Abstract
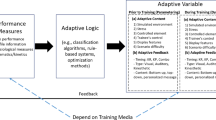
With advances in consumer-grade virtual reality (VR) devices, VR training gains unprecedented attention in research and industries. Although the nature of VR training encourages trainees to actively learn through exploring and gathering information in a simulated virtual environment, designing effective virtual training environments is non-trivial. We propose an adaptive approach that guides trainees to develop psychomotor skills in a simulated virtual environment. As a showcase, we demonstrate our novel approach for restaurant service using a game-based VR application. By incorporating the trainee’s performance and learning progress into optimization objectives, our approach uses mixed integer programming (MIP) to generate VR training sessions iteratively. Through collecting the trainee’s performance in VR training, our approach adapts the VR training sessions by considering the trainee’s strengths and weaknesses, guiding the trainee to improve over training sessions. We validated our approach through two experimental studies. In the first study, we compared our approach with a random training task assignment approach and a performance-only MIP approach through performing simulated restaurant service training. In the second study, we compared our approach with the random assignment approach by evaluating trainees’ skill developments in restaurant services. The results show that our skill-driven adaptive training approach outperforms the random assignment approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Aati, K., Chang, D., Edara, P., Sun, C.: Immersive work zone inspection training using virtual reality. Transp. Res. Rec. 2674(12), 224–232 (2020)
Ashtari, N., Bunt, A., McGrenere, J., Nebeling, M., Chilana, P.K.: Creating augmented and virtual reality applications: current practices, challenges, and opportunities. In: Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1–13 (2020)
Carlson, P., Peters, A., Gilbert, S.B., Vance, J.M., Luse, A.: Virtual training: learning transfer of assembly tasks. IEEE Trans. Visual Comput. Graphics 21(6), 770–782 (2015)
Collins, J.W., O’Brien, N.P.: The Greenwood dictionary of education. ABC-CLIO (2003)
Conges, A., Evain, A., Benaben, F., Chabiron, O., Rebiere, S.: Crisis management exercises in virtual reality. In: 2020 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), pp. 87–92. IEEE (2020)
Doneda, A.L., de Oliveira, J.C.: Helicopter visual signaling simulation: integrating VR and ml into a low-cost solution to optimize brazilian navy training. In: 2020 22nd Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality (SVR), pp. 434–442. IEEE (2020)
Fitts, P.M.: Human performance (1967)
Franzwa, C., Tang, Y., Johnson, A.: Serious game design: motivating students through a balance of fun and learning. In: 2013 5th International conference on games and virtual worlds for serious applications (VS-GAMES), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2013)
Graves, L.E., Ridgers, N.D., Williams, K., Stratton, G., Atkinson, G.T.: The physiological cost and enjoyment of wii fit in adolescents, young adults, and older adults. J. Phys. Activity Health 7(3), 393–401 (2010)
Heintz, S., Law, E.L.C.: Digital educational games: methodologies for evaluating the impact of game type. ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Int. (TOCHI) 25(2), 1–47 (2018)
Huang, G., et al.: Adaptutar: an adaptive tutoring system for machine tasks in augmented reality. In: Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1–15 (2021)
Ipsita, A., et al.: Towards modeling of virtual reality welding simulators to promote accessible and scalable training. In: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1–21 (2022)
Johnsen, K., Raij, A., Stevens, A., Lind, D.S., Lok, B.: The validity of a virtual human experience for interpersonal skills education. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1049–1058 (2007)
Kaplan, A.: Higher Education at the Crossroads of Disruption: The University of the 21st Century. Emerald Group Publishing, Bingley (2021)
Karahan, M., Kerkhoffs, G.M., Randelli, P., Tuijthof, G.J.: Effective Training of Arthroscopic Skills. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44943-1
Kendzierski, D., DeCarlo, K.J.: Physical activity enjoyment scale: two validation studies. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 13(1) (1991)
Lang, Y., Liang, W., Xu, F., Zhao, Y., Yu, L.F.: Synthesizing personalized training programs for improving driving habits via virtual reality. In: IEEE Virtual Reality (2018)
Lee, J., Kim, H., Kim, K.H., Jung, D., Jowsey, T., Webster, C.S.: Effective virtual patient simulators for medical communication training: a systematic review. Med. Educ. 54(9), 786–795 (2020)
