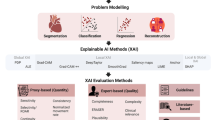
Abstract
The challenge of explaining the results generated by artificial intelligence (AI) is a significant obstacle to their widespread acceptance, which is why increased attention has been paid to the explainability in AI (XAI) in recent years. Given its impact on the medical sector, the survey seeks to demonstrate the important role of XAI in ensuring the reliability and accountability of AI in the domains of diagnosis and surgery. Therefore, we conduct an in-depth look at the applications and challenges of XAI in these areas by reviewing articles published between 2022 and 2023. The survey aims to explore the categorization of XAI techniques, establish their taxonomy, address trade-offs between model performance and interpretability and emphasize the importance of achieving a balance in practical applications. The findings of this study confirm the potential of XAI in medicine as a promising avenue for exploration, providing guidance for the development of medical XAI applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The initial, slow phase of ventricular repolarization.
References
Alloghani, M., Al-Jumeily, D., Aljaaf, A.J., Khalaf, M., Mustafina, J., Tan, S.Y.: The application of artificial intelligence technology in healthcare: a systematic review. In: Khalaf, M.I., Al-Jumeily, D., Lisitsa, A. (eds.) ACRIT 2019. CCIS, vol. 1174, pp. 248–261. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38752-5_20
Jacovi, A., Marasović, A., Miller, T., Goldberg, Y.: Formalizing trust in artificial intelligence: prerequisites, causes and goals of human trust in AI. In: FAccT 2021: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (2020)
Owens, E., Sheehan, B., Mullins, M., Cunneen, M., Ressel, J., Castignani, G.: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in insurance. Risks 10(12), 230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/risks10120230
Zhang, C.A., Cho, S., Vasarhelyi, M.: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in auditing. Int. J. Acc. Inf. Syst. 46, 100572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accinf.2022.100572
van der Velden, B.H.M., Kuijf, H.J., Gilhuijs, K.G.A., Viergever, M.A.: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 79(102470), 102470 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102470
Zhang, Y., Weng, Y., Lund, J.: Applications of explainable artificial intelligence in diagnosis and surgery. Diagnostics (Basel) 12(2), 237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020237
Pham, H.H., Nguyen, H.Q., Nguyen, H.T., Le, L.T., Khanh, L.: An accurate and explainable deep learning system improves interobserver agreement in the interpretation of chest radiograph. IEEE Access 10, 104512–104531 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3210468
Vishwarupe, V., Joshi, P.M., Mathias, N., Maheshwari, S., Mhaisalkar, S., Pawar, V.: Explainable AI and interpretable machine learning: a case study in perspective. Procedia Comput. Sci. 204, 869–876 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.08.105
Troncoso-García, A.R., Martínez-Ballesteros, M., Martínez-Álvarez, F., Troncoso, A.: Explainable machine learning for sleep apnea prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 207, 2930–2939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.09.351
Nigar, N., Umar, M., Shahzad, M.K., Islam, S., Abalo, D.: A deep learning approach based on explainable artificial intelligence for skin lesion classification. IEEE Access 10, 113715–113725 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3217217
Civit-Masot, J., Bañuls-Beaterio, A., Domínguez-Morales, M., Rivas-Pérez, M., Muñoz-Saavedra, L., Rodríguez Corral, J.M.: Non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis aid with histopathological images using explainable deep learning techniques. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 226, 107108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.107108
Loh, H.W., et al.: Deep neural network technique for automated detection of ADHD and CD using ECG signal. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 241(107775), 107775 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107775
Zou, L., et al.: Ensemble image explainable AI (XAI) algorithm for severe community-acquired pneumonia and COVID-19 respiratory infections. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 4(2), 242–254 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAI.2022.3153754
Khater, T., et al.: An explainable artificial intelligence model for the classification of breast cancer. IEEE Access 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3308446
Amado-Caballero, P., Casaseca-de-la-Higuera, P., Alberola-López, S., Andrés-de-Llano, J.M., López-Villalobos, J.A., Alberola-López, C.: Insight into ADHD diagnosis with deep learning on actimetry: quantitative interpretation of occlusion maps in age and gender subgroups. Artif. Intell. Med. 143(102630), 102630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2023.102630
Yilmaz, R., Yagin, F.H., Raza, A., Colak, C., Akinci, T.C.: Assessment of hematological predictors via explainable artificial intelligence in the prediction of acute myocardial infarction. IEEE Access 11, 108591–108602 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3321509
