Abstract
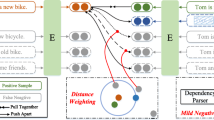
Recent advancements in contrastive learning have revolutionized self-supervised representation learning and achieved state-of-the-art performance on benchmark tasks. While most existing methods focus on applying contrastive learning on input data modalities like images, natural language sentences, or networks, they overlook the potential of utilizing output from previously trained encoders. In this paper, we introduce SimSkip, a novel contrastive learning framework that specifically refines the input embeddings for downstream tasks. Unlike traditional unsupervised learning approaches, SimSkip takes advantage of the output embedding of encoder models as its input. Through theoretical analysis, we provide evidence that applying SimSkip does not lead to larger upper bounds on downstream task errors than that of the original embedding which is SimSkip’s input. Experiment results on various open datasets demonstrate that the embedding by SimSkip improves the performance on downstream tasks.
L. Liu—Work conducted while the author was an intern at Amazon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordes, A., N, U.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26 (2013)
Chen, M., Zhang, W., Yuan, Z., Jia, Y., Chen, H.: FedE: embedding knowledge graphs in federated setting. In: The 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Graphs, IJCKG 2021, pp. 80–88. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3502223.3502233
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: III, H.D., Singh, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 119, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/chen20j.html
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding (2019)
Dolan, W.B., Brockett, C.: Automatically constructing a corpus of sentential paraphrases. In: Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Paraphrasing (IWP2005) (2005). https://aclanthology.org/I05-5002
Gao, T., Yao, X., Chen, D.: SimCSE: simple contrastive learning of sentence embeddings. In: Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (2021)
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks (2016). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1607.00653, https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.00653
Hamilton, W., Ying, Z., Leskovec, J.: Inductive representation learning on large graphs. In: Guyon, I., et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30. Curran Associates, Inc. (2017). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/file/5dd9db5e033da9c6fb5ba83c7a7ebea9-Paper.pdf
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Houlsby, N., et al.: Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP (2019)
Hu, M., Liu, B.: Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2004, pp. 168–177. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1014052.1014073
Jiang, H., Wang, R., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Transferable contrastive network for generalized zero-shot learning. CoRR abs/1908.05832 (2019). http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.05832
Khosla, P., et al.: Supervised contrastive learning. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 18661–18673. Curran Associates, Inc. (2020). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2020/file/d89a66c7c80a29b1bdbab0f2a1a94af8-Paper.pdf
Khosla, P., et al.: Supervised contrastive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.11362 (2020)
Liu, L., Du, B., Fung, Y.R., Ji, H., Xu, J., Tong, H.: KompaRe: a knowledge graph comparative reasoning system. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2021, pp. 3308–3318. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2021)
Liu, L., Du, B., Ji, H., Zhai, C., Tong, H.: Neural-answering logical queries on knowledge graphs. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2021, pp. 1087–1097. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2021)
Liu, L., Hill, B., Du, B., Wang, F., Tong, H.: Conversational question answering with reformulations over knowledge graph. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.17269 (2023)
Liu, L., Ji, H., Xu, J., Tong, H.: Comparative reasoning for knowledge graph fact checking. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) (2022)
Liu, L., Tong, H.: Knowledge graph reasoning and its applications. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 5813–5814 (2023)
Liu, L., et al.: Knowledge graph comparative reasoning for fact checking: problem definition and algorithms. Data Eng. 45, 19–38 (2022)
Liu, Y., et al.: RoBERTa: a robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach (2019)
Luo, Z., Xu, W., Liu, W., Bian, J., Yin, J., Liu, T.Y.: KGE-CL: contrastive learning of tensor decomposition based knowledge graph embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, pp. 2598–2607. International Committee on Computational Linguistics, Gyeongju (2022). https://aclanthology.org/2022.coling-1.229
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Burges, C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26. Curran Associates, Inc. (2013). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2013/file/9aa42b31882ec039965f3c4923ce901b-Paper.pdf
Nickel, M., Kiela, D.: Poincaré embeddings for learning hierarchical representations. In: Guyon, I., et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30, pp. 6341–6350. Curran Associates, Inc. (2017). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7213-poincare-embeddings-for-learning-hierarchical-representations.pdf
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.P.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2011, pp. 809–816. Omnipress, Madison (2011)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: A sentimental education: sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization based on minimum cuts (2004). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.CS/0409058, https://arxiv.org/abs/cs/0409058
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Seeing stars: exploiting class relationships for sentiment categorization with respect to rating scales. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2005), pp. 115–124. Association for Computational Linguistics, Ann Arbor (2005). https://doi.org/10.3115/1219840.1219855, https://aclanthology.org/P05-1015
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: DeepWalk: online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2014, pp. 701–710. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623732
Robinson, J., Chuang, C.Y., Sra, S., Jegelka, S.: Contrastive learning with hard negative samples (2021)
Saunshi, N., Ash, J., Goel, S.: Understanding contrastive learning requires incorporating inductive biases. arXiv (2022)
Saunshi, N., Plevrakis, O., Arora, S., Khodak, M., Khandeparkar, H.: A theoretical analysis of contrastive unsupervised representation learning. In: Chaudhuri, K., Salakhutdinov, R. (eds.) Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 97, pp. 5628–5637. PMLR (2019). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/saunshi19a.html
Socher, R., et al.: Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1631–1642. Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle (2013). https://aclanthology.org/D13-1170
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need (2017)
Voorhees, E.M., Tice, D.M.: Building a question answering test collection. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, SIGIR 2000, pp. 200–207. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2000)
Wang, L., Zhao, W., Wei, Z., Liu, J.: SimKGC: simple contrastive knowledge graph completion with pre-trained language models. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin (2022)
Wiebe, J., Wilson, T., Cardie, C.: Annotating expressions of opinions and emotions in language. Lang. Resour. Eval. 39, 165–210 (2005)
Yang, B., tau Yih, W., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L.: Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases (2015)
You, Y., Chen, T., Sui, Y., Chen, T., Wang, Z., Shen, Y.: Graph contrastive learning with augmentations. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 33, pp. 5812–5823 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, L., Kim, J., Bansal, V. (2024). Can Contrastive Learning Refine Embeddings. In: Meroño Peñuela, A., et al. The Semantic Web. ESWC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14664. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60626-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60626-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-60625-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-60626-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)