Abstract
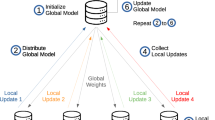
Federated Learning (FL) is a distributed technique that allows multiple users to train models collaboratively without accessing private and sensitive data. Iteratively, each user trains a “local” model in a specific machine consuming private data and then sends the model updates to a server for their fusion into a centralized one. Although FL represents a step forward, the training duration in each iteration directly depends on the several configurations set, e.g., hyperparameters. Analyzing hyperparameters during the FL workflow allows for dynamic fine-tuning that can improve the performance of FL regarding training time and quality of results. However, due to its exploratory nature, the user may lose track of which configurations have been used to train the model with the best accuracy if the choices are not correctly registered. Provenance is the natural choice to represent data derivation traces to help hyperparameters fine-tuning by providing a global data-oriented picture of the FL workflow. Yet, the existing FL frameworks do not provide dynamic fine-tuning nor support provenance capturing. Therefore, this paper introduces an FL framework named Flower-PROV that uses provenance data for tracking configurations and evaluation metrics during the FL execution to allow for dynamic fine-tuning of hyperparameters, thus saving training time. We show a use case with Cross-Silo FL where Flower-PROV dynamic fine-tuning reduced the FL training time up to 94.24% when compared with the fine-tuning using grid-search.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
dataset-splitter - https://github.com/alan-lira/dataset-splitter.
References
Bandara, E., Shetty, S., Rahman, A., Mukkamala, R., Zhao, J., Liang, X.: Bassa-ML – a blockchain and model card integrated federated learning provenance platform. In: IEEE 19th Annual Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), pp. 753–759 (2022)
Beutel, D.J., et al.: Flower: a friendly federated learning research framework. arXiv (2020)
Fernandes, E., Moro, S., Cortez, P.: Data science, machine learning and big data in digital journalism: a survey of state-of-the-art, challenges and opportunities. Expert Syst. Appl. 221, 119795 (2023)
Freire, J., Koop, D., Santos, E., Silva, C.T.: Provenance for computational tasks: a survey. Comput. Sci. Eng. 10(3), 11–21 (2008)
Gharibi, G., Walunj, V., Nekadi, R., Marri, R., Lee, Y.: Automated end-to-end management of the modeling lifecycle in deep learning. Empir. Softw. Eng. 26, 1–33 (2021)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2016)
Groth, P., Moreau, L.: W3C PROV - an overview of the prov family of documents (2013). https://www.w3.org/TR/prov-overview/
Kamm, S., Veekati, S.S., Müller, T., Jazdi, N., Weyrich, M.: A survey on machine learning based analysis of heterogeneous data in industrial automation. Comput. Ind. 149, 103930 (2023)
Krizhevsky, A.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Technical report. University of Toronto (2009)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated learning: challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 37(3), 50–60 (2020)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Zaheer, M., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems (MLSys). mlsys.org (2020)
Lourenço, R., Freire, J., Simon, E., Weber, G., Shasha, D.E.: BugDoc. VLDB J. 32(1), 75–101 (2023)
McMahan, B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., Arcas, B.A.: Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In: Proceedings of the 20th (AISTATS), vol. 54, pp. 1273–1282. PMLR (2017)
Nair, D.G., Aswartha Narayana, C.V., Jaideep Reddy, K., Nair, J.J.: Exploring SVM for federated machine learning applications. In: Rout, R.R., Ghosh, S.K., Jana, P.K., Tripathy, A.K., Sahoo, J.P., Li, K.C. (eds.) Advances in Distributed Computing and Machine Learning. LNNS, vol. 427, pp. 295–305. Springer, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1018-0_25
Nogay, H.S., Adeli, H.: Diagnostic of autism spectrum disorder based on structural brain MRI images using, grid search optimization, and convolutional neural networks. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control. 79(Part), 104234 (2023)
de Oliveira, D.C.M., Liu, J., Pacitti, E.: Data-Intensive Workflow Management: For Clouds and Data-Intensive and Scalable Computing Environments. Synthesis Lectures on Data Management. Morgan & Claypool Publishers, San Rafael (2019)
Parmar, J., Chouhan, S.S., Raychoudhury, V., Rathore, S.S.: Open-world machine learning: applications, challenges, and opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 55(10), 205:1–205:37 (2023)
Peregrina, J.A., Ortiz, G., Zirpins, C.: Towards a metadata management system for provenance, reproducibility and accountability in federated machine learning. In: Zirpins, C., et al. (eds.) ESOCC 2022. CCIS, vol. 1617, pp. 5–18. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23298-5_1
Pina, D.B., Chapman, A., de Oliveira, D., Mattoso, M.: Deep learning provenance data integration: a practical approach. In: Ding, Y., Tang, J., Sequeda, J.F., Aroyo, L., Castillo, C., Houben, G. (eds.) Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023. WWW 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April 2023–4 May 2023, pp. 1542–1550. ACM (2023)
Pina, D., Kunstmann, L., de Oliveira, D., Valduriez, P., Mattoso, M.: Provenance supporting hyperparameter analysis in deep neural networks. In: Glavic, B., Braganholo, V., Koop, D. (eds.) IPAW 2020-2021. LNCS, vol. 12839, pp. 20–38. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80960-7_2
Pina, D., et al.: Capturing provenance from deep learning applications using Keras-Prov and Colab: a practical approach. J. Inf. Data Manag. 13(5) (2022)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Schelter, S., Boese, J.H., Kirschnick, J., Klein, T., Seufert, S.: Automatically tracking metadata and provenance of machine learning experiments. In: Machine Learning Systems Workshop at NIPS (2017)
da Silva, F., Casanova, R., et al.: Workflows community summit: bringing the scientific workflows research community together (2021)
Silva, V., et al.: Dfanalyzer: runtime dataflow analysis tool for computational science and engineering applications. SoftwareX 12, 100592 (2020)
Vartak, M., Madden, S.: MODELDB: opportunities and challenges in managing machine learning models. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 41(4), 16–25 (2018)
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., Tong, Y.: Federated machine learning: concept and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 10(2) (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lopes, C., Nunes, A.L., Boeres, C., Drummond, L.M.A., de Oliveira, D. (2024). Provenance-Based Dynamic Fine-Tuning of Cross-Silo Federated Learning. In: Barrios H., C.J., Rizzi, S., Meneses, E., Mocskos, E., Monsalve Diaz, J.M., Montoya, J. (eds) High Performance Computing. CARLA 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1887. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52186-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52186-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52185-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52186-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)