Abstract
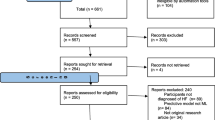
Accurately predicting the risk of readmission for patients with heart failure is of utmost importance for their prognostic management. In this study, prediction models for 6-month unplanned readmission in heart failure patients were developed using a cohort of 1888 individuals. The cohort was divided into training and testing sets in an 8:2 ratio. Variable selection was performed using Lasso regression, and the prediction models were trained using logistic regression, random forest, decision tree, Bayesian classifier, and support vector machines algorithms. A set of 17 predictive indicators were identified, including age, gender, basophil ratio, monocyte count, neutrophil count, calcium, sodium, glomerular filtration rate, uric acid, prothrombin activity, dementia, type of heart failure, consciousness, cardiac function classification, diabetes, chronic kidney disease and length of hospital stay. Among the models tested, the Bayesian classifier model exhibited a relatively stronger predictive performance (Area under the curve: 0.60, sensitivity: 0.81, specificity: 0.38). Additionally, a user-friendly software application based on the R Shiny package was developed to facilitate the practical implementation of the prediction models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392, 1789–1858 (2018)
In, C.T., Hu, S.S.: Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2021: an updated summary. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 20, 399–430 (2023)
Al-Omary, A.M.S., et al.: Mortality and readmission following hospitalisation for heart failure in Australia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 27, 917–927 (2018)
Savarese, G., Becher, P.M., Lund, L.H., Seferovic, P., Rosano, G., Coats, A.: Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 118, 3272–3287 (2023)
Tian, J., et al.: Machine learning prognosis model based on patient-reported outcomes for chronic heart failure patients after discharge. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 21, 31 (2023)
Li, J., Liu, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, L., Mao, Y., Liu, J.: Predicting mortality in intensive care unit patients with heart failure using an interpretable machine learning model: retrospective cohort study. J. Med. Internet Res. 24, e38082 (2022)
Zheng, L., Smith, N.J., Teng, B.Q., Szabo, A., Joyce, D.L.: Predictive model for heart failure readmission using nationwide readmissions database. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual Outcomes 6, 228–238 (2022)
Zhang, Z., Cao, L., Chen, R., Zhao, Y., Lv, L., Xu, Z., et al.: Electronic healthcare records and external outcome data for hospitalized patients with heart failure. Sci. Data 8, 46 (2021)
Acknowledgments
The work of this paper is supported by Acute Myocardial Infarction Electrocardiogram Intelligent Pre-Hospital Monitoring and Early Warning, Guangdong and Guangxi Cooperation R&D Talent Introduction (No. AC22035089) and Research and Application Demonstration of Medical Image-Assisted Disease Diagnosis Based on Artificial Intelligence Technology, Training Plan for Thousands of Young and Middle-Aged Backbone Teachers in Colleges and Universities in Guangxi (The Fifth Phase).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hu, J., Mo, C. (2024). Development and Application of a Machine Learning-Based Prediction Model for 6-Month Unplanned Readmission in Heart Failure Patients. In: Duffy, V.G. (eds) Digital Human Modeling and Applications in Health, Safety, Ergonomics and Risk Management. HCII 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14710. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61063-9_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61063-9_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-61062-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-61063-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)