pp. 39–49. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39627-9_4
Aydoğan, E., Akcayol, M.A.: A comprehensive survey for sentiment analysis tasks using machine learning techniques. In: 2016 International Symposium on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (INISTA), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2016)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Dubey, A.D.: Twitter sentiment analysis during covid-19 outbreak. Available at SSRN 3572023 (2020)
Gage, P.: A new algorithm for data compression. C Users J. 12(2), 23–38 (1994)
Hafemann, L., Sabourin, R., Oliveira, L.: Learning features for offline handwritten signature verification using deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn. 70, 163–176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.05.012
Liu, Y., et al.: Roberta: a robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 (2019)
Mdhaffar, S., Bougares, F., Esteve, Y., Hadrich-Belguith, L.: Sentiment analysis of tunisian dialects: linguistic ressources and experiments. In: Third Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop (WANLP), pp. 55–61 (2017)
Messaoudi, A., Haddad, H., Ben HajHmida, M., Fourati, C., Ben Hamida, A.: Learning word representations for Tunisian sentiment analysis. In: Djeddi, C., Kessentini, Y., Siddiqi, I., Jmaiel, M. (eds.) MedPRAI 2020. CCIS, vol. 1322, pp. 329–340. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71804-6_24
Sayadi, K., Liwicki, M., Ingold, R., Bui, M.: Tunisian dialect and modern standard Arabic dataset for sentiment analysis: Tunisian election context. In: Second International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics, ACLING, pp. 35–53 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mechti, S., Faiz, R., Khoufi, N., Antit, S., Krichen, M. (2024). Sentiment Analysis: Effect of Combining BERT as an Embedding Technique with CNN Model for Tunisian Dialect. In: Saad, I., Rosenthal-Sabroux, C., Gargouri, F., Chakhar, S., Williams, N., Haig, E. (eds) Advances in Information Systems, Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Management. ICIKS 2023. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 486. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51664-1_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51664-1_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-51663-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-51664-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)