Abstract
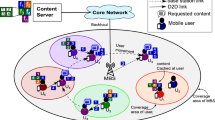
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is a technology that enables on-demand the provision of computing and storage services as close to the user as possible. In an MEC environment, frequently visited content can be deployed and cached upon edge servers to boost the efficiency of content delivery and thus improving user-perceived experience. However, due to the dynamic nature of MEC, it remains a great challenge how to fully exploit mobility information in yielding high-quality content caching decisions for delay-sensitive real-time mobile applications. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a novel mobility-aware caching method by leveraging a Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based (MAACC) Approach model. The proposed method synthesizes a content fitness algorithm for estimating the priority of caching content with high user fitness and a collaborative caching strategy built upon a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning model. Empirical results clearly show that MAACC outperforms its peers regarding cache hit rate and transfer delay time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farooq, M.J., Zhu, Q.: A multi-layer feedback system approach to resilient connectivity of remotely deployed mobile internet of things. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Networking 4(2), 422–432 (2018)
Cao, K., Liu, Y., Meng, G., Sun, Q.: An overview on edge computing research. IEEE Access 8, 85714–85728 (2020)
Chen, Z., Chen, Z., Ren, Z., Liang, L., Wen, W., Jia, Y.: Joint optimization of task caching, computation offloading and resource allocation for mobile edge computing. China Commun. 19, 142–159 (2022)
Qiao, G., Leng, S., Maharjan, S., Zhang, Y., Ansari, N.: Deep reinforcement learning for cooperative content caching in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(1), 247–257 (2020)
He, Y., Yu, F.R., Zhao, N., Leung, V.C.M., Yin, H.: Software-defined networks with mobile edge computing and caching for smart cities: a big data deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55(12), 31–37 (2017)
Wang, R., Li, M., Peng, L., Hu, Y., Hassan, M.M., Alelaiwi, A.: Cognitive multi-agent empowering mobile edge computing for resource caching and collaboration. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 102, 66–74 (2020)
Xia, X., Chen, F., He, Q., Grundy, J., Abdelrazek, M., Jin, H.: Online collaborative data caching in edge computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 32(2), 281–294 (2021)
Zhao, J., Sun, X., Li, Q., Ma, X.: Edge caching and computation management for real-time internet of vehicles: an online and distributed approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(4), 2183–2197 (2021)
Zeng, Y., et al.: Smart caching based on user behavior for mobile edge computing. Inf. Sci. 503, 444–468 (2019)
Yao, T., Chai, Y., Wang, S., Miao, X., Bu, X.: Radio signal automatic modulation classification based on deep learning and expert features. IEEE Xplore (2020)
Musa, S.S., Zennaro, M., Libsie, M., Pietrosemoli, E.: Mobility-aware proactive edge caching optimization scheme in information-centric IoV networks. Sensors 22(4), 1387 (2022)
Wei, H., Luo, H., Sun, Y.: Mobility-aware service caching in mobile edge computing for internet of things. Sensors 20(3), 610 (2020)
Sadeghi, A., Sheikholeslami, F., Giannakis, G.B.: Optimal and scalable caching for 5g using reinforcement learning of space-time popularities. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 12(1), 180–190 (2018)
Jiang, W., Feng, G., Qin, S., Liang, Y.-C.: Learning-based cooperative content caching policy for mobile edge computing. In: ICC 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). IEEE (2019)
Zhong, C., Gursoy, M.C., Velipasalar, S.: Deep reinforcement learning-based edge caching in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Networki. 6(1), 48–61 (2020)
Song, J., Sheng, M., Quek, T.Q.S., Xu, C., Wang, X.: Learning-based content caching and sharing for wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 65(10), 4309–4324 (2017)
Jeong, S., Simeone, O., Kang, J.: Mobile edge computing via a UAV-mounted cloudlet: optimization of bit allocation and path planning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(3), 2049–2063 (2018)
Cassandra, A.R., Littman, M.L., Zhang, N.L.: Incremental pruning: a simple, fast, exact method for partially observable Markov decision processes. arXiv:1302.1525 cs (2013)
Li, Y., Zhou, A., Ma, X., Wang, S.: Profit-aware edge server placement. IEEE Internet Things J. 9(1), 55–67 (2022)
Harper, F.M., Konstan, J.A.: The MovieLens datasets. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 5(4), 1–19 (2015)
Cui, L., et al.: CREAT: blockchain-assisted compression algorithm of federated learning for content caching in edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 9(16), 14151–14161 (2022)
Xiao, H., Zhao, J., Pei, Q., Feng, J., Liu, L., Shi, W.: Vehicle selection and resource optimization for federated learning in vehicular edge computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 28, 11073–11087 (2021)
Banerjee, B., Kulkarni, A., Seetharam, A.: Greedy Caching: an optimized content placement strategy for information-centric networks. Comput. Networks 140, 78–91 (2018)
Acknowledgment
This article is supported by the Innovation Fund Project of Jiangxi Normal University(YJS2022065) and Domestic Visiting Program of Jiangxi Normal University. Additionally, this work is supported in part by Henan Province Science and Technology Projects (232102210024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, H. et al. (2024). A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Approach to Mobility-Aware Caching. In: Gao, H., Wang, X., Voros, N. (eds) Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing. CollaborateCom 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 562. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54528-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54528-3_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-54527-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-54528-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)