Abstract
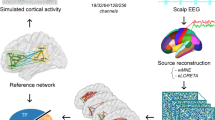
Whole-brain network modeling (WBM) offers a pivotal tool to explore the large-scale spatiotemporal dynamics of the brain at rest, during cognitive tasks, and under external stimulation. However, it is unclear how to fuse multi-modal neural dynamics in a united WBM framework and predict the whole-brain spatiotemporal neural responses to electrical stimulation. In this study, we present a computational framework with whole-brain network modeling, parameter optimization, and model validation using simultaneous EEG-SEEG data during intracranial brain stimulation. To test the efficacy of WBM in revealing brain-wide neural dynamics, our experiments utilize synthetic electrophysiological data, real EEG data, and real EEG-SEEG signals. Experimental results demonstrate that our WBM framework accurately captures the spatiotemporal brain activities by jointly leveraging the higher spatial resolution from SEEG and the whole-brain coverage from EEG. Notably, our model shows a higher correlation between the functional connectivity (FC) matrix of EEG and that of the inferred whole-brain neural dynamics from WBM (r=0.86), compared to the FC from EEG source localization (r=0.48). Together, we demonstrate the capability and flexibility of WBM framework to uncover the whole-brain spatiotemporal neural activity and its potential to provide new insights into the input-response mechanism of the brain.
This work was funded in part by the National Key R &D Program of China (2021YFF1200804), UQ-Research Training Program (UQ-RTP) Scholarship, National Natural Science Foundation of China (62001205), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (2022410129, KCXFZ2020122117340001).
K. Lou and J. Li—Co-first authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antony, A.R., et al.: Simultaneous scalp EEG improves seizure lateralization during unilateral intracranial EEG evaluation in temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizure 64, 8–15 (2019)
Castaldo, F., et al.: Multi-modal and multi-model interrogation of large-scale functional brain. NeuroImage 277, 120236 (2023)
Deco, G., et al.: Perturbation of whole-brain dynamics in silico reveals mechanistic differences between brain states. Neuroimage 169, 46–56 (2018)
Deco, G., Jirsa, V., McIntosh, A.R., Sporns, O., Kötter, R.: Key role of coupling, delay, and noise in resting brain fluctuations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(25), 10302–10307 (2009)
Drew, P.J.: Neurovascular coupling: motive unknown. Trends Neurosci. 45(11), 809–819 (2022)
Fischl, B.: FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 62(2), 774–781 (2012)
Gramfort, A., et al.: MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 7(267), 1–13 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00267
Gramfort, A., et al.: MNE software for processing MEG and EEG data. Neuroimage 86, 446–460 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.027
Griffiths, J.D., Bastiaens, S.P., Kaboodvand, N.: Whole-brain modelling: past, present, and future. In: Giugliano, M., Negrello, M., Linaro, D. (eds.) Computational Modelling of the Brain: Modelling Approaches to Cells, Circuits and Networks, pp. 313–355. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89439-9_13
Hashemi, M., et al.: Amortized Bayesian inference on generative dynamical network models of epilepsy using deep neural density estimators. Neural Netw. 163, 178–194 (2023)
Hebbink, J., Huiskamp, G., van Gils, S.A., Leijten, F.S., Meijer, H.G.: Pathological responses to single-pulse electrical stimuli in epilepsy: the role of feedforward inhibition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 51(4), 1122–1136 (2020)
Hosseini, S.A.H., Sohrabpour, A., He, B.: Electromagnetic source imaging using simultaneous scalp EEG and intracranial EEG: an emerging tool for interacting with pathological brain networks. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129(1), 168–187 (2018)
Jung, K., et al.: Whole-brain dynamical modelling for classification of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Commun. 5(1), fcac331 (2023)
Ley, M., Peláez, N., Principe, A., Langohr, K., Zucca, R., Rocamora, R.: Validation of direct cortical stimulation in Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 137, 38–45 (2022)
Liu, Q., Farahibozorg, S., Porcaro, C., Wenderoth, N., Mantini, D.: Detecting large-scale networks in the human brain using high-density electroencephalography. Hum. Brain Mapp. 38(9), 4631–4643 (2017)
Makhalova, J., et al.: Virtual epileptic patient brain modeling: relationships with seizure onset and surgical outcome. Epilepsia 63(8), 1942–1955 (2022)
Mi, L., et al.: Connectome-constrained latent variable model of whole-brain neural activity. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2021)
Momi, D., Wang, Z., Griffiths, J.D.: TMS-evoked responses are driven by recurrent large-scale network dynamics. Elife 12, e83232 (2023)
Mouthaan, B.E., et al.: Single pulse electrical stimulation to identify epileptogenic cortex: clinical information obtained from early evoked responses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 127(2), 1088–1098 (2016)
Parmigiani, S., et al.: Simultaneous stereo-EEG and high-density scalp EEG recordings to study the effects of intracerebral stimulation parameters. Brain Stimul. 15(3), 664–675 (2022)
Paszke, A., et al.: PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Pathak, A., Roy, D., Banerjee, A.: Whole-brain network models: from physics to bedside. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 16, 866517 (2022)
Schaefer, A., et al.: Local-global parcellation of the human cerebral cortex from intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Cereb. Cortex 28(9), 3095–3114 (2018)
Shu, S., et al.: Informed MEG/EEG source imaging reveals the locations of interictal spikes missed by SEEG. Neuroimage 254, 119132 (2022)
Sip, V., Hashemi, M., Dickscheid, T., Amunts, K., Petkoski, S., Jirsa, V.: Characterization of regional differences in resting-state fMRI with a data-driven network model of brain dynamics. Sci. Adv. 9(11), eabq7547 (2023)
Siu, P.H., Müller, E., Zerbi, V., Aquino, K., Fulcher, B.D.: Extracting dynamical understanding from neural-mass models of mouse cortex. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 16, 847336 (2022)
Van der Vlag, M., Kusch, L., Destexhe, A., Jirsa, V., Diaz-Pier, S., Goldman, J.S.: Vast TVB parameter space exploration: a modular framework for accelerating the multi-scale simulation of human brain dynamics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.13337 (2023)
Wang, H.E., et al.: Delineating epileptogenic networks using brain imaging data and personalized modeling in drug-resistant epilepsy. Sci. Transl. Med. 15(680), eabp8982 (2023)
Withers, C.P., et al.: Identifying sources of human interictal discharges with travelling wave and white matter propagation. Brain 146(12), 5168–5181 (2023)
Yalcinkaya, B.H., et al.: Personalized virtual brains of Alzheimer’s disease link dynamical biomarkers of fMRI with increased local excitability. medRxiv pp. 2023–01 (2023)
Yang, G.J., et al.: Functional hierarchy underlies preferential connectivity disturbances in Schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113(2), E219–E228 (2016)
Zhuang, J., et al.: AdaBelief optimizer: adapting Stepsizes by the belief in observed gradients. In: Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2020)
Acknowledgements
We thank the researchers and participants who provided the open-source datasets used in this study. We are grateful for the insightful discussions with Dr. Chen Yao at Shenzhen Second Hospital, Dr. Liang Chen and Dr. Shuhao Mei at Huashan Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lou, K., Li, J., Barth, M., Liu, Q. (2024). A Data-Driven Framework for Whole-Brain Network Modeling with Simultaneous EEG-SEEG Data. In: Shi, Z., Torresen, J., Yang, S. (eds) Intelligent Information Processing XII. IIP 2024. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 703. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57808-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57808-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-57807-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-57808-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)