Abstract
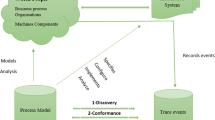
AI planning plays a crucial role in the design and optimization of business processes, providing optimal plans, i.e., sequence of activities, based on manually crafted or formally documented rules. When these plans are executed in business processes, the supporting information systems record a wealth of event data. Analyzing such event data facilitates understanding implicit patterns and recommendations that have the potential to refine planning strategies significantly. In this paper, we introduce a systematic approach to mining these recommendations from event data and integrating them into AI planning, thus creating plans that are informed by both the regulatory hard rules and the flexibility of soft recommendations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Twijri, M.I., Luna, J.M., Herrera, F., Ventura, S.: Course recommendation based on sequences: an evolutionary search of emerging sequential patterns. Cogn. Comput. 14(4), 1474–1495 (2022)
Bienvenu, M., Fritz, C., McIlraith, S.A.: Planning Qual. temporal preferences. KR 6, 134–144 (2006)
Britto, J., Prabhu, S., Gawali, A., Jadhav, Y.: A machine learning based approach for recommending courses at graduate level. In: ICSSIT, pp. 117–121 (2019)
Das, M., Odom, P., Islam, M.R., Doppa, J.R., Roth, D., Natarajan, S.: Preference-guided planning: an active elicitation approach. In: André, E., Koenig, S., Dastani, M., Sukthankar, G. (eds.) AAMAS 2018, pp. 1921–1923 (2018)
Desmarais, M.C., de Baker, R.S.J.: A review of recent advances in learner and skill modeling in intelligent learning environments. User Model. User Adapt. Interact. 22(1–2), 9–38 (2012)
Fikes, R., Nilsson, N.J.: STRIPS: a new approach to the application of theorem proving to problem solving. Artif. Intell. 2(3/4), 189–208 (1971)
Fox, M., Long, D., Magazzeni, D.: Explainable planning (2017)
Giannakopoulou, D., Lerda, F.: From states to transitions: improving translation of LTL formulae to Büchi automata. In: FORTE, pp. 308–326 (2002)
Jiang, W., Pardos, Z.A., Wei, Q.: Goal-based course recommendation. In: LAK, pp. 36–45 (2019)
de Leoni, M., Marrella, A.: Aligning real process executions and prescriptive process models through automated planning. Expert Syst. Appl. 82, 162–183 (2017)
Li, M., Wang, H., Qi, C., Zhou, C.: Handling temporal constraints with preferences in HTN planning for emergency decision-making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 30(4), 1881–1891 (2016)
Mantik, S., Li, M., Porteous, J.: A preference elicitation framework for automated planning. Expert Syst. Appl. 208, 118014 (2022)
Marrella, A.: Automated planning for business process management. J. Data Semant. 8(2), 79–98 (2019)
Myers, K.L., Jarvis, P., Tyson, M., Wolverton, M.: A mixed-initiative framework for robust plan sketching. In: Giunchiglia, E., Muscettola, N., Nau, D.S. (eds.) ICAPS, pp. 256–266 (2003)
Pesic, M., Schonenberg, H., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: DECLARE: full support for loosely-structured processes. In: EDOC, pp. 287–300 (2007)
Polyzou, A., Nikolakopoulos, A.N., Karypis, G.: Scholars walk: a Markov chain framework for course recommendation. In: Desmarais, M.C., Lynch, C.F., Merceron, A., Nkambou, R. (eds.) EDM (2019)
Rafiei, M., et al.: Extracting rules from event data for study planning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.02735 (2023)
Sohrabi, S., Baier, J.A., McIlraith, S.A.: HTN planning with preferences. In: Boutilier, C. (ed.) IJCAI, pp. 1790–1797 (2009)
Tan, J., Chang, L., Liu, T., Zhao, X.: Attentional autoencoder for course recommendation in MOOC with course relevance. In: CyberC, pp. 190–196 (2020)
Urdaneta-Ponte, M.C., Mendez-Zorrilla, A., Oleagordia-Ruiz, I.: Recommendation systems for education: systematic review. Electronics 10(14), 1611 (2021)
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) for the joint project AIStudyBuddy (grant no. 16DHBKI016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, G., Rafiei, M., Helal, H., Lakemeyer, G., van der Aalst, W.M.P. (2024). Incorporating Behavioral Recommendations Mined from Event Logs into AI Planning. In: Islam, S., Sturm, A. (eds) Intelligent Information Systems. CAiSE 2024. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 520. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61000-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61000-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-60999-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-61000-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)