Saravanan, S., Ramkumar, K., Narasimhan, K., Vairavasundaram, S., Kotecha, K., Abraham, A.: Explainable artificial intelligence (EXAI) models for early prediction of Parkinson’s disease based on spiral and wave drawings. IEEE Access 11, 68366–68378 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3291406
Camacho, M., et al.: Explainable classification of Parkinson’s disease using deep learning trained on a large multi-center database of T1-weighted MRI datasets. NeuroImage Clin. 38(103405), 103405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103405
Sheu, R.-K., Pardeshi, M.S., Pai, K.-C., Chen, L.-C., Wu, C.-L., Chen, W.-C.: Interpretable classification of pneumonia infection using eXplainable AI (XAI-ICP). IEEE Access 11, 28896–28919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3255403
Lysdahlgaard, S.: Utilizing heat maps as explainable artificial intelligence for detecting abnormalities on wrist and elbow radiographs. Radiography (Lond.) 29(6), 1132–1138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2023.09.012
Islam, M.K., Rahman, M.M., Ali, M.S., Mahim, S.M., Miah, M.S.: Enhancing lung abnormalities detection and classification using a deep convolutional neural network and GRU with explainable AI: a promising approach for accurate diagnosis. Mach. Learn. Appl. 14(100492), 100492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2023.100492
Ramírez-Mena, A., Andrés-León, E., Alvarez-Cubero, M.J., Anguita-Ruiz, A., Martinez-Gonzalez, L.J., Alcala-Fdez, J.: Explainable artificial intelligence to predict and identify prostate cancer tissue by gene expression. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 240, 107719 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107719
Bellantuono, L., et al.: An eXplainable artificial intelligence analysis of Raman spectra for thyroid cancer diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 16590 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-43856-7
Hossain, M.M., et al.: Cardiovascular disease identification using a hybrid CNN-LSTM model with explainable AI. Inform. Med. Unlocked 42(101370), 101370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2023.101370
Moreno-Sánchez, P.A.: Data-driven early diagnosis of chronic kidney disease: development and evaluation of an explainable AI model. IEEE Access 11, 38359–38369 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3264270
Nayak, T., et al.: Deep learning based detection of monkeypox virus using skin lesion images. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 18, 100243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medntd.2023.100243
Muscato, F., Corti, A., Gambaro, F.M., Chiappetta, K., Loppini, M., Corino, V.D.A.: Combining deep learning and machine learning for the automatic identification of hip prosthesis failure: development, validation and explainability analysis. Int. J. Med. Inf. 176, 105095 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105095
Varam, D., et al.: Wireless capsule endoscopy image classification: an explainable AI approach. IEEE Access 11, 105262–105280 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3319068
Massafra, R., et al.: Analyzing breast cancer invasive disease event classification through explainable artificial intelligence. Front. Med. 10, 1116354 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1116354
Nkengue, M.J., Zeng, X., Koehl, L., Tao, X.: X-RCRNet: an explainable deep-learning network for COVID-19 detection using ECG beat signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 87(105424), 105424 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105424
Jiménez-García, J., et al.: An explainable deep-learning architecture for pediatric sleep apnea identification from overnight airflow and oximetry signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 87(105490), 105490 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105490
Cozma, G.V., Onchis, D., Istin, C., Petrache, I.A.: Explainable machine learning solution for observing optimal surgery timings in thoracic cancer diagnosis. Appl. Sci. (Basel) 12(13), 6506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136506
Tao, S., Ravindranath, R., Wang, S.Y.: Predicting glaucoma progression to surgery with artificial intelligence survival models. Ophthalmol. Sci. 3(4), 100336 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xops.2023.100336
To, T., et al.: Deep learning classification of deep ultraviolet fluorescence images toward intra-operative margin assessment in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 13, 1179025 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1179025
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported by FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the R&D Units Project Scope: UIDB/00319/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Henriques, A., Parola, H., Gonçalves, R., Rodrigues, M. (2024). Integrating Explainable AI: Breakthroughs in Medical Diagnosis and Surgery. In: Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Poniszewska-Marańda, A. (eds) Good Practices and New Perspectives in Information Systems and Technologies. WorldCIST 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 986. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60218-4_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60218-4_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-60217-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-60218-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)