Abstract
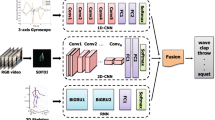
Both Visual and inertial are important modals of human action recognition and have a wide range of applications in virtual reality, human-computer interaction, action perception, and other fields. Currently, most of the work has achieved significant results by utilizing both visual and inertial sensor data, as well as deep learning methods. This method of integrating multimodal information makes the system more robust and adaptable to different environments and action scenarios. However, these works still have the drawbacks of data fusion and high demand for computing resources. In this article, a method for continuous human action recognition based on visual and inertial sensors using attention is proposed. Specifically, a deep visual inertial attention network(VIANet) architecture was designed to integrate spatial, channel and temporal attention into visual 3D CNN, integrate temporal attention mechanism into inertial 2D CNN, and perform decision level fusion on it. Experimental verification was conducted on the C-MHAD public dataset. The experiment shows that the proposed VIANet outperforms previous baseline in multi-modal human action recognition.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, Z., Ke, Q., Rahmani, H., Bennamoun, M., Wang, G., Liu, J.: Human action recognition from various data modalities: a review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(3), 3200–3225 (2022)
Dawar, N., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Real-time continuous detection and recognition of subject-specific smart tv gestures via fusion of depth and inertial sensing. IEEE Access 6, 7019–7028 (2018)
Majumder, S., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Vision and inertial sensing fusion for human action recognition: a review. IEEE Sens. J. 21(3), 2454–2467 (2020)
Li, T., Yu, H.: Visual - inertial fusion based human pose estimation: a review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 72, 1–16 (2023)
Diete, A., Sztyler, T., Stuckenschmidt, H.: Vision and acceleration modalities: Partners for recognizing complex activities. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), pp. 101–106. IEEE (2019)
Wei, H., Chopada, P., Kehtarnavaz, N.: C-MHAD: continuous multimodal human action dataset of simultaneous video and inertial sensing. Sensors 20(10), 2905 (2020)
Wei, H., Jafari, R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Fusion of video and inertial sensing for deep learning-based human action recognition. Sensors 19(17), 3680 (2019)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Wei, H., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Simultaneous utilization of inertial and video sensing for action detection and recognition in continuous action streams. IEEE Sens. J. 20(11), 6055–6063 (2020)
Wang, Y., et al.: A multi-dimensional parallel convolutional connected network based on multi-source and multi-modal sensor data for human activity recognition. IEEE Internet Things J. 10, 14873–14885 (2023)
Chen, C., Jafari, R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Utd-MHAD: a multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 168–172. IEEE (2015)
Bock, M., Kuehne, H., Van Laerhoven, K., Moeller, M.: Wear: An outdoor sports dataset for wearable and egocentric activity recognition (2023)
Ofli, F., Chaudhry, R., Kurillo, G., Vidal, R., Bajcsy, R.: Berkeley MHAD: a comprehensive multimodal human action database. In 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 53–60. IEEE (2013)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6299–6308 (2017)
Chao, X., Hou, Z., Mo, Y.: CZU-MHAD: a multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and 10 wearable inertial sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 22(7), 7034–7042 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hua, L., Huang, Y., Liu, C., Zhu, T. (2024). Utilizing Attention for Continuous Human Action Recognition Based on Multimodal Fusion of Visual and Inertial. In: Shi, Z., Torresen, J., Yang, S. (eds) Intelligent Information Processing XII. IIP 2024. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 704. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57919-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57919-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-57918-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-57919-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)