Abstract
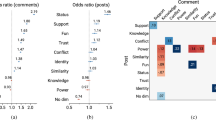
Social media has long served as a platform for discussions on public agendas. However, the dissemination of expert advice on social media is facing a crisis of public trust. To explore the factors influencing the adoption of expert advice on social media, this paper focuses on 326 Weibo trending topics related to expert advice and user comments. Drawing upon theories related to information adoption, professional opinion leadership, and science communication, this study examines the impact of factors at the expert level, media level, and information level on user information adoption behavior. The results indicate that factors including the expert’s field, the expert’s academic affiliation, media type, topic type, use of multimedia, level of detail, information framing, and narrative style have an impact on user information adoption. This study expands the theory of science communication on social media and provides guidance for social media platforms and media entities on how to effectively disseminate expert advice.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The earliest data available from the trending search engine is May 2020.
References
An, S., Li, H.: China social media users’ usage behavior research report 2020–2021. In: Hu, Z., Huang, C., Wu, X. (eds.) Annual Report on the Development of New Media in China, pp. 119–138. Social Science Literature Press, Beijing (2022)
Lei, L.: Weibo’s, “trending list” and the regulation of Internet information services. Journalist 10, 81–87 (2019)
Hardoš, P.: Who exactly is an expert? On the problem of defining and recognizing expertise. Sociológia-Slovak Sociol. Rev. 50(3), 268–288 (2018)
Wang, Y.: From celebrity to “micro celebrity”: a study on the identity change and influence of opinion leaders in the mobile social era. Shanghai Journalism Rev. 457(03), 27–39 (2021)
Meng, S., Shang, J., Zhang, F., Yang, F., Liu, M.: Research on the impact of COVID-19 science information dissemination on social media and the factors influencing the choice of crisis coping strategies: an empirical analysis based on popular micro-blog texts of scientists’ groups. Libr. Inf. Serv. 66(13), 91–101 (2022)
Liu, Y., Zhan, J.: Voices of the National “Great Gods of Life”: dominant roles and multi-identities of the medical opinion leaders during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journalism Mass Commun. Monthly 05, 44–56 (2020)
Kuang, W., Fang, Y.: Multi-subject participation model of science communication in public health emergencies——an analysis based on six scientific issues of COVID-19. J. Northwest Normal Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 59(05), 56–64 (2022)
Workers’ Daily. “Advise experts not to advise” is to expect experts to speak properly (2022). https://m.thepaper.cn/baijiahao_18278985
Petty, R., Cacippo, J.: Communication and Persuasion: Central and Peripheral Routes to Attitude Change. Springer, New York (1986)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13(3), 319–340 (1989)
Ajzen, I., Fishbein, M.: Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Social Behavior, p. 278, Englewood Cliffs (1980)
Sussman, S.W., Siegal, W.S.: Informational influence in organizations: an integrated approach to knowledge adoption. Inf. Syst. Res. 14(1), 47–65 (2003)
Erkan, I., Evans, C.: The influence of eWOM in social media on consumers’ purchase intentions: an extended approach to information adoption. Comput. Hum. Behav. 61, 47–55 (2016)
Huo, C., Zhang, M., Ma, F.: Factors influencing people’s health knowledge adoption in social media: the mediating effect of trust and the moderating effect of health threat. Library Hi Tech 36(1), 129–151 (2018)
Wang, Z., Sun, Z.: Can the adoption of health information on social media be predicted by information characteristics? Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 73(1), 80–100 (2021)
Zhang, J., Ito, N., Wu, W., Li, Z.: “Don’t Let Me Think!” Chinese adoption of travel information on social media: moderating effects of self-disclosure. In: Schegg, R., Stangl, B. (eds.) Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2017, pp. 639–653. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51168-9_46
Katz, E.: The two-step flow of communication: an up-to-date report on an hypothesis. Public Opin. Q. 21(1), 61–78 (1957)
Xu, Q., Yu, N., Song, Y.: User engagement in public discourse on genetically modified organisms: the role of opinion leaders on social media. Sci. Commun. 40(6), 691–717 (2018)
Leißner, L., Stehr, P., Rössler, P., Döringer, E., Morsbach, M., Simon, L.: Parasocial opinion leadership: media personalities’ influence within parasocial relations: theoretical conceptualization and preliminary results. Publizistik 59, 247–267 (2014)
Napoli, P.M.: Audience Evolution: New Technologies and the Transformation of Media Audiences. Columbia University Press, New York (2011)
Cho, M., Schweickart, T., Haase, A.: Public engagement with nonprofit organizations on Facebook. Public Relat. Rev. 40(3), 565–567 (2014)
Burns, T.W., O’Connor, D.J., Stocklmayer, S.M.: Science communication: contemporary definition. Public Underst. Sci. 12(2), 183–202 (2003)
Dahlgren, P.: Media, knowledge, and trust: the deepening epistemic crisis of democracy. Javnost-The Public 25(1–2), 20–27 (2018)
Van Dijck, J., Alinejad, D.: Social media and trust in scientific expertise: debating the Covid-19 pandemic in the Netherlands. Soc. Media+ Soc. 6(4), 2056305120981057 (2020)
Rothman, A.J., Bartels, R.D., Wlaschin, J., Salovey, P.: The strategic use of gain-and loss-framed messages to promote healthy behavior: how theory can inform practice. J. Commun. 56(suppl_1), S202–S220 (2006)
Shoemaker, P.J., Reese, S.D.: Mediating the Message, pp. 781–795. Longman, White Plains (1996)
Rothman, A.J., Salovey, P.: Shaping perceptions to motivate healthy behavior: the role of message framing. Psychol. Bull. 121(1), 3 (1997)
Weibo trending search engine homepage. https://weibo.zhaoyizhe.com/. Accessed 2 Sept 2023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liao, J. (2024). Exploring Influential Factors in Expert Advice Adoption on Social Media: Insights from Weibo Trending Topics. In: Sserwanga, I., et al. Wisdom, Well-Being, Win-Win. iConference 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14597. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57860-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57860-1_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-57859-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-57860-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)