Li, W., Huang, H., Solomon, T., Esmaeili, B., Yu, L.F.: Synthesizing personalized construction safety training scenarios for VR training. IEEE Trans. Visual Comput. Graph. 28(5), 1993–2002 (2022)
Li, W., Talavera, J., Samayoa, A.G., Lien, J.M., Yu, L.F.: Automatic synthesis of virtual wheelchair training scenarios. In: 2020 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), pp. 539–547. IEEE (2020)
Lindlbauer, D., Feit, A.M., Hilliges, O.: Context-aware online adaptation of mixed reality interfaces. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pp. 147–160 (2019)
Michael, J.: Where’s the evidence that active learning works? Adv. Physiol. Educ. (2006)
Mutual Mobile: Walmart (2022). https://mutualmobile.com/work/walmart
Nishiyama, Y., Sezaki, K.: Experience sampling tool for repetitive skills training in sports using voice user interface. In: Adjunct Proceedings of the 2021 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2021 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, pp. 54–55 (2021)
Peng, H., Ma, S., Spector, J.M.: Personalized adaptive learning: an emerging pedagogical approach enabled by a smart learning environment. Smart Learn. Environ. 6(1), 1–14 (2019)
Romiszowski, A.: The development of physical skills: instruction in the psychomotor domain. Inst.-Des. Theories Models New Paradigm Inst. Theory 2, 457–481 (1999)
Schott, D., et al.: A VR/AR environment for multi-user liver anatomy education. In: 2021 IEEE Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), pp. 296–305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/VR50410.2021.00052
Shao, Q., et al.: Teaching American sign language in mixed reality. Proc. ACM Interac. Mobile Wearable Ubiq. Technol. 4(4), 1–27 (2020)
Shen, S., et al.: Effects of level of immersion on virtual training transfer of bimanual assembly tasks. Front. Virtual Real. 2, 58 (2021)
STRIVR: Protecting verizon’s frontline workforce: Strivr testimonial (2021). https://www.strivr.com/resources/webinars/verizon-customer-experience/
Tavassoli, F., Howell, D.M., Black, E.W., Lok, B., Gilbert, J.E.: Jayla (junior agent to typify levels of autism): a virtual training platform to teach severity levels of autism. Front. Virtual Real. 2, 96 (2021)
Van Merriënboer, J.J., Clark, R.E., De Croock, M.: Blueprints for complex learning: the 4c/id-model. Educ. Tech. Research Dev. 50(2), 39–61 (2002)
Vanbecelaere, S., Van den Berghe, K., Cornillie, F., Sasanguie, D., Reynvoet, B., Depaepe, F.: The effectiveness of adaptive versus non-adaptive learning with digital educational games. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 36(4), 502–513 (2020)
VR, I.: Vr for workplace training (2021). https://immersionvr.co.uk/about-360vr/vr-for-workplace-training/
Wickens, C.D., Hutchins, S., Carolan, T., Cumming, J.: Effectiveness of part-task training and increasing-difficulty training strategies: a meta-analysis approach. Hum. Fact. 55(2), 461–470 (2013)
Xie, B., et al.: A review on virtual reality skill training applications. Front. Virt. Real. 2, 1–19 (2021)
Yao, H., de Siqueira, A.G., Foster, A., Galynker, I., Lok, B.: Toward automated evaluation of empathetic responses in virtual human interaction systems for mental health scenarios. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, pp. 1–8 (2020)
Yuksel, B.F., et al.: Learn piano with bach: an adaptive learning interface that adjusts task difficulty based on brain state. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Chi Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 5372–5384 (2016)
Zhao, R., Li, V., Barbosa, H., Ghoshal, G., Hoque, M.E.: Semi-automated 8 collaborative online training module for improving communication skills. Proc. ACM Interact. Mobile Wearable Ubiq. Technol. 1(2), 1–20 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported in part by NSF 1942531 and NSF 2128867. The user study was funded by NSF grants with the OSU IRB approval number 1690834-1. NIST’s role was limited to activities not involved with the human subjects research. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Certain commercial products are identified in this paper in order to specify the experimental procedure adequately. Such identification is not intended to imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, nor is it intended to imply that the products identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Yan, C., Huang, H., Su, S., Yu, LF. (2024). Mixed-Integer Programming for Adaptive VR Workflow Training. In: Chen, J.Y.C., Fragomeni, G. (eds) Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality. HCII 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14708. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61047-9_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61047-9_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-61046-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-61047-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)