Abstract
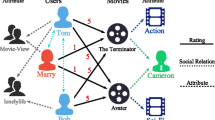
Knowledge Graph (KG) contains rich semantic information and supports knowledge reasoning. In recent years, introducing KG as auxiliary information into the recommender system has become one common measure for improving recommendation quality. The unified graph, which is constructed from the KG and user-item matrix in recommender systems, contains meta-paths formed by single-hop/continuous multi-hop connectivity relationships, and these meta-paths can assist modeling of user preferences. The quality of manually designed meta-paths is prone to the type and number of human-defined meta-paths. Moreover, the process of defining meta-paths is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and inadequate sufficient considerations in design will have an adverse impact on the quality of recommendations. We propose a self-supervised meta-path generation approach that does not rely on domain knowledge to select valuable path information from the unified graph and can deliver high-quality recommendations and reduce noises. Previous studies on meta-paths mainly focused on the neighbor information of nodes and ignored the edges that represents relationships between nodes. We develop a meta-path-based relational path-aware strategy to discover the relational information included within the meta-path. To make the use of the global structure in the unified graph and the information within the local scope in the user-item bipartite graph and KG, a two-level relationship aggregator to fully aggregate the fine-grained semantic information and multi-hop semantic associations is also proposed. We conducted experiments on two public datasets, MovieLens and Book-Crossing to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. The experimental results show that the recommendation algorithm outperforms the baseline models in terms of AUC, Recall@K, and F1 in most cases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji, S., Pan, S., Cambria, E., Marttinen, P., Yu, P.: A survey on knowledge graphs: representation, acquisition, and applications. Journal 33(2), 494–514 (2022)
Zou, D., et al.: Multi-level cross-view contrastive learning for knowledge-aware recommender system. In: 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval,pp.1358–1368. ACM, Madrid, Spain (2022)
Zou, D., et al.: Improving knowledge-aware recommendation with multi-level interactive contrastive learning. In: 31st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 2817–2826. ACM, Atlanta, GA, USA (2022)
Yu, X., Ren, X., Gu, Q., Sun, Y., Han, J.: Collaborative filtering with entity similarity regularization in heterogeneous information networks. Journal, 27 (2013)
Luo, C., Pang, W., Wang, Z., Lin, C.: Hete-CF: social-based collaborative filtering recommendation using heterogeneous relations. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 917–922. IEEE Computer Society, Shenzhen, China (2014)
Zhao, H., Yao, Q., Li, J., Song, Y., Lee, D.: Meta-graph based recommendation fusion over heterogeneous information networks. In: 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 635–644. ACM, Halifax, NS, Canada (2017)
Dong, Y., Chawla, N., Swami, A.: Metapath2Vec: scalable representation learning for heterogeneous networks. In: 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 135–144. ACM, Halifax, NS, Canada (2017)
Hu, B., Shi, C., Zhao, W., Yu, P.: Leveraging meta-path based context for top-N recommendation with a neural co-attention model. In: 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1531–1540. ACM, London, UK (2018)
Yun, S., et al.: Graph transformer networks: learning meta-path graphs to improve GNNs. Journal 153, 104–119 (2022)
Wang, X., He, X., Cao, Y., Liu, M., Chua, T.: KGAT: knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. In: 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 950–958. ACM, Anchorage, AK, USA (2019)
Wang, H., Zhao, M., Xie, X., Li, W., Guo, M.: Knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommender systems. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 3307–3313. ACM, San Francisco, CA, USA (2019)
Wang, X., Wang, D., Xu, C., He, X., Cao, Y., Chua, T.: Explainable reasoning over knowledge graphs for recommendation. In: 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 5329–5336. AAAI Press, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (2019)
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: Node2Vec: scalable feature learning for networks. In: 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data mining, pp. 855–864. ACM, San Francisco, CA, USA (2016)
Rendle, S., Freudenthaler, C., Gantner, Z., Thieme, L.: BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback. In: 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 452–461. AUAI Press, Montreal, QC, Canada (2009)
Zhang, F., Yuan, N., Lian, D., Xie, X., Ma, W.: Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems. In: 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 353–362. ACM, San Francisco, CA, USA (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Y., Zhou, J., Ji, Y., Liu, Q., Wei, J. (2024). A Recommendation Algorithm Based on Automatic Meta-path Generation and Relationship Aggregation. In: Shi, Z., Torresen, J., Yang, S. (eds) Intelligent Information Processing XII. IIP 2024. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 703. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57808-3_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57808-3_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-57807-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-57808-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)