Abstract
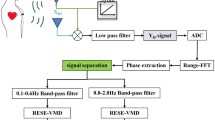
Conducting real-time monitoring of aviation safety personnel’s vital signs during their duty, like respiration and heart rate, is essential for ensuring the safety of civil aviation operations, especially in promptly detecting fatigue-related anomalies. Traditional contact or wearable measurement systems are inevitably inconvenient and even bring new operational hazards when applied in working scenarios. The Linear Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave Radar (FMCW) provides a non-contact vital signal monitoring means for pilots and air traffic controllers in their working environments. The Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) method is a typical time domain solution to retrieve time-varying vital sign signals. However, this method is subjected to the modal aliasing effect due to the respiration rate and heartbeat rate being close in frequency. The Time-Varying Filtered Empirical Mode Decomposition (TVF-EMD) method is then introduced to address this issue, which enhances signal separation performance by adaptively adjusting the local cutoff frequency of the signal. This method successfully resolves the issue of modal aliasing in retrieving respiration and heartbeat signals from mm-wave radar echoes. In addition, heartbeat waveforms are effectively reconstructed using the Instantaneous Mode Functions (IMFs) decomposed by TVF-EMD. This enables precise estimation of Inter-Beat Interval (IBI) and various Heart Rate Variability (HRV) metrics. Simulations and experiment results validate the effectiveness of the TVF-EMD method in accurately extracting vital sign information from millimeter-wave radar measurement signals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muñoz-Ferreras, J.M., Peng, Z., Gómez-García, R., et al.: Random body movement mitigation for FMCW-radar-based vital-sign monitoring. In: 2016 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS), pp. 22–24. IEEE (2016)
Ernst, R., Nilsson, E., Viberg, P.A.: 60GHz vital sign radar using 3D-printed lens. IEEE Sens. 1–3 (2016)
Lee, H., Kim, B.H., Park, J.K., et al.: A resolution enhancement technique for remote monitoring of the vital signs of multiple subjects using a 24 GHz bandwidth-limited FMCW radar. IEEE Access 8, 1240–1248 (2019)
Ren, W., Hou, K., Wang, G., Liu, Q., et al.: Multi-target respiration detection using FMCW MmWave radar. J. Signal Process 37(9), 1581–1588 (2021)
Ernst, R., Nilsson, E., Viberg, P A.: 60GHz vital sign radar using 3D-printed lens. In: 2016 IEEE Sensors, pp. 1–3 (2016)
Lee, H., Kim, B.H., Park, J.K., et al.: A resolution enhancement technique for remote monitoring of the vital signs of multiple subjects using a 24 GHz bandwidth-limited FMCW radar. IEEE Access 8, 1240–1248 (2019)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., et al.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for non-linear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. A 54(1971), 903–995 (1998)
Hou, W.: Research on Detecting Driver's Fatigue Based on Millimeter Wave Radar. Dalian University of Technology (2020). (in Chinese)
Zhu, Z., Yang, D., Zhao, R., et al.: Vital sign signal extraction method based on permutation entropy and EMD algorithm for ultra-wideband radar. In: Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, Piscataway, NJ, pp. 1268–1273. IEEE (2019)
Lin, J., Liu, L., Li, G., et al.: A method for removing baseline drift in ECG signal based on improved EEMD. J. Data Acquis. Process. 33(05), 880–890 (2018)
Hu, W., Zhao, Z., Wang, Y., et al.: Noncontact accurate measurement of cardiopulmonary activity using a compact quadrature dopple radar sensor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(3), 72535 (2014)
Zheng, J.D., Cheng, J.S., Yang, Y.: Partly ensemble empirical mode. Decomposition: An improved noise-assisted method for eliminating modal aliasing. Signal Process. 96, 362–374 (2014)
Li, H., Li, Z., Mo, W.: A time varying filter approach for empirical mode decomposition. Signal Process. 138, 146–158 (2017)
Yang, Z., Ma, C., Qi, Q., et al.: Applications of TVF-EMD in vital signal detection for UWB radar. J. Sens. (2021)
Chuang, H., Kuo, H., Chou, C.: A simple muscle-sphere model to approximate the radar cross section of the man heart for vital-signs detection range problem at different RF frequencies. In: 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, pp. 1–3. IEEE (2019)
Jing, C. H., Bai, Y.J., Zeng, K., et al.: Destiny detection method based on 77 ghz millimeterwave radar perception. Electron. Measur. Technol. 45(22), 55–63(2022)
Jha, C., Kolekar, M.: Empirical mode decomposition and wavelet transform based ECG data compression scheme. IRBM 42(1), 65–72 (2021)
Lee, H., Kim, B., Yook, J.: Path loss compensation method for multiple target vital sign detection with 24-GHz FMCW radar. In: 2018 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP), Auckland, pp. 100–101. IEEE (2018)
Fang, Y.Y., Zhang, Y.J.: Application of heart rate variability in acute coronary syndrome. Modern Pharmaceut. Hygiene 39(6), 1011–1014 (2023)
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Graduate Research Innovation Program of Civil Aviation University of China (grant number 2015/1455001024).
Funding
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lu, X., Ma, X., Suo, C., Zhang, Z. (2024). A Non-contact Vital Signs Retrieving Method for Aviation Safety Personnel Using TVF-EMD. In: Harris, D., Li, WC. (eds) Engineering Psychology and Cognitive Ergonomics. HCII 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14693. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60731-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60731-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-60730-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-60731-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)