Abstract
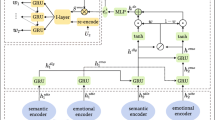
Most methods of emotional dialogue generation focus on how to make the generated replies express the set emotion categories, while ignoring the control over the semantic content of the replies. To this end, in this paper, we propose a emotion- and content-controllable response generation model, ECCRG. ECCRG allows for text-controlled conditions and integration into the decoding process of the language model through a self-attention layer, enabling more precise control over the content of the generated responses. We use a variety of optimization objectives including self-reconfiguration loss and adversarial learning loss to jointly train the model. Experimental results show that ECCRG can embody the set target content in the generated responses, allowing us to achieve controllability on both emotion and textual content.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asghar, N., Poupart, P., Hoey, J., Jiang, X., Mou, L.: Affective neural response generation. In: Pasi, G., Piwowarski, B., Azzopardi, L., Hanbury, A. (eds.) ECIR 2018. LNCS, vol. 10772, pp. 154–166. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76941-7_12
Chan, A., Ong, Y.-S., Pung, B., Zhang, A., Fu, J.: CoCon: a self-supervised approach for controlled text generation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2020)
Colombo, P., Witon, W., Modi, A., Kennedy, J., Kapadia, M.: Affect-driven dialog generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02793 (2019)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Gao, J., Bi, W., Liu, X., Li, J., Shi, S.: Generating multiple diverse responses for short-text conversation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 6383–6390 (2019)
Huang, C., Zaiane, O.R., Trabelsi, A., Dziri, N.: Automatic dialogue generation with expressed emotions. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers), pp. 49–54 (2018)
Li, J., Galley, M., Brockett, C., Gao, J., Dolan, B.: A diversity-promoting objective function for neural conversation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.03055 (2015)
Lin, Z., Madotto, A., Bang, Y., Fung, P.: The adapter-bot: all-in-one controllable conversational model. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 16081–16083 (2021)
Liu, Y., et al.: Roberta: a robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 (2019)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.-J.: Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 311–318 (2002)
Partala, T., Surakka, V.: The effects of affective interventions in human-computer interaction. Interact. Comput. 16(2), 295–309 (2004)
Polzin, T.S., Waibel, A.: Emotion-sensitive human-computer interfaces. In: ISCA Tutorial and Research Workshop (ITRW) on Speech and Emotion (2000)
Radford, A., et al.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 1(8), 9 (2019)
Skowron, M.: Affect listeners: acquisition of affective states by means of conversational systems. In: Esposito, A., Campbell, N., Vogel, C., Hussain, A., Nijholt, A. (eds.) Development of Multimodal Interfaces: Active Listening and Synchrony. LNCS, vol. 5967, pp. 169–181. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12397-9_14
Song, Z., Zheng, X., Liu, L., Xu, M., Huang, X.-J.: Generating responses with a specific emotion in dialog. In: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 3685–3695 (2019)
Zhang, Y., et al.: Dialogpt: large-scale generative pre-training for conversational response generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.00536 (2019)
Zheng, C., Liu, Y., Chen, W., Leng, Y., Huang, M.: Comae: a multi-factor hierarchical framework for empathetic response generation. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021, pp. 813–824 (2021)
Zhong, P., Wang, D., Li, P., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Miao, C.: Care: commonsense-aware emotional response generation with latent concepts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.08377 (2020a)
Zhong, P., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Miao, C.: Towards persona-based empathetic conversational models. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 6556–6566 (2020b)
Zhou, H., Huang, M., Zhang, T., Zhu, X., Liu, B.: Emotional chatting machine: Emotional conversation generation with internal and external memory. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Zhou, L., Gao, J., Li, D., Shum, H.-Y.: The design and implementation of xiaoice, an empathetic social chatbot. Comput. Linguist. 46(1), 53–93 (2020)
Zhou, X., Wang, W.Y.: Mojitalk: generating emotional responses at scale. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 1128–1137 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, H., Wang, B., Yang, K., Song, Y. (2024). ECCRG: A Emotion- and Content-Controllable Response Generation Model. In: Gao, H., Wang, X., Voros, N. (eds) Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing. CollaborateCom 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 562. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54528-3_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54528-3_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-54527-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-54528-